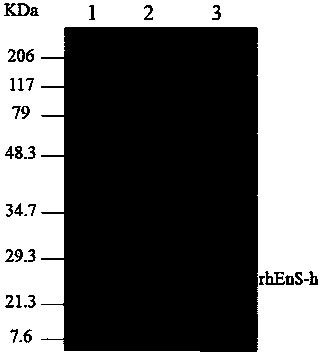
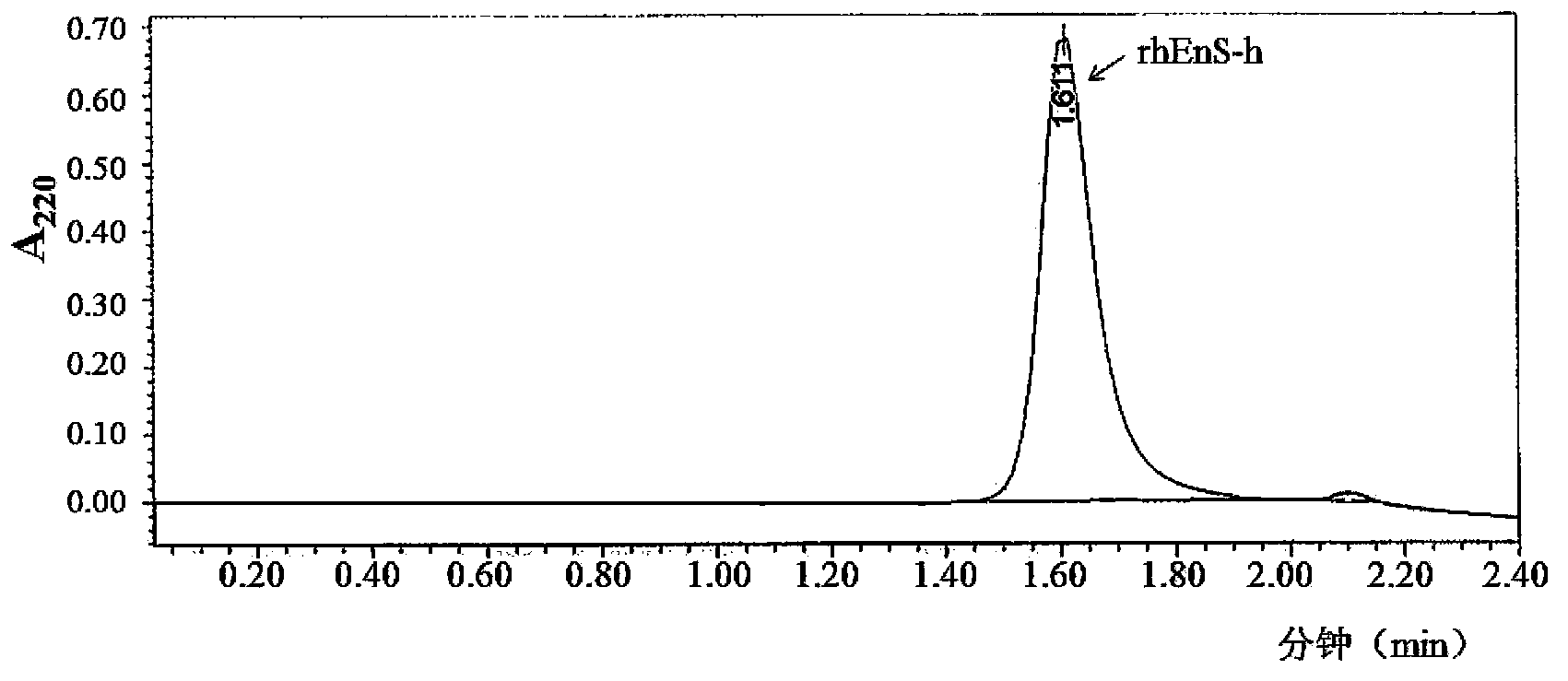
Recombinant human neovascularization inhibin and pharmaceutical composition thereof
A new blood vessel and inhibin technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of weakening drugs to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation, expensive drug production costs and prices, and incomplete retention of biological activity, so as to improve the efficiency of refolding and purification, Increased refolding and purification yields, reduced time and labor-intensive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Cloning of the gene for expression of recombinant human neoangiostatin with C-terminal and N-terminal additional amino acids.
[0060] According to the C-terminal and N-terminal amino acid sequences of the novel recombinant human neoangiostatin of the present invention, primers are designed, and the DNA sequence encoding recombinant human neoangiostatin is amplified from a human liver cDNA library by standard RT-PCR technology. Primers used in PCR are:
[0061] Upstream primer (SEQ ID No.5): 5'-CGCCATATGCGGGGATCCCACAGCCACCGCGACTTC-3', containing an Nde I site;
[0062] Downstream primer (SEQ ID No. 6): 5'-GTCTCAAGCTTAATGGTGATGGTGATGGTGCTTGGAGGCAGTCATGAA-3', including a stop codon followed by a Hind III site.
[0063] The PCR reaction conditions were: 30 PCR cycles, denaturation at 94°C for 1 minute, annealing at 57°C for 1 minute, and extension at 72°C for 1.5 minutes.
Embodiment 2
[0065] Construction of recombinant human neoangiostatin expression strain with C-terminal and N-terminal additional sequences.
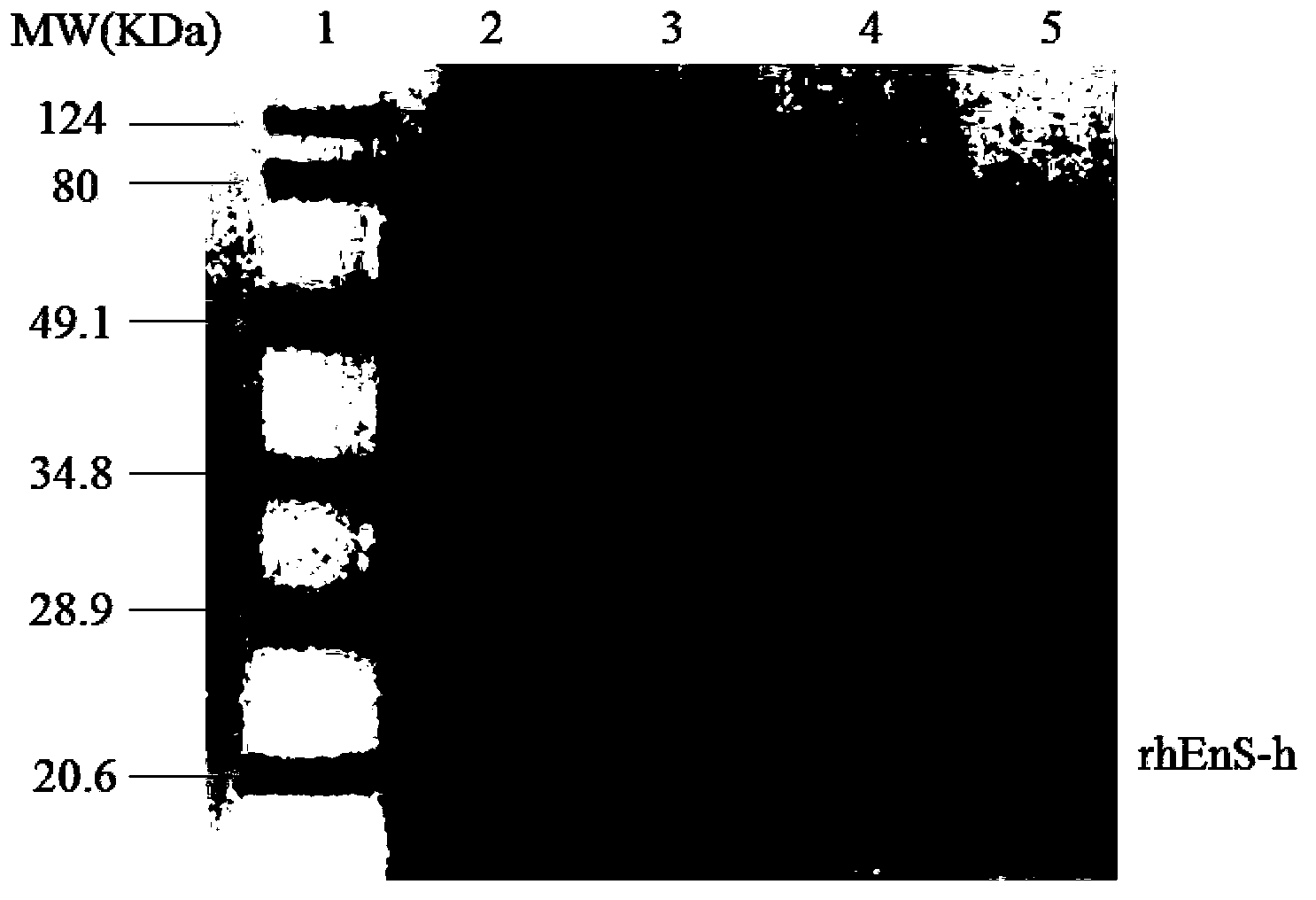
[0066] The 598bp PCR amplification product was treated with two restriction endonucleases Nde I and Hind III, and then enzyme-linked with the pET22b vector digested with Nde I and Hind III for 10 hours under the action of T4 ligase to obtain Expression vector rhEnS-h-pET22b. The expression vector rhEnS-h-pET22b was transformed into competent cells of Escherichia coli M15 and JM109 strains, and then spread on solid medium plates containing ampicillin resistance, and the transformants were screened for high protein expression strains and constructed Gene identification. Finally, a highly expressed strain of rhEnS-h (hereinafter referred to as E.coli M15 (rhEnS-h)) was successfully obtained from the E. coli M15 transformant, in which the expression of rhEnS-h accounted for about 50% of the total protein of the bacteria; sequence identification The res...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Production, refolding and purification of recombinant human neoangiostatin (rhEnS-h) with additional C- and N-terminal sequences.
[0069] (1) Preparation of engineering bacteria for industrial production
[0070] Pick the engineered strain E.coli M15 (rhEnS-h) and inoculate it into the TYP (recipe: sodium chloride 5g / L, peptone 11g / L, yeast extract 11g / L) plate medium with ampicillin resistance Incubate at 37°C. Pick 10 colonies and inoculate them into 10ml of TYP liquid medium with ampicillin resistance, shake culture until the OD600 is 0.9, add a final concentration of 1.5mM IPTG to all cultures to induce protein expression, and continue to culture for 5 hours , using SDS-PAGE with a gel concentration of 15% to detect the expression level of rhEnS-h, and select the one with the highest expression level as the seed culture medium (the expression level of rhEnS-h accounts for about 50% of the total bacterial protein).
[0071] (2) Preparation of fermented seed liquid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com