A preparation method of grafted cellulose medicinal molecules with ph/temperature responsiveness
A temperature-responsive, cellulose technology, applied in the fields of polymer materials and biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of difficult separation of grafted cellulose molecules, strong volatility, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve shortened time and controllable reaction process. , the effect of improving the catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
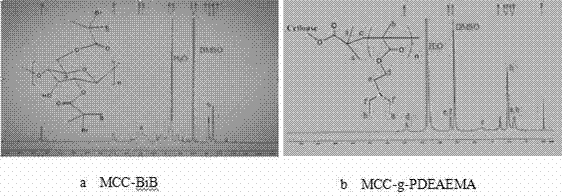
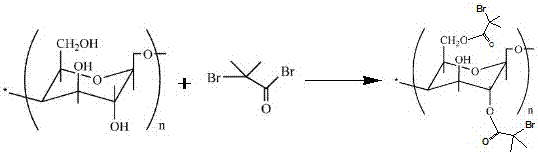
[0032] 1. Synthesis of cellulose macroinitiator MCC-BiB
[0033] Add 0.509 g of microcrystalline cellulose and 10.075 g of [AMIM]Cl into a 100 mL three-neck flask, pass N 2 Protected, magnetically stirred for 1 h in an oil bath at 80 °C to ensure that the microcrystalline cellulose was completely dissolved, and then cooled to obtain a light brown transparent solution with a MCC / [AMIM]Cl (mass ratio) of about 5%. Add 8mL of 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide dropwise at room temperature, stir for 0.5h, react for 24h at room temperature, pour it into a 500mL beaker, add excess distilled water to it, precipitate a white precipitate, suction filter, and repeat After washing 3 times, the product was freeze-dried to obtain the macromolecular initiator MCC-BiB, and the grafting efficiency of the obtained macromolecular initiator could reach 97%.
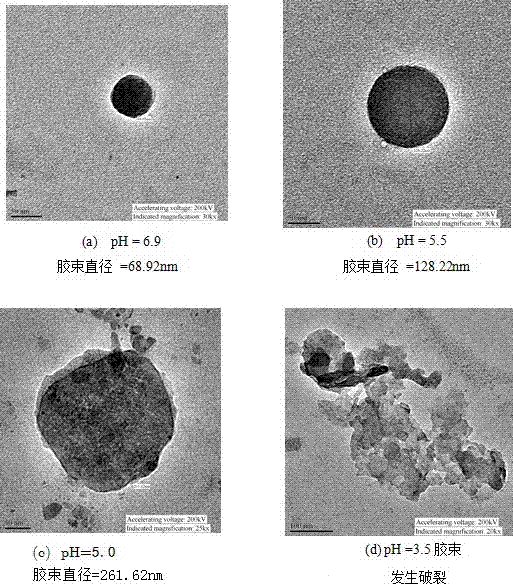
[0034] 2. Synthesis of pH-sensitive cellulose graft copolymer MCC-g-PDEAEMA
[0035] Accurately weigh 0.050g of macromolecular initiator MCC-BiB ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grafting efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grafting efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com