Method for preparing superfine nano-silicon by taking silicon-containing biomass as raw material as well as prepared superfine nano-silicon and application thereof
An ultra-fine nano-biomass technology, applied in the comprehensive field of biological waste resources, can solve the problems of pollution, complicated steps, harsh conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of wide source of raw materials, simple and easy steps, and not easy to reunite
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) 5g of rice husk is acid boiled to remove inorganic salt ion impurities, and then dried after repeated cleaning;
[0025] (2) annealing the rice husk after acid boiling in (1) at 700°C for 4 hours in the air to obtain white silica;
[0026] (3) Mix silicon dioxide, magnesium powder, and sodium chloride by ball milling at a molar ratio of 1:2.5:10, and then put the mixture into a tube furnace and heat it to 650°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min. 3h, after the product was cooled to room temperature with the furnace, it was taken out;
[0027] (4) Wash and stir the obtained product in 0.1 mol / L hydrochloric acid for 12 h, then wash and stir in 0.1 mol / L hydrofluoric acid for 12 h, filter and dry to obtain ultrafine nano-silicon.
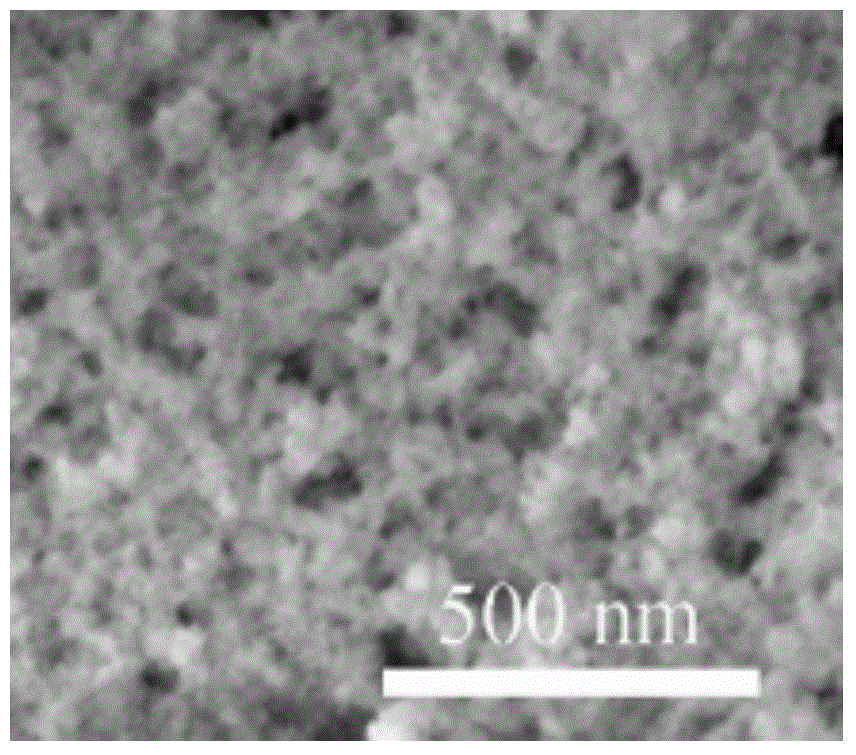
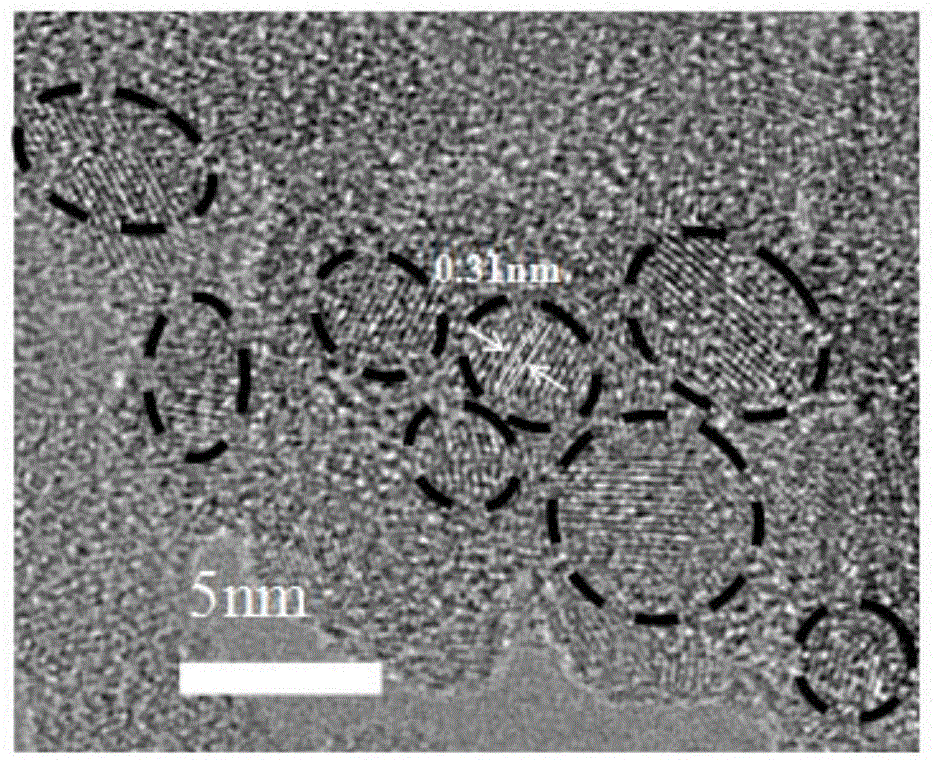
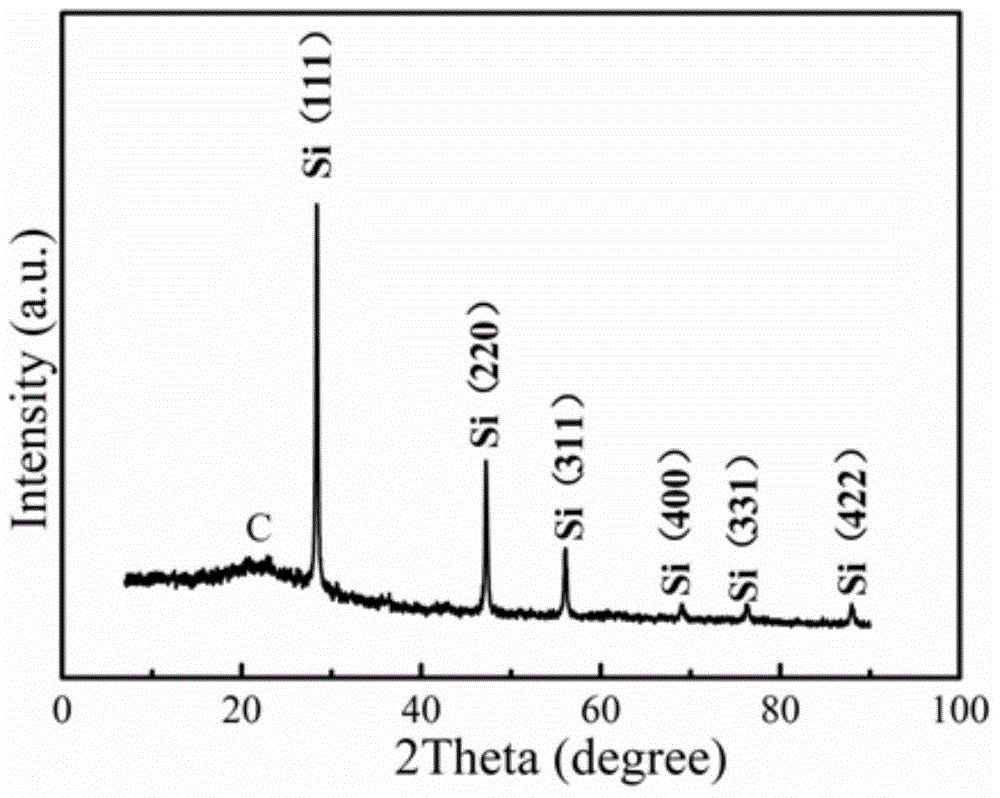
[0028] Depend on figure 1 The scanning electron microscope image of and figure 2 It can be seen from the transmission electron microscope image that the particle size of the silicon nanoparticles prepared in this embodiment is about 20nm, and...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) 5g of bamboo leaf acid is boiled to remove inorganic salt ion impurities, and then dried after repeated cleaning;
[0031] (2) annealing the rice husk after acid boiling in (1) at 400° C. for 12 hours in air to obtain white silica;
[0032] (3) Mix silicon dioxide, magnesium powder, and sodium chloride by ball milling at a molar ratio of 1:1.5:5, and then put the mixture into a tube furnace and heat it to 600°C at a heating rate of 1°C / min. 12h, after the product was cooled to room temperature with the furnace, it was taken out;
[0033] (4) The obtained product was washed and stirred in 1 mol / L sulfuric acid and stirred for 9 h, then washed and stirred in 1 mol / L hydrofluoric acid for 9 h, filtered and dried to obtain ultrafine nano-silicon.
[0034] Nano-silicon is used as the negative electrode material of lithium-ion batteries, packaged into button cells, and subjected to charge and discharge tests. The charge and discharge specific capacities are 1834mAh / g and...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) 5g of stalks are acid boiled to remove inorganic salt ion impurities, and then dried after repeated washing;
[0037] (2) annealing the rice husk after acid boiling in (1) at 500°C for 8 hours in the air to obtain white silica;
[0038] (3) Mix silicon dioxide, magnesium powder, and sodium chloride by ball milling in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:3, and then put the mixture into a tube furnace and heat it to 500°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min. 9h, after the product was cooled to room temperature with the furnace, it was taken out;
[0039] (4) Wash and stir the obtained product in 3 mol / L nitric acid for 6 h, then wash and stir in 3 mol / L hydrofluoric acid for 6 h, filter and dry to obtain ultrafine nano-silicon.
[0040] Nano-silicon is used as the negative electrode material of lithium-ion batteries, packaged into button cells, and subjected to charge and discharge tests. The charge and discharge specific capacities are 1878mAh / g and 1628mAh / g at 0.1C, and the first Co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com