Method and device for condensing and co-producing refined magnesium by evaporating and endothermic magnesium vapor from magnesium liquid
A technology of evaporative heat absorption and magnesium vapor, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of energy waste, serious smoke pollution, and failure to remove impurities, so as to save the circulating water cooling system and cooling tower system, and increase the condensation rate , The effect of convenient outflow and recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] As one of the silicothermal magnesium smelting reduction reactors, the large-scale vacuum electrothermal magnesium smelting reduction furnace can produce 5-20 tons of magnesium per hour under the premise of adopting the energy-saving measures of hot charging and hot delivery and high-power electric heating. The magnesium vapor generator 901 in the example continuously provides magnesium vapor. At the smelting temperature of 1600°C, the equilibrium pressure of magnesium vapor can be close to atmospheric pressure. In the industrial production process, in order to accelerate the reaction, the pressure in the magnesium smelting reactor is controlled to be slightly higher than 10000Pa, and 5% argon is mixed in the magnesium vapor gas.
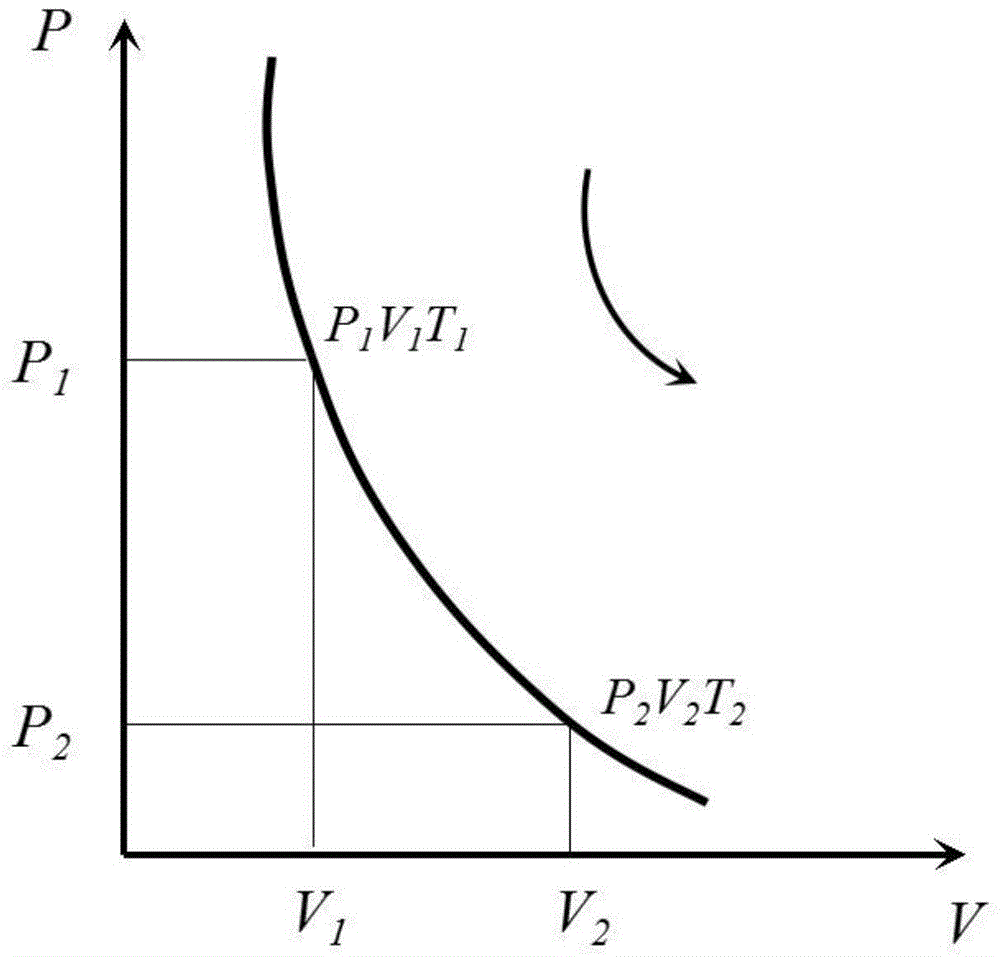
[0105] The initial magnesium vapor at 1600°C and partial pressure of 10000Pa undergoes isentropic expansion through an expansion pipe 801, such as figure 1 As shown, in the process of isentropic expansion, there is no heat exchange between ...
Embodiment 2
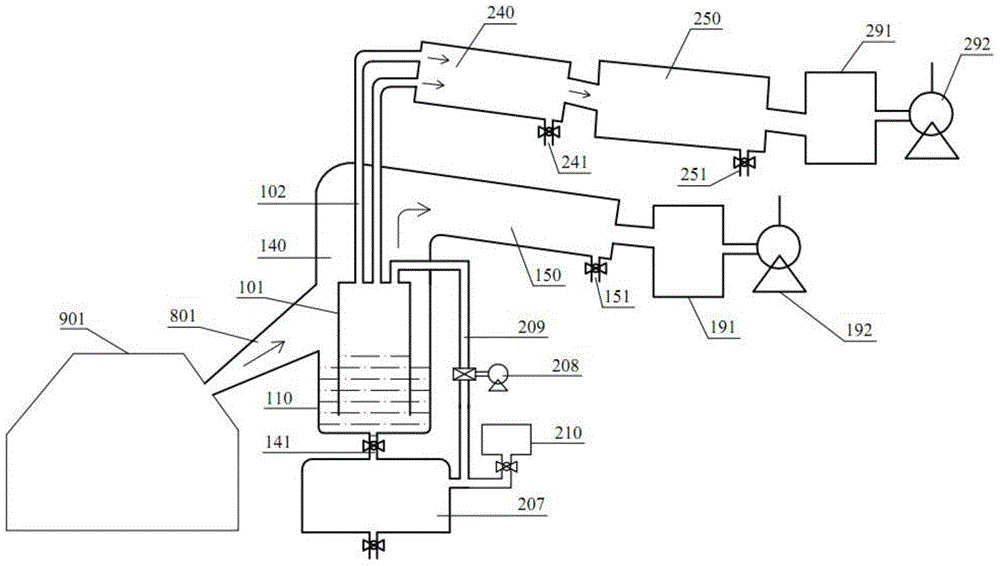
[0131] In this example, if Figure 6 As shown, the magnesium liquid evaporator 101 is a container with a closed bottom, which is isolated from the initial magnesium liquid collector 110 by the container wall. The purified magnesium liquid is injected into the magnesium liquid storage tank 207 to be purified, the liquid suction pump 208 is turned on to inject the magnesium liquid to be purified into the magnesium liquid evaporator 101 through the magnesium liquid delivery pipe 209, and then the liquid suction pump 208 is turned off. All subsequent replenishment of the magnesium liquid to be purified also enters the magnesium liquid evaporator 101 through the magnesium liquid injection tank 210 , the purified magnesium liquid storage tank 207 , the pump 208 , and the magnesium liquid delivery pipe 209 .
[0132] All other processes and devices are the same as in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0134] In the present embodiment, the second condensing section 150 of the primary magnesium vapor and the second condensing section 250 of the refined magnesium vapor each have two parallel secondary cooling monomers 155, such as Figure 7 As shown, the secondary cooling monomer 155 of the initial magnesium vapor is used to explain, and the second condensation section 250 of refined magnesium vapor is completely similar to this. Each secondary cooling unit 155 has an air intake control valve 152 and an air outlet control valve 153 to control the inflow and outflow of primary magnesium vapor. The interior of the secondary cooling unit 155 is a secondary cooling condensation chamber 154 .
[0135] During the condensing operation, close the intake control valve 152 and the air outlet control valve 153 of one of the secondary cooling units 155, and the secondary cooling unit will leave the working state of “cooling and condensing” and turn to the working state of “heating and reme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com