Micro-nano-scale konjac glucomannan fiber scaffold material preparation method
The technology of konjac glucoside and konjac glucomannan is applied in the preparation of micro-nano-level konjac glucoside fibrous scaffold material, and in the field of biomedical materials, achieving easy processing, large specific surface area and small fiber diameter. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
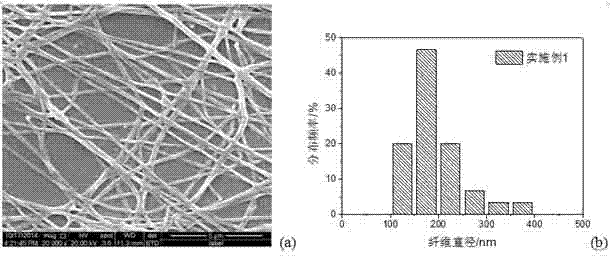
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
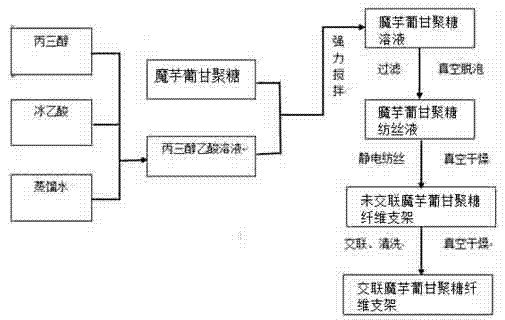
[0037] The preparation method of the micronano-scale konjac glucosidan fiber scaffold material described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0038] (1) Use a graduated cylinder to measure 30ml of distilled water and place it in a 100ml beaker, add 3ml of glycerol and 7ml of glacial acetic acid in turn and stir to fully dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0039] (2) Add 0.8g konjac glucosidan to solution A, and stir well (40min) to obtain semi-thick solution B;
[0040] (3) Filter solution B through a 400-mesh sieve, and vacuum degassing in a vacuum dryer for 6 hours;
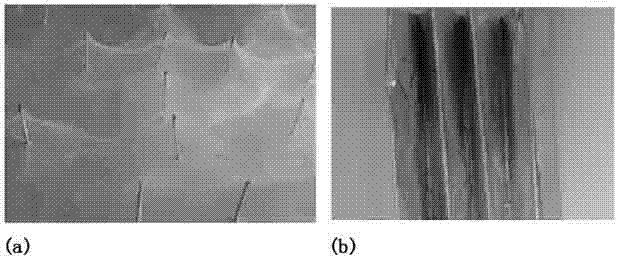
[0041] (4) Use a medical syringe to extract 1~3ml of solution, select a stainless steel needle with a 0.07mm aperture, control the ambient temperature to 30°C, adjust the positive voltage to 10Kv, and the receiving distance to 10cm. Such as figure 2 (a)), and finally complete the electrostatic spinning process;
[0042] (5) Dry the sample at room temperature for 24 hours at a vacuum ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The preparation method of the micronano-scale konjac glucosidan fiber scaffold material described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0050] (1) Use a measuring cylinder to measure 30ml of distilled water and place it in a 100ml beaker, add 5ml of ethylene glycol and 5ml of formic acid in turn and stir to fully dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0051] (2) Add 1.7g konjac glucosidan to solution A, stir well (40min) to obtain semi-thick solution B;
[0052] (3) Filter solution B through a 400-mesh sieve, and vacuum degassing in a vacuum dryer for 6 hours;
[0053] (4) Use a medical syringe to extract 1~3ml of solution, select a stainless steel needle with a 0.5mm aperture, control the ambient temperature at 40°C, adjust the positive voltage to 15 Kv, and the receiving distance to 15cm. bent sheet metal, such as figure 2 (b)), and finally complete the electrostatic spinning process;
[0054] (5) Dry the sample at room temperature for 24 hours...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The preparation method of the micronano-scale konjac glucosidan fiber scaffold material described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0061] (1) Use a graduated cylinder to measure 30ml of distilled water and place it in a 100ml beaker, add 6ml of propylene glycol and 4ml of formic acid in turn and stir to fully dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0062] (2) Add 1.8g konjac glucosidan to solution A, stir well (40min), and get semi-thick solution B;
[0063] (3) Filter solution B through a 400-mesh sieve, and vacuum degassing in a vacuum dryer for 6 hours;
[0064] (4) Use a medical syringe to draw at least 1~3ml, select a stainless steel needle with an aperture of 1.04mm, control the ambient temperature to 50°C, adjust the positive voltage to 20Kv, and the receiving distance to 20cm. The receiving method is non-uniform plate (needle plate) , and finally complete the electrostatic spinning process;
[0065] (5) Dry the sample at room temperatur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com