Method for producing hydrogen by utilizing ascorbic acid to promote glucose photoelectrocatalytic oxidation
An ascorbic acid, photoelectric catalysis technology, applied in electrodes, electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of high overpotential and low utilization rate of electric energy, and achieve the effect of simple and portable electrode, simple operation and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1 constructs photoelectrochemical fuel cell
[0030] The cadmium sulfide / ITO electrode of this embodiment is prepared by the following method:
[0031] (1) Prepare 50mL 0.50mol / L cadmium chloride, 10mL 1.0mol / L sodium thiosulfate aqueous solution and pH=2.0 hydrochloric acid aqueous solution;
[0032] (2) Using cyclic voltammetry electrodeposition technology, in the three-electrode system, the working electrode is ITO conductive glass, the counter electrode is a titanium electrode, the reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and the electrolyte is the above-mentioned cadmium chloride, sulfo Sodium sulfate and hydrochloric acid aqueous solution mixed solution with a volume ratio of 1:5:44, the potential range of deposition is -0.3V~-0.9V, the number of circles is 100 circles, and the sweep speed is 0.05V s -1 ;
[0033] (3) Put the deposited electrode into an oven and dry at a constant temperature under the condition of 35-45° C. to obtain a ca...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Ascorbic acid promotes the photocatalytic oxidation of glucose
[0037] To clarify the photocatalysis of ascorbic acid and ascorbic acid promoting glucose in the cadmium sulfide / ITO electrode in the photocatalytic fuel cell constructed in Example 1, the specific operation steps are as follows:
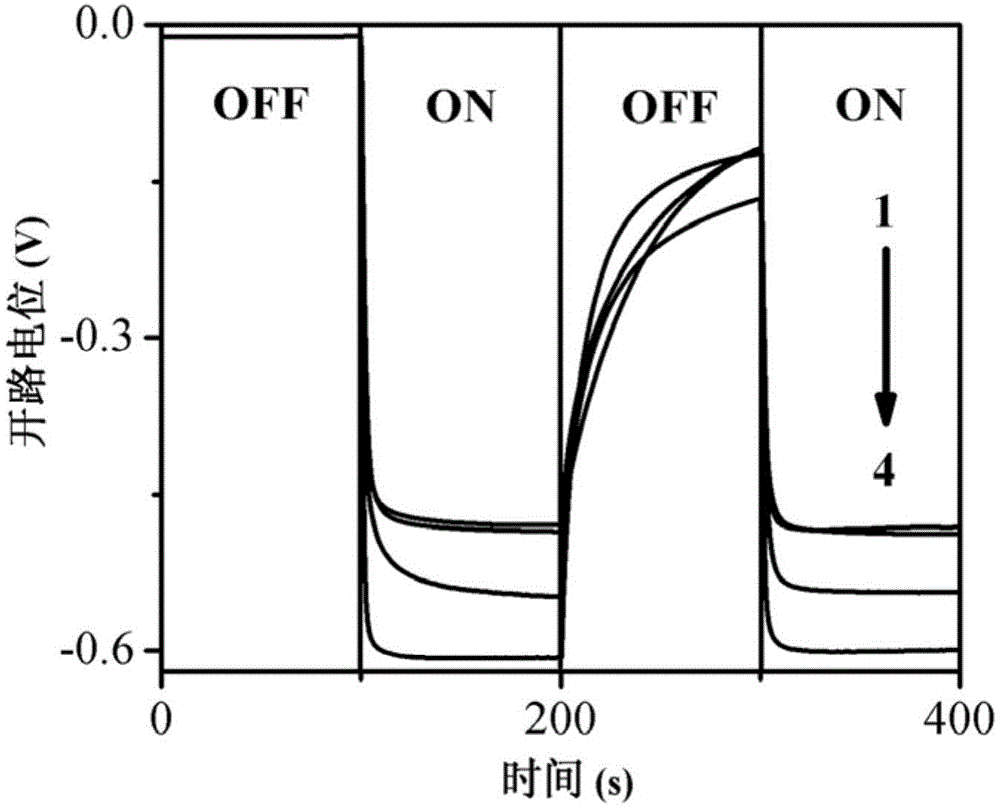
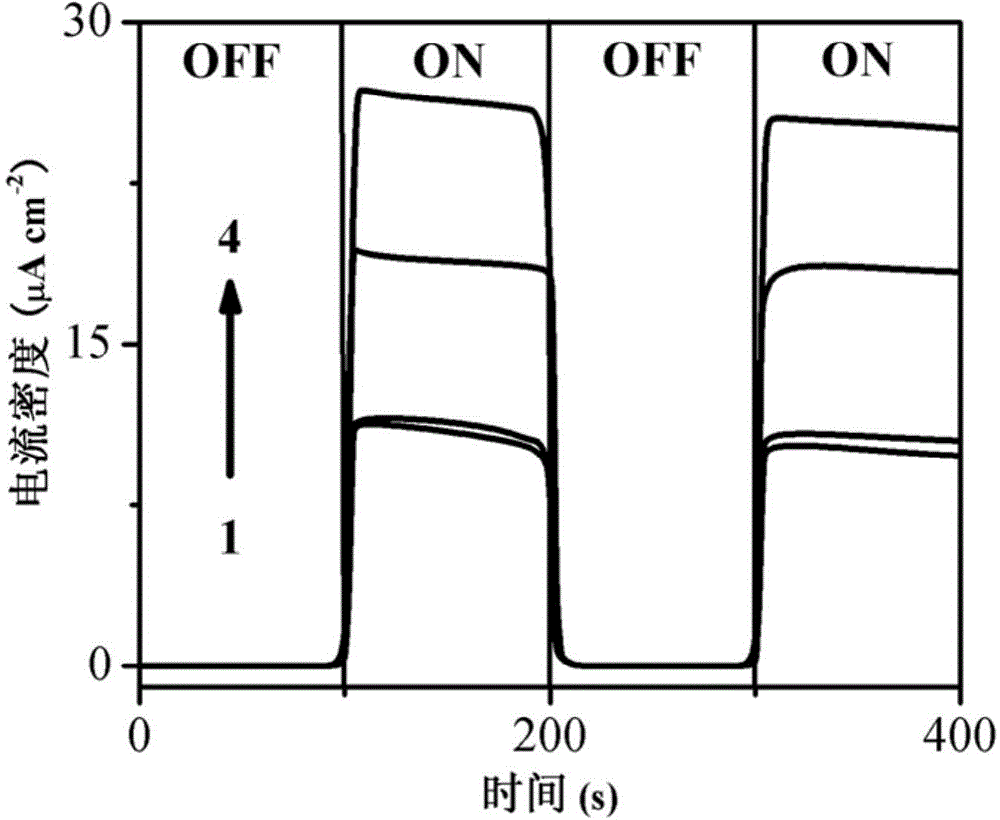
[0038] (1) The following four solutions were loaded into the anode cell to clarify the photocatalytic effect of cadmium sulfide / ITO electrode on ascorbic acid and ascorbic acid-promoted glucose. 1 is 0.5mol / L sodium sulfate solution (blank), 2 is 0.5mol / L sodium sulfate solution and 0.1mol / L glucose, 3 is 0.5mol / L sodium sulfate solution and 0.1mol / L ascorbic acid, 4 is 0.5mol / L L sodium sulfate solution, 0.1mol / L ascorbic acid and 0.1mol / L glucose.
[0039] (2) Use the electrochemical workstation to measure the open circuit potential of the photocatalytic fuel cell within 400s, and compare the effects of ascorbic acid and glucose on the open circuit potential. The re...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3 photocatalytic fuel cell performance
[0043] To the test of the photocatalytic fuel cell performance that embodiment 1 builds, concrete operation steps are as follows:
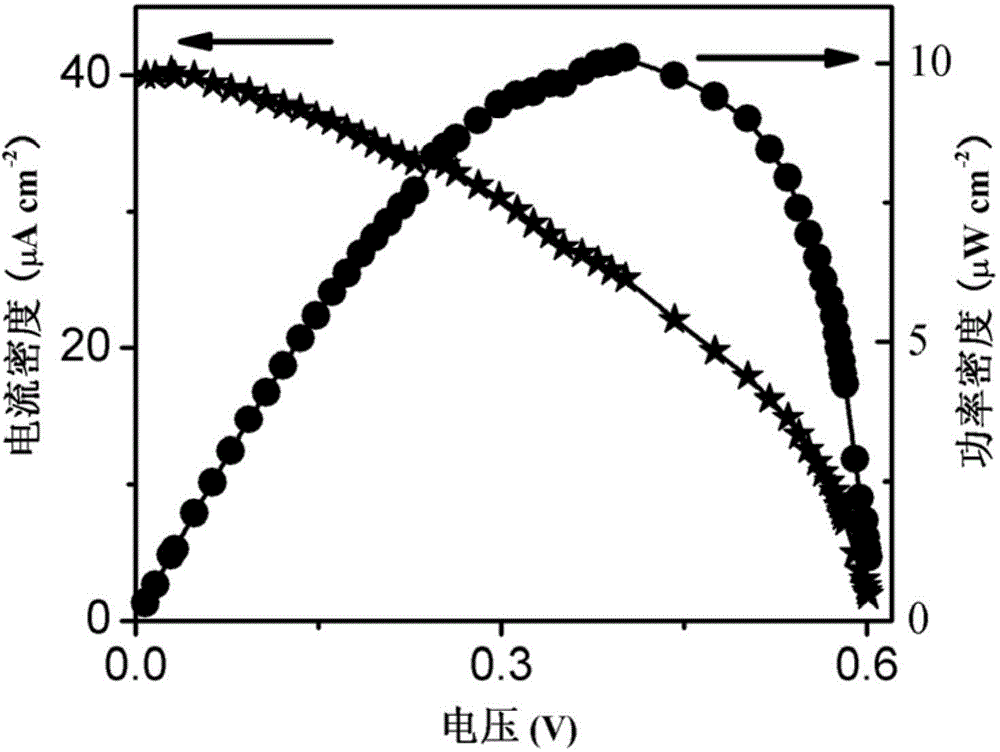
[0044] Adjust the resistance value of the resistance box connected between the anode and the cathode of the photocatalytic fuel cell, measure and calculate the power density and current density of the photocatalytic fuel cell with the change curve of the voltage, the result is as follows image 3 shown. At 0.18mW·cm -2 Under visible light irradiation, the short-circuit photocurrent density of the photocatalytic fuel cell constructed in Example 1 was 40 μA cm -2 , with a maximum power density of 10.1 μW cm at 0.40 V -2 , the photoelectric conversion efficiency reaches 5.6%, indicating that the constructed photocatalytic fuel cell has good battery performance and can realize the conversion of visible light energy and chemical energy into electrical energy at the same time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com