Spectroelectro-chemistry sensing composite probe for measuring colloidal quantum dot thin film
A spectroelectrochemical and quantum dot technology, applied in the field of photoelectrochemical testing, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, limited sensing mode, difficult cleaning, etc., and achieve the effects of high test sensitivity, good controllability and cost saving.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 QDs absorption spectrum signal measurement
[0039] The present embodiment measures the ultraviolet adsorption spectrum (Abs spectrum) of CdS quantum dots synthesized by gas-hydrothermal reaction according to the following steps, wherein the synthesis method of CdS quantum dots is referred to: Yang, T.; Lu, M.; Mao, X.; Liu ,W.; Wan,L.; Miao,S.; Xu,J.,Synthesis of CdS quantum dots(QDs)via a hot-bubbling route and co-sensitized solar cells assembly.Chem.Eng.J.2013,225 ,(0),776-783.
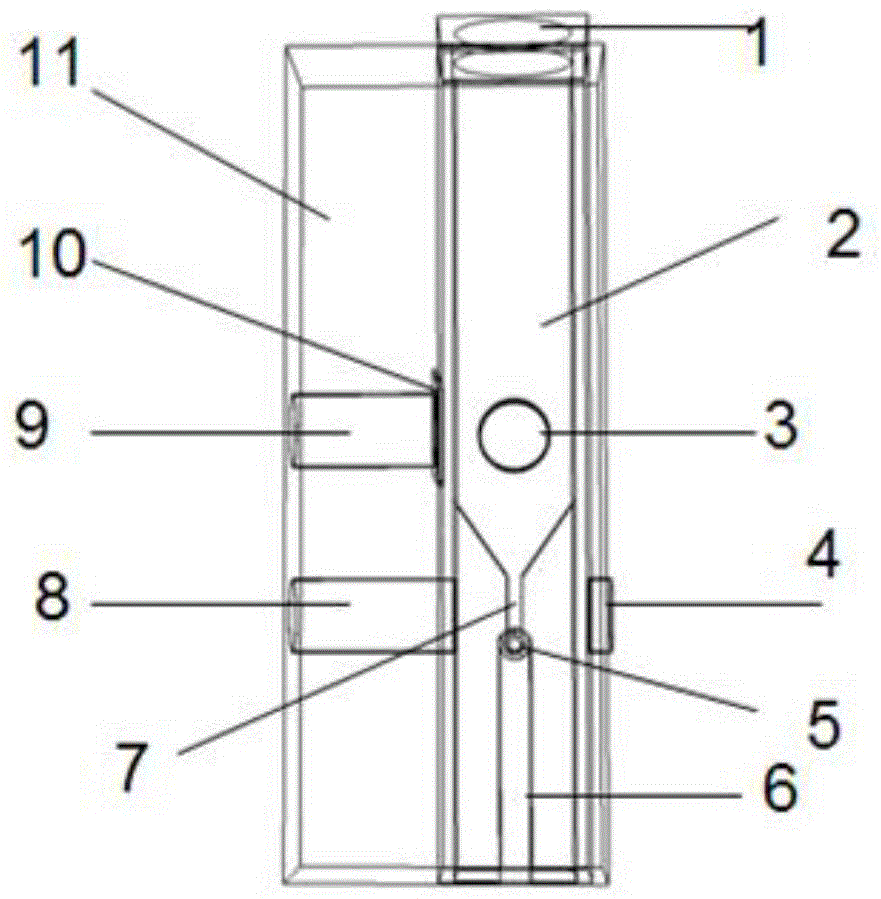
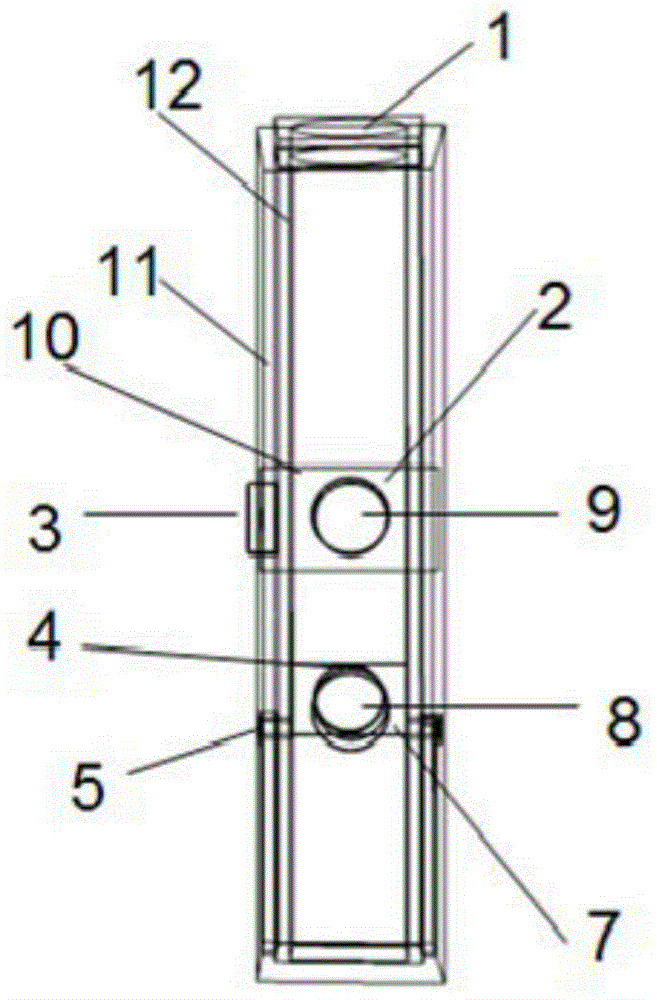
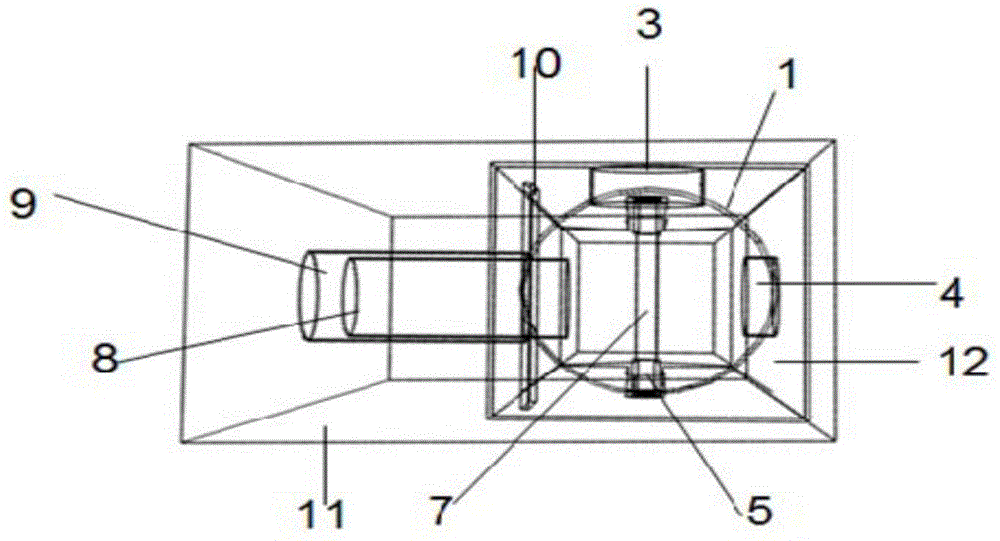
[0040] In the present embodiment, the liquid to be tested that contains CdS quantum dots is poured into the quartz photometric cell 12, the liquid to be tested is immersed in the thin layer cavity 7, and the polytetrafluoroethylene cover 11 is covered; the light source (deuterium lamp or tungsten lamp) ) is fixed on the lower optical path channel 8, and the optical fiber interface b4 is connected to the optical fiber to output the spectral signal, and the ultraviolet absorption...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Measurement of QDs fluorescence spectrum signal
[0042] The present embodiment measures the fluorescence spectrum (PL) of CdS quantum dots synthesized by gas-hydrothermal reaction according to the following steps:
[0043] Pour the CdS quantum dot test solution obtained at a reaction temperature of 40°C and a reaction time of 0.5h, at a reaction temperature of 180°C and a reaction time of 0.5h, and at a reaction temperature of 260°C and a reaction time of 0.5h into a quartz photometric cell, so that the test solution is full of macro Measure the solution test chamber 2, cover with a polytetrafluoroethylene cover 11, use a diode light source as the excitation light of the fluorescence spectrum (PL) and fix it on the upper optical path channel 9, connect the optical fiber to the optical fiber interface a 3 on the side to output the fluorescence spectrum signal , measure the fluorescence spectrum of quantum dots, the results are as follows Figure 7 As shown, i...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Determination of QDs electroluminescent signal
[0045] The present embodiment measures Cd according to the following steps 6 P 7 The electroluminescence spectrum (EL) of colloidal quantum dots, test its fluorescence spectrum (PL) simultaneously by embodiment 2 identical mode:
[0046] The electrolyte (4-(dimercaptomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(p-dimethylaminostyryl)-4H-pyran (containing supporting electrolyte tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (0.1M) ) is poured into the quartz photometric cell, so that the electrolyte is filled with the macro solution test chamber 2, Cd 6 P 7 Colloidal quantum dots are prepared on a clean ITO glass through a uniform gel process, and a layer of aluminum (about 400nm) is thermally evaporated on the quantum dot film through a mask plate as a working electrode ([Miao, S.; Yang, T.; Hickey, S.G.; Lesnyak, V.; Rellinghaus, B.; Xu, J.; Eychmueller, A., Emissive ZnOZn3P2 Nanocrystals: Synthesis, Optical, and Optoelectrochemical Properties....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com