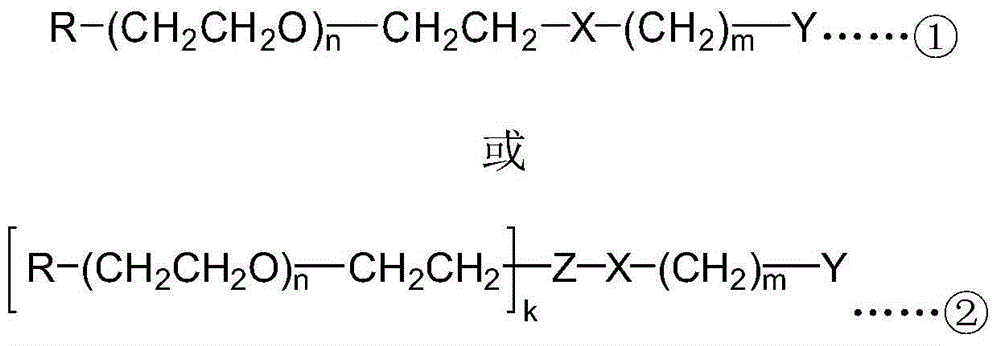Protein polypeptide drug N-terminal fixed-point polyethylene glycol modification method
A polyethylene glycol, protein polypeptide technology, applied in the preparation methods of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to effectively control product quality, storage and use, affecting the production process, and expensive raw materials. Conducive to storage for backup, avoids easy failure, and has the effect of convenient source
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
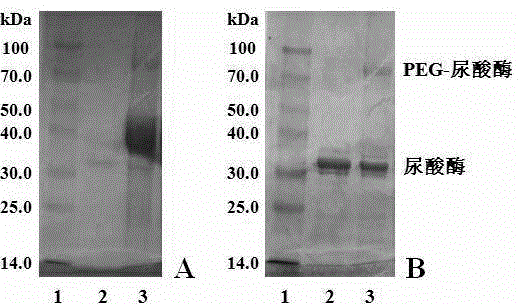
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The method for N-terminal site-directed polyethylene glycol modification of protein polypeptide drugs in this embodiment includes the following steps:
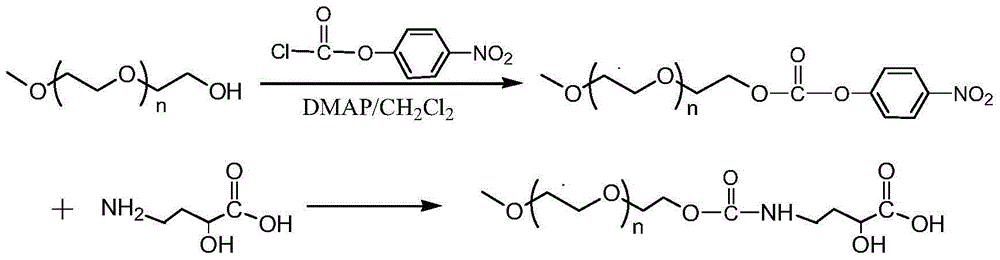
[0032] (1) Change the terminal hydroxyl group of PEG into a group with higher activity to obtain a PEG active intermediate, and then use the PEG active intermediate to combine with a small group of o-hydroxyl, α-hydroxy acid, β-amino alcohol or α-amino ketone structure Molecular compounds are reacted to obtain polyethylene glycol intermediates; specifically, the PEG active intermediates used in this example are prepared by converting the terminal hydroxyl groups of PEG with single-end blocking into groups with higher activity. In this embodiment, monomethoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG5000, with an average relative molecular weight of 5000) was chosen. The terminal hydroxyl group of mPEG5000 is converted into p-nitrophenyl carbonate to obtain PEG active intermediate, and then reacted with small molecular compound 4-amino-2...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The method for N-terminal site-directed polyethylene glycol modification of protein polypeptide drugs in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0045] (1) The PEG active intermediate selected in the present embodiment is double-chain polyethylene glycol lysine succinimide ester (2mPEG5000-Lys-NHS, the average relative molecular weight of each polyethylene glycol chain is 5000), and It reacts with the small molecular compound 3-amino-1,2-propanediol to obtain the polyethylene glycol intermediate 2mPEG5000-Lys-o-diol, whose structural formula is Wherein n is 113 on average, m is 1, k is 2, R is a methoxy group, X is an amide bond, Y is an adjacent hydroxyl structure, and Z is lysine (Lys).
[0046] (2) The polyethylene glycol intermediate 2mPEG5000-Lys-o-diol is oxidized with sodium periodate into polyethylene glycol aldehyde derivatives with active aldehyde groups at the end, which can be used for protein and polypeptide drugs after dialysis The fixed-point po...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The method for N-terminal site-directed polyethylene glycol modification of protein polypeptide drugs in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0056] (1) The PEG active intermediate selected in this embodiment is monomethoxypolyethylene glycol amino hydrochloride (mPEG20000-NH 2 HCl, the average relative molecular weight is 20000), react it with the small molecule compound N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-serine, and then remove the Boc group to obtain the polyethylene glycol intermediate monomethoxypolyethylene glycol Serine (mPEG20000-Ser), its structural formula is Wherein the average n is 454, m is 0, R is a methoxyl group, X is an amide bond, and Y is a β-aminoalcohol structure.
[0057] (2) The polyethylene glycol intermediate mPEG20000-Ser is oxidized with sodium periodate into polyethylene glycol aldehyde derivatives with active aldehyde groups at the end, which can be used for the fixed-point polymerization of the N-terminus of protein and polypeptide drugs ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com