Biochemical-thermochemical multi-point cross-linking method and system for treating biomass waste
A biomass waste and biochemical technology, applied in the field of biochemical-thermochemical multi-point cross-linking treatment of biomass waste, can solve the problems of low solid-liquid separation efficiency, low competitiveness, easy corruption, etc., and shorten the anaerobic process. Effect of reaction time, reduction of pollution and energy consumption, and acceleration of methane production rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
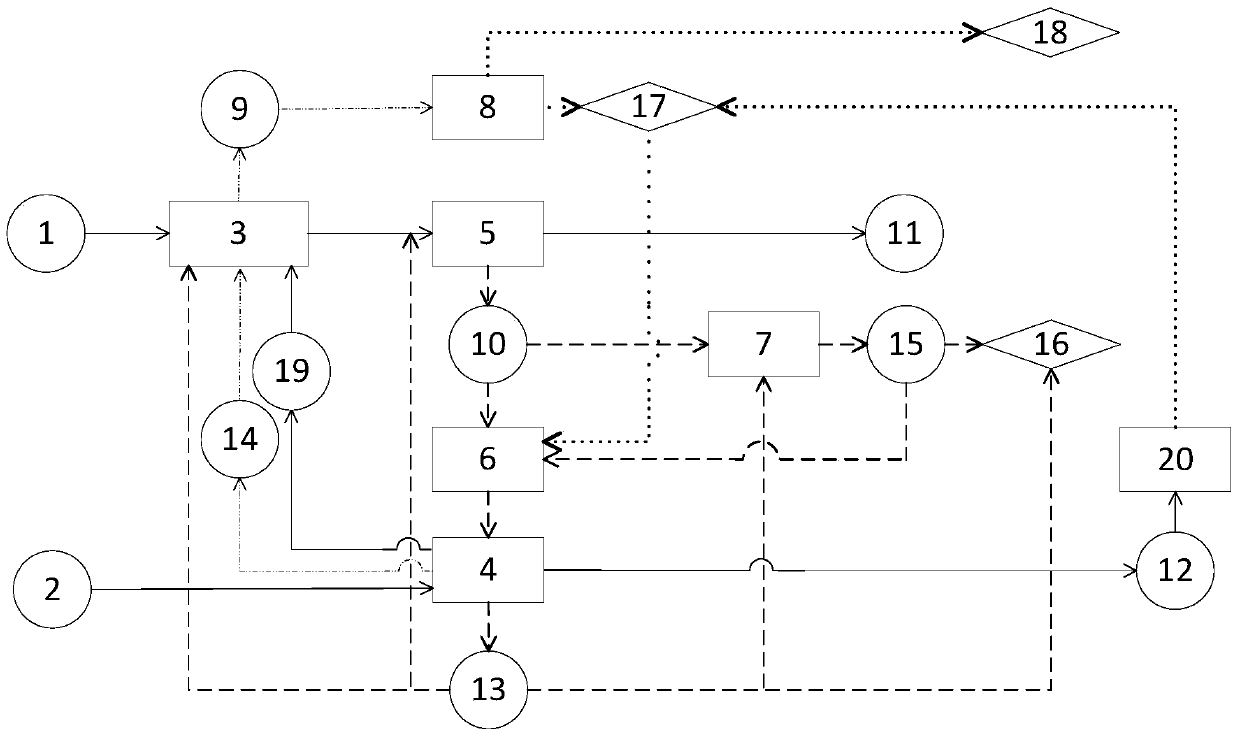
[0039] Biochemical-thermochemical multi-point cross-linking method for treating biomass waste, using figure 1 The process shown, the realization of this method comprises the following steps: (1) dry biomass waste 2 is converted into pyrolysis gas 14, biochar 13, pyrolysis oil 12, water phase condensate 19 through pyrolysis unit 4; (2) Pyrolysis gas 14 and water phase condensate 19 enter the anaerobic digestion unit 3 for processing wet biomass waste 1; (3) biochar 13 enters the anaerobic digestion unit 3, and enters the solid-liquid separation unit 5 along with the digestion residue (4) The digested residue is divided into biogas slurry 11 and biogas residue 10 through the solid-liquid separation unit 5, and biochar 13 can be added before the solid-liquid separation unit 5; (5) The biogas residue 10 is post-processed in the composting unit 7 , forming a compost product 15, which can be used as a soil conditioner 16; biochar 13 can be replenished in the composting unit 7; (6) t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com