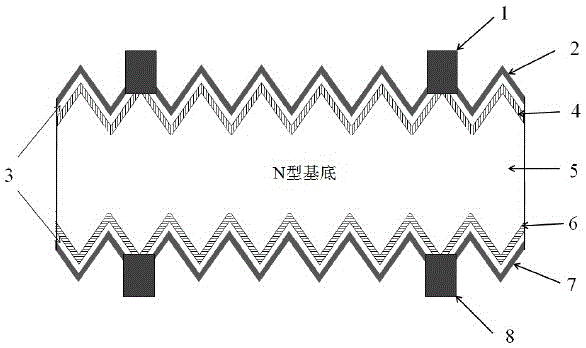
Double-sided N-type crystalline silicon cell and preparation method thereof
A crystalline silicon battery, N-type technology, applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of complicated preparation steps, high cost per watt, and limited price reduction potential, so as to simplify the process flow and reduce surface suspension. Bond density, the effect of reducing the interfacial recombination rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for preparing a double-sided N-type crystalline silicon solar cell, comprising the steps of:
[0025] (1) Using N-type monocrystalline silicon as the substrate, the silicon wafer is cleaned and textured. The resistivity of the N-type monocrystalline silicon substrate is 1~12Ω·cm, and the thickness is 170~200mm;
[0026] (2) Place the above-mentioned silicon chip face-to-face for single-sided boron diffusion. The boron diffusion surface of the silicon chip is the front side, and the sheet resistance is 60Ω / □, using BBr 3 Liquid source diffusion, the diffusion temperature is 970°C, and the time is 50min;
[0027] (3) During the cooling process after the boron diffusion propulsion is completed, a certain flow of oxygen is introduced to oxidize the borosilicate glass and its interface with silicon until the temperature is lowered to 790°C. The flow rate of oxygen is 3-16slm, preferably 5slm, The oxidation time is 3-40min, preferably 20min;
[0028] (4) Deposit a ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for preparing a double-sided N-type crystalline silicon solar cell, comprising the steps of:
[0040] (1) Using N-type monocrystalline silicon as the substrate, the silicon wafer is cleaned and textured. The resistivity of the N-type monocrystalline silicon substrate is 1~12Ω·cm, and the thickness is 170~200mm;
[0041] (2) Place the above-mentioned silicon chip face-to-face for single-sided boron diffusion. The boron diffusion surface of the silicon chip is the front side, and the sheet resistance is 65Ω / □, using BBr 3 Liquid source diffusion, the diffusion temperature is 950°C, and the time is 50min;
[0042] (3) During the cooling process after the boron diffusion propulsion is completed, a certain flow of oxygen is introduced to oxidize the borosilicate glass and its interface with silicon until the temperature is lowered to 790°C. The flow rate of oxygen is 3-16slm, preferably 5slm, The oxidation time is 3-40min, preferably 20min;
[0043] (4) on the bor...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for preparing a double-sided N-type crystalline silicon solar cell, comprising the steps of:
[0055] (1) Using N-type monocrystalline silicon as the substrate, the silicon wafer is cleaned and textured. The resistivity of the N-type monocrystalline silicon substrate is 1~12Ω·cm, and the thickness is 170~200mm;
[0056] (2) Place the above-mentioned silicon chip face-to-face for single-sided boron diffusion. The boron diffusion surface of the silicon chip is the front side, and the sheet resistance is 50Ω / □, using BBr 3 Liquid source diffusion, the diffusion temperature is 970°C, and the time is 60min;
[0057] (3) During the cooling process after the boron diffusion propulsion is completed, a certain flow of oxygen is introduced to oxidize the borosilicate glass and its interface with silicon until the temperature is lowered to 790°C. The flow rate of oxygen is 3-16slm, preferably 5slm, The oxidation time is 3-40min, preferably 20min;
[0058] (4) Deposit a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com