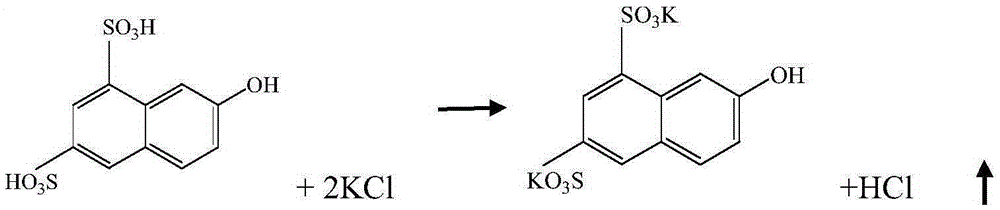
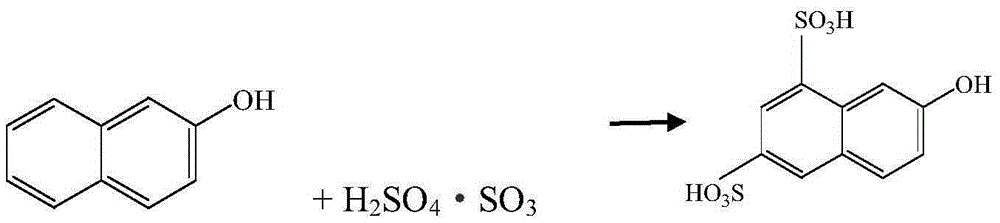Improved K acid synthesis technology
A synthesis process, acid analysis technology, applied in the field of improved K-acid synthesis process, to achieve the effects of mild reaction conditions, easy industrialization, and less land occupation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
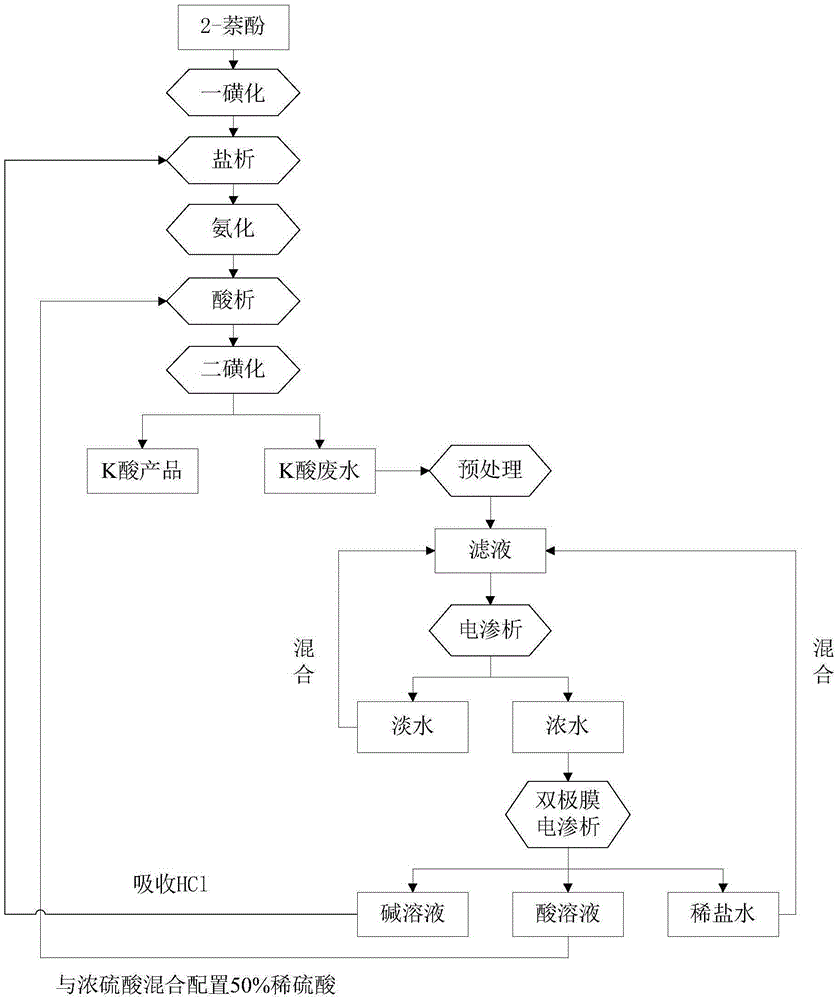
[0060] K acid wastewater, black, COD 25000-26000mg / L, pH 2.
[0061] (1) Pretreatment: wet oxidation
[0062] Take K-acid wastewater, adjust the pH of the wastewater to about 7 with potassium hydroxide solution, place it in a wet oxidation reaction kettle, and perform a wet oxidation reaction at a pressure of 3 MPa and a temperature of 220°C for 120 minutes, then filter to obtain the filtrate, and its COD is measured to be 1724 mg / L.
[0063] (2) Concentration by electrodialysis: the filtrate obtained in the above steps is treated by an ordinary electrodialysis device, and the concentrated water obtained is the concentrated salt solution, and the obtained fresh water is mixed with the pretreated filtrate and concentrated by electrodialysis. Reaction conditions of electrodialysis: 2% sodium sulfate solution is used as the polar liquid, and the current density is 200A / m 2 , and the reaction temperature was 30°C.
[0064] (3) Bipolar membrane desalination: The concentrated wa...
Embodiment 2
[0067] K acid wastewater, black, COD 25000-26000mg / L, pH 2.
[0068] (1) Pretreatment: catalytic wet oxidation
[0069] Take the K-acid wastewater, adjust the pH to about 7 with potassium hydroxide solution, and add 0.5% copper sulfate (based on the quality of the K-acid wastewater), put it in a wet oxidation reactor, at a pressure of 3MPa, at a temperature of 220°C, wet oxidation After oxidizing for 90 minutes, filter to obtain the filtrate, whose COD was determined to be 1467 mg / L.
[0070] (2) Concentration by electrodialysis: The filtrate is treated by ordinary electrodialysis equipment, and the obtained concentrated water is the concentrated salt solution, and the obtained fresh water is then mixed with the pretreated filtrate and concentrated by electrodialysis. Reaction conditions of electrodialysis: 2% sodium sulfate solution is used as the polar liquid, and the current density is 200A / m 2 , and the reaction temperature was 30°C.
[0071] (3) Bipolar membrane desali...
Embodiment 3
[0074] K acid wastewater, black, COD 25000-26000mg / L, pH 2.
[0075] (1) Pretreatment: diazotization-micro-electrolysis-flocculation-adsorption
[0076] Diazotization: Take K acid wastewater and place it in an ice bath at 0-10°C, then add dropwise a 30% sodium nitrite aqueous solution until the starch potassium iodide test paper turns blue, use sulfuric acid to keep the pH of the system constant, and stir for 1 hour. After the reaction was completed, stand still for 1 h, and filter to obtain the filtrate.
[0077] Micro-electrolysis: Add 0.3% activated carbon and 0.2% iron powder (based on the quality of K-acid wastewater) to the above-mentioned filtrate after diazotization reaction, stir for 4 hours, and always maintain the system pH=3, filter and separate to obtain the filtrate .
[0078] Flocculation: Use potassium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the above filtrate to 8-9, stir quickly at 300-500rpm for 5-10min, stir slowly at 1-200rpm for 10-20min, add 0.1% activa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com