A kind of preparation method of porous nano material yttrium vanadate
A nano-material, yttrium vanadate technology, applied in the field of materials science, can solve problems such as poor catalytic effect of photocatalysts, achieve the effects of improving reaction rate and efficiency, high sample purity, and cheap raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) Dissolve 5g of glucose in 40ml of deionized water to form a clear aqueous solution, then put the above-mentioned aqueous solution in a 50ml hydrothermal reactor, and conduct hydrothermal reaction at 150°C for 4h. Then cooled to room temperature naturally, and the carbon balls were separated out by a centrifuge. They were washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, respectively, and dried at 70 °C.
[0021] (2) Weigh 0.2258g (1 mmol) of Y 2 O 3 and 0.2340 g (2 mmol) of NH 4 VO 3 It was dissolved in dilute nitric acid with a mass fraction of 15% to 20%. After it was completely dissolved, 2.52 g of citric acid (12 mmol) was added as a chelating agent. After stirring for 1.5 h, a uniform gel was formed.
[0022] (3) 0.05 g of carbon powder obtained in step (1) was added to the gel, stirred for 3 h, and then placed in an oven and dried at 90 °C for 12 h. Finally, the obtained product was calcined in a muffle furnace at 350 °C for 2 h, and then calc...
Embodiment 2
[0025] 1) take by weighing the YVO gained in 0.02g embodiment 1 4 The photocatalyst was dispersed in 100 mL (10 mg / L) rhodamine B (RhB) solution, and magnetically stirred in the dark for 20 min.
[0026] 2) An ultraviolet lamp with a dominant wavelength of 320 nm was placed 10 cm above the glass reactor, and 2-3 mL of solution was taken every 10 min after the photocatalysis started.
[0027] 3) After the collected samples were centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 10 min, the RhB concentration was determined by a spectrophotometer.
[0028] 4) Weigh 0.02 g of pure bismuth vanadate and repeat the first three-step experiment.
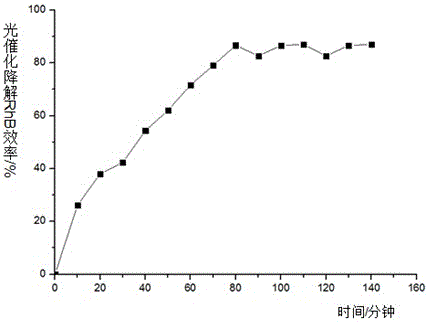
[0029] figure 2 In order to implement the results obtained in the experiment of Case 2, it can be seen from the figure that the RhB degradation efficiency of the photocatalyst prepared by the method of the present invention is 86.7% after 80min of illumination.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com