Preparation method of Nd-Fe-B magnet
A technology of neodymium iron boron and magnets, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of reduced coercive force Hcj, increased difficulty of the preparation process, and reduced residual magnetism Br, etc., to achieve improved Effects of processing performance, impact reduction, and stable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
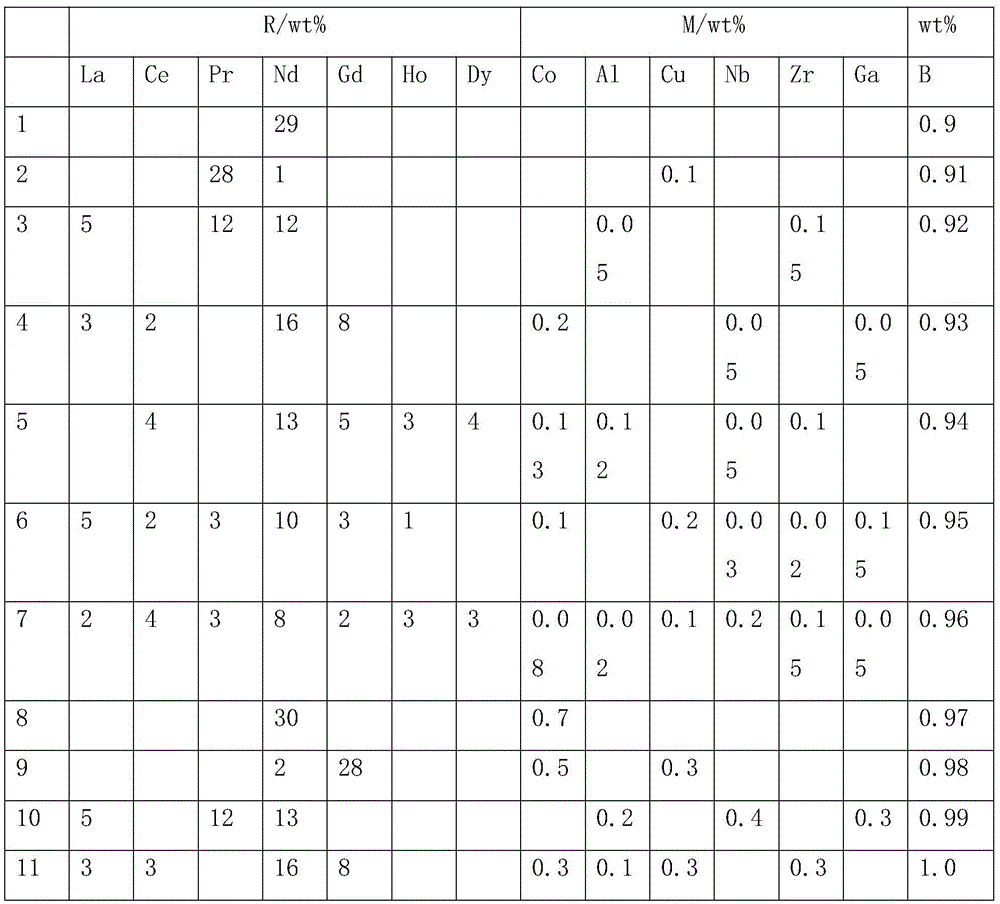
[0028]In this embodiment, the alloy composition is (PrNd)27.2Gd4.0Al0.8Cu0.2Co1.0B0.98Febal (content is weight percent, wt%), which is smelted in a vacuum induction casting furnace to prepare an alloy cast sheet of this composition. Then the alloy cast flakes are crushed into a coarse powder with an average particle size of 50 μm by hydrogen crushing, and then ultrafinely pulverized by a high-pressure water jet to grind the coarse powder into a fine powder with an average particle size of 3.3 μm. The micropowder is divided into two groups: the first group is the micropowder without adding titanium powder, which is mixed by a three-dimensional mixer, and the mixing time is 6 hours, and then sifted with a 200-mesh sifter; the second group is Add the micropowder of titanium powder, add the titanium powder that weight percent is 0.2wt% in micropowder, the average particle size of titanium powder is 15 μ m, carry out mixing by three-dimensional mixing machine, mixing time is 6 hours...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In this embodiment, the alloy composition is (PrNd)27.2Gd4.0Al0.8Cu0.2Co1.0B0.98Febal (content is weight percent, wt%), which is smelted in a vacuum induction casting furnace to prepare an alloy cast sheet of this composition. Then the alloy cast flakes are crushed into a coarse powder with an average particle size of 100 μm by hydrogen breaking, and then ultrafinely pulverized by a high-pressure water jet to grind the coarse powder into a fine powder with an average particle size of 2.7 μm. Add the titanium powder that weight percent is 0.2wt% to micropowder, the average particle size of titanium powder is 8 μ m, carry out mixing by three-dimensional mixing machine, mixing time is 6 hours, then use mesh number to be 200 mesh powder sieving machines to sieve powder . The micropowder is respectively pressed and formed in a closed press under the protection of nitrogen. The size of the green compact is a square of 57.5×30×48, and the oxygen content in the closed press is ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] In this embodiment, the alloy composition is (PrNd)27.2Gd4.0Al0.8Cu0.2Co1.0B0.98Febal (content is weight percent, wt%), which is smelted in a vacuum induction casting furnace to prepare an alloy cast sheet of this composition. Then the alloy cast flakes are crushed into a coarse powder with an average particle size of 200 μm by hydrogen crushing, and then ultrafinely pulverized by a high-pressure water jet to grind the coarse powder into a fine powder with an average particle size of 3.8 μm. Add titanium powder with a weight percentage of 0.2wt% in the micropowder, the average particle size of the titanium powder is 47 μm, mix the mixture through a three-dimensional mixer, the mixing time is 6 hours, and then sieve the powder with a 200-mesh sifter . The micropowder is respectively pressed and formed in a closed press under nitrogen protection. The size of the compact is 57.5×30×48 squares, and the oxygen content in the closed press is required to be lower than 970ppm. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com