A method for treating vanadium industrial wastewater by using magnesium desulfurization waste
A technology for desulfurization waste and industrial wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, neutralized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the pyrolysis temperature of desulfurization products, poor quality of magnesium sulfate, Oxidation equipment and other problems, to solve the problems of pollution and land occupation, simplify the treatment process and treatment time, and reduce the treatment cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
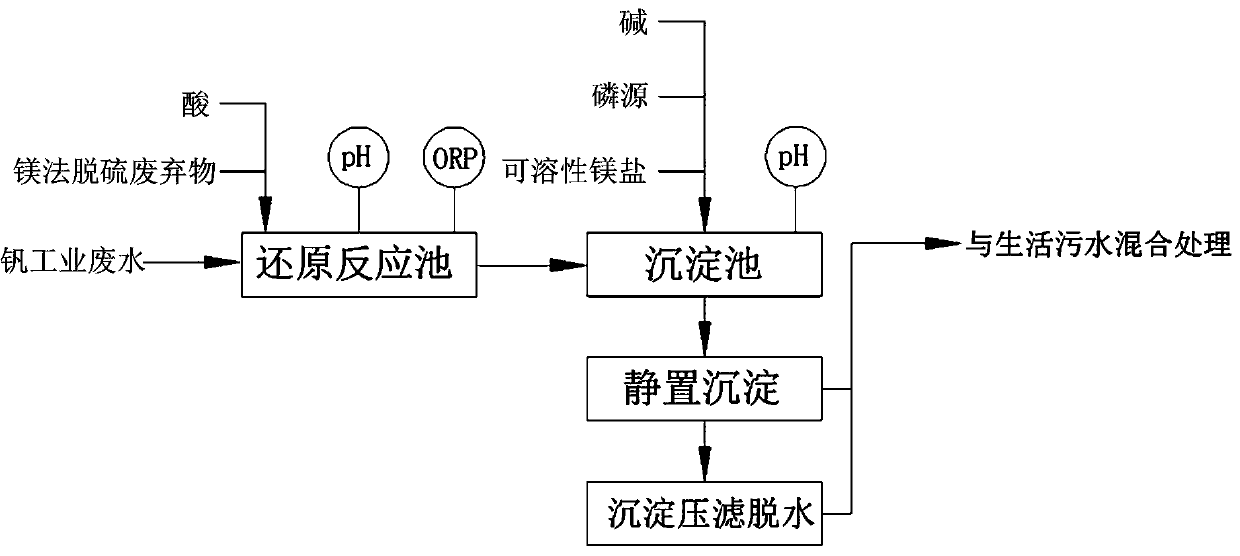
[0025] The method of adopting the magnesium method desulfurization waste of the present embodiment to treat the vanadium industrial wastewater, such as figure 1 shown, follow the steps below:
[0026] (1) The vanadium industrial wastewater from a factory in Hebei was introduced into the reduction reaction pool, and the magnesium desulfurization waste was added to the vanadium industrial wastewater and stirred. The amount of magnesium desulfurization waste added was Cr in the vanadium industrial wastewater. 6+ and V 5+ 10 times the total mass, adjust pH=3.0 with sulfuric acid, control ORP300mv, react for 30 minutes, and reduce high-valence vanadium and chromium to low-valence states during the reaction;
[0027] (2) Introduce the reduced waste water into the sedimentation tank, add easily soluble magnesium salt magnesium chloride to the reduced waste water and continue to stir, the magnesium chloride is 0.5-1.5 times the molar amount of ammonia nitrogen in the reduced waste wa...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The method of adopting the magnesium method desulfurization waste of the present embodiment to treat the vanadium industrial wastewater, such as figure 1 shown, follow the steps below:
[0031] (1) The vanadium industrial wastewater from a factory in Heilongjiang was introduced into the reduction reaction pool, and the magnesium desulfurization waste was added to the vanadium industrial wastewater and stirred. The amount of magnesium desulfurization waste added was equal to Cr in the vanadium industrial wastewater 6+ and V 5+ 8 times the total mass, adjust pH=2.5 with hydrochloric acid, control ORP270mv, react for 10 minutes, and reduce high-valence vanadium and chromium to low-valence states during the reaction;
[0032] (2) Introduce the reduced wastewater into the sedimentation tank, add magnesium sulfate to the reduced wastewater and continue stirring. After the magnesium sulfate is completely dissolved, continue stirring and add phosphoric acid. The amount of phos...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The method of adopting the magnesium method desulfurization waste of the present embodiment to treat the vanadium industrial wastewater, such as figure 1 shown, follow the steps below:
[0036] (1) The vanadium industrial wastewater from a factory in Heilongjiang was introduced into the reduction reaction pool, and the magnesium desulfurization waste was added to the vanadium industrial wastewater and stirred. The amount of magnesium desulfurization waste added was equal to Cr in the vanadium industrial wastewater 6+ and V 5+ 5 times the total mass, adjust pH=1.0 with nitric acid, control ORP350mv, react for 20 minutes, and reduce high-valence vanadium and chromium to low-valence states during the reaction;
[0037] (2) Introduce the reduced wastewater into the sedimentation tank, add magnesium oxide to the reduced wastewater and continue stirring. The amount of magnesium oxide added is 1 times the molar amount of ammonia nitrogen in the reduced wastewater. After the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com