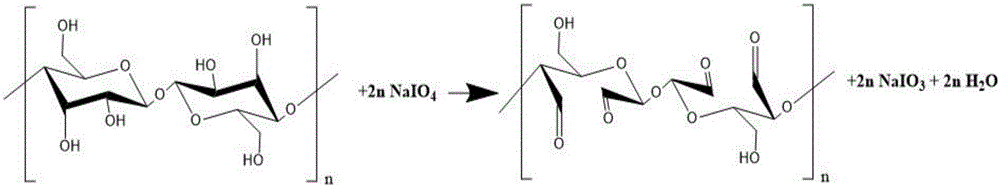
Self-crosslinked hydroformylated bacterial cellulose functional porous nano-material and preparation method thereof
A bacterial cellulose and nano-bacteria technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical science, absorbent pads, etc., can solve the problems of uneven dispersion of bacterial cellulose, poor skin adhesion, easy to fall off, etc., and achieve excellent biocompatibility and Cell affinity, controllable pore size, and the effect of improving the application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Step 1, taking a certain amount of chitosan and dissolving it in the acetic acid solution to prepare a chitosan solution with a chitosan mass fraction of 5%. Put the solution on a magnetic stirrer, stir at a low speed until the chitosan is evenly dissolved, and after ultrasonic dispersion for 30 minutes, place it in a constant temperature and humidity box to stand still for defoaming.
[0034] Step 2. Soak the flake nano-bacteria cellulose in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil at 90°C for 120min, rinse with distilled water several times, and then sterilize by ultraviolet light; soak the sterilized nano-bacteria cellulose in distilled water for 2 ~4 times, use pH test paper to lightly press the film to measure the pH value, and control the pH value of the nano-bacterial cellulose to 7.2;
[0035] Step 3: Weighing a certain amount of the above-mentioned nano-bacterial cellulose into a certain amount of deionized water, and uniformly dispersing it with a high-speed disperser to ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Step 1, taking a certain amount of amino polysaccharide and dissolving it in an acid solution to prepare an amino polysaccharide solution with a chitosan mass fraction of 6%. Put the solution on a magnetic stirrer, stir at a low speed until the amino polysaccharide is evenly dissolved, and after ultrasonic dispersion for 30 minutes, place it in a constant temperature and humidity box to defoam.
[0040] Step 2. Soak the flake nano-bacteria cellulose in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil at 90°C for 120min, rinse with distilled water several times, and then sterilize by ultraviolet light; soak the sterilized nano-bacteria cellulose in distilled water for 2 ~4 times, use pH test paper to lightly press the film to measure the pH value, and control the pH value of the nano-bacterial cellulose to 7.2;
[0041] Step 3: Weighing a certain amount of the above-mentioned nano-bacterial cellulose into a certain amount of deionized water, and uniformly dispersing it with a high-speed dis...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Step 1: Take a certain amount of polylysine and dissolve it in an aqueous solution to prepare a polylysine solution with a mass fraction of polylysine of 8%. Put the solution on a magnetic stirrer, stir at a low speed until the polylysine is evenly dissolved, and after ultrasonic dispersion for 30 minutes, place it in a constant temperature and humidity box to defoam.
[0046] Step 2. Soak nano-bacterial cellulose in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil at 80-90°C for 120 minutes, rinse with distilled water several times, and then sterilize by ultraviolet light; soak the sterilized nano-bacterial cellulose in distilled water for 2 ~4 times, use pH test paper to lightly press the film to measure the pH value, and control the pH value of the nano-bacterial cellulose to 7.2;
[0047] Step 3: Weighing a certain amount of the above-mentioned nano-bacterial cellulose into a certain amount of deionized water, and uniformly dispersing it with a high-speed disperser to obtain dispersed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com