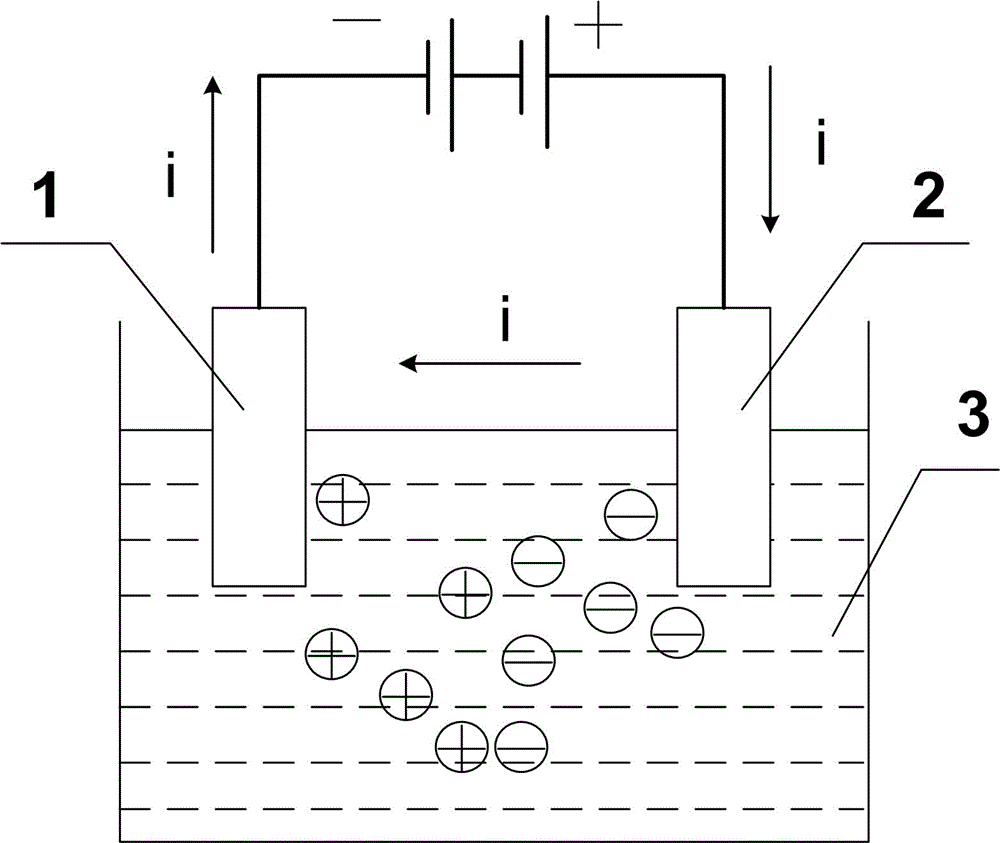
Plating assisting regulation type magnesium and steel dissimilar metal laser welding-brazing method
A technology of dissimilar materials and brazing methods, applied in welding equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in flexible control of interlayer thickness, burning loss and evaporation of magnesium alloys, and large difference in melting and boiling points. Achieve the effect of stable and reliable welding process, reduce burning loss and evaporation, and easy wetting and spreading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Step 1: Selection and processing of plates. Select a 1.5mm thick Q235 steel plate with a size of 50mm×100mm. Use silicon carbide sandpaper with a particle size of 360 to polish the steel plate to remove its surface oxide, and then use an ultrasonic cleaner in acetone to degrease and decontaminate. Choose 1mm thick AZ31 magnesium alloy, the size is 50mm×100mm. Before welding, grind the surface and side wall of the magnesium alloy plate with a winch mill to remove the oxide film existing on the surface.
[0046] Step 2: Nickel plating operation on the steel plate. The electroplating solution used for nickel plating consists of: nickel sulfate 200g / L, sodium chloride 9g / L, boric acid 32g / L, anhydrous sodium sulfate 70g / L, magnesium sulfate 65g / L. The process parameters of nickel electroplating can be: cathode current density 1 (A / dm2), pH of the plating solution is 5.5, and temperature of the plating solution is 35°C. Select a pure nickel plate with a purity of 99.9% a...
Embodiment 2
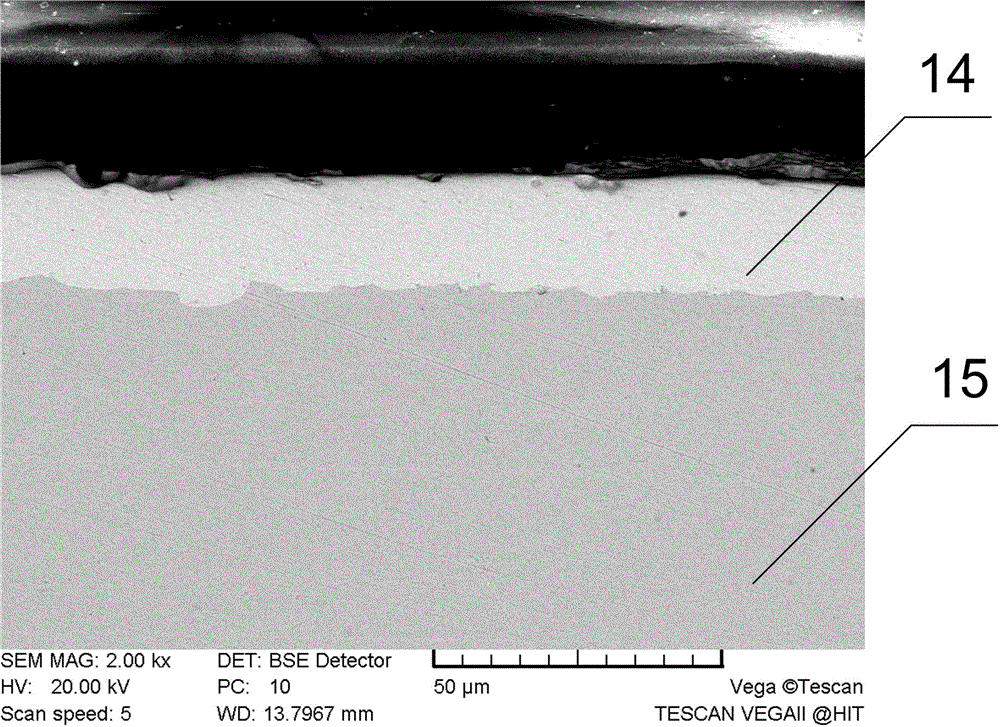
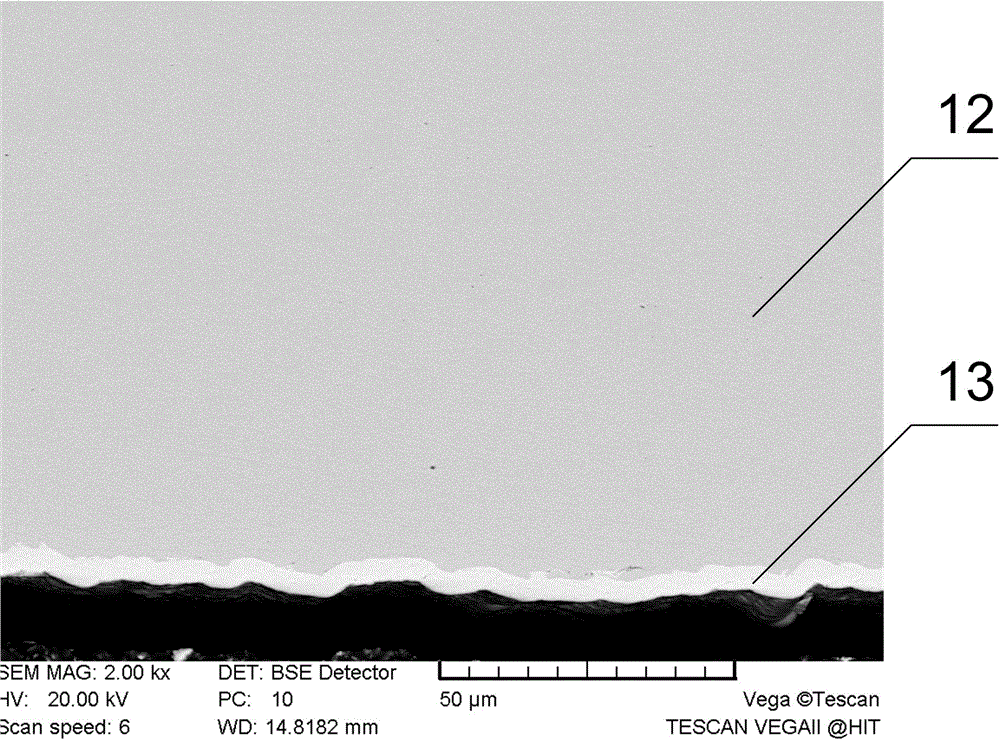
[0054] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: step 2 nickel plating operation: the electroplating time is 120min, and the thickness of the nickel coating on the steel surface can be obtained to be 20 μm (micrometer), and the SEM image of the nickel-plated steel section is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the SEM image of the magnesium / nickel-plated steel joint interface in step 5 is as follows Figure 9 As shown, the average tensile shear force of the joint obtained in step 6 can reach 220N / mm, which is 85% of the tensile shear force of the magnesium alloy base metal. Others are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: step 2 nickel plating operation: the electroplating time is 180min, the thickness of the nickel coating on the steel surface can be obtained to be 40 μm, and the SEM image of the nickel-plated steel section is as follows Image 6 As shown, the SEM image of the magnesium / nickel-plated steel joint interface in step 5 is as follows Figure 10 As shown, the average tensile shear force of the joint obtained in step 6 is 195N / mm, which is 72% of the tensile shear force of the magnesium alloy base metal. Others are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Layer thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com