Application of OsSAPK9 protein and coding gene thereof in improving resistance to rice bacterial leaf blight
A technology for transgenic rice and leaf blight, which is applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in using disease-resistant genes and loss of variety resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
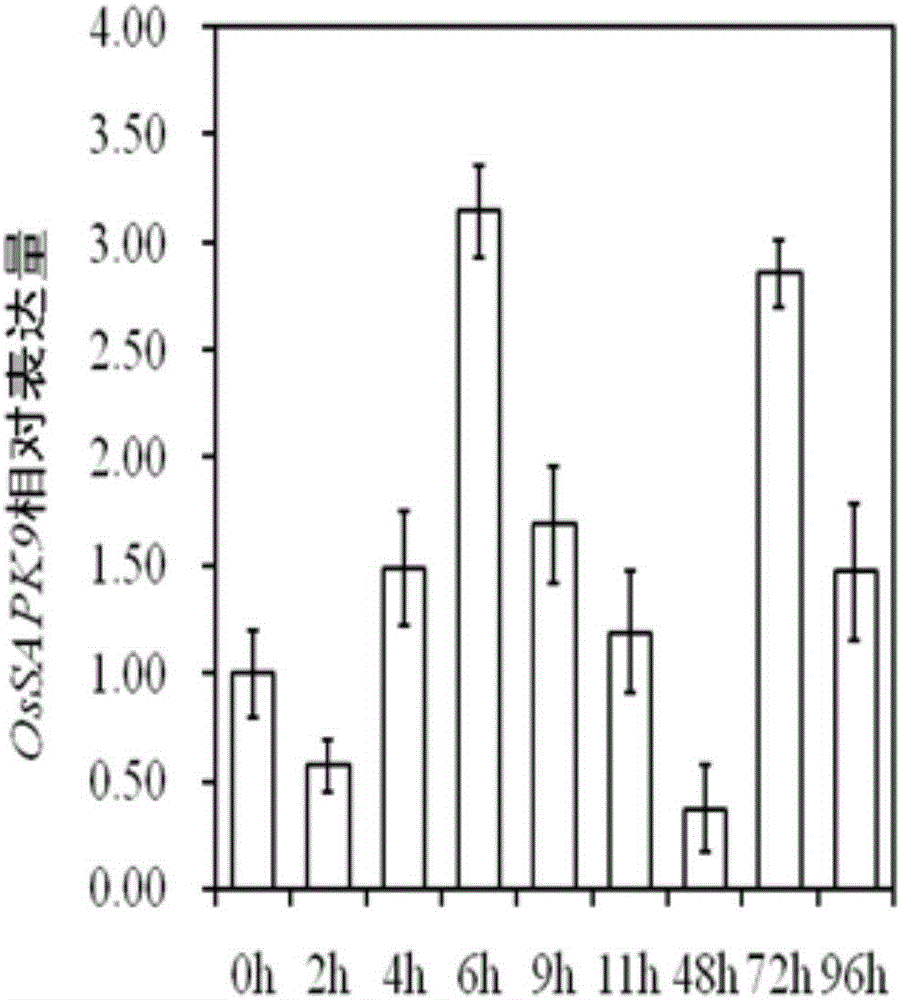
[0064] Example 1, OsSAPK9 gene expression analysis
[0065] 1. Sow the 9804 rice seeds in a seedling tray filled with sterilized soil, cultivate them in a greenhouse for 25 days, and then transplant them into a net room for single planting.
[0066] 2. During the tillering stage of the rice plants in step 1, the Xoo strain ZHE173 was used to artificially inoculate the rice plants by the leaf-cutting method, and each plant was inoculated with 5 leaves.
[0067] 3. Complete the 0, 2, 4, 6, 9, 11, 48, 72, 96 h of manual inoculation in step 2, cut the inoculated leaves, and quickly put them in liquid nitrogen for quick freezing, and take three biological replicates for each sample. All samples were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -70°C.
[0068] 4. Take the sample obtained in step 3, extract the total RNA of the sample, and reverse transcribed it into cDNA.
[0069] 5. Using the cDNA obtained in step 4 as a template, perform qRT-PCR reaction, use primer F and primer R to de...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2, OsSAPK9 gene function analysis
[0078] 1. OsSAPK9 gene RNAi vector construction
[0079] 1. Extract total RNA from 9804 rice leaves and reverse transcribed into cDNA.
[0080] 2. Using the cDNA obtained in step 1 as a template, the primer attB-F and the primer attB-R are used for PCR amplification to obtain the amplified product.
[0081] attB-F: 5′- GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTGC CAGGTTGACACACTGCGAA-3′;
[0082] attB-R: 5′- GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGT AGTGCTTATCCTCAACTTCGC-3'.
[0083] 3. Through the BP reaction, the amplified product obtained in step 2 is introduced into the vector pDONR201 to obtain the positive entry clone plasmid pDONR201-OsSAPK9i containing the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 3 of the sequence list (verified by sequencing).
[0084] BP reaction system: amplified product 2.7μL (50-100ng), vector pDONR201 1.0μL (30-50ng), 5×BPReaction Buffer 1.0μL, BP Enzyme mix 0.3μL.
[0085] BP reaction conditions: 25℃ warm bath for 1h.
[0086...
Embodiment 3
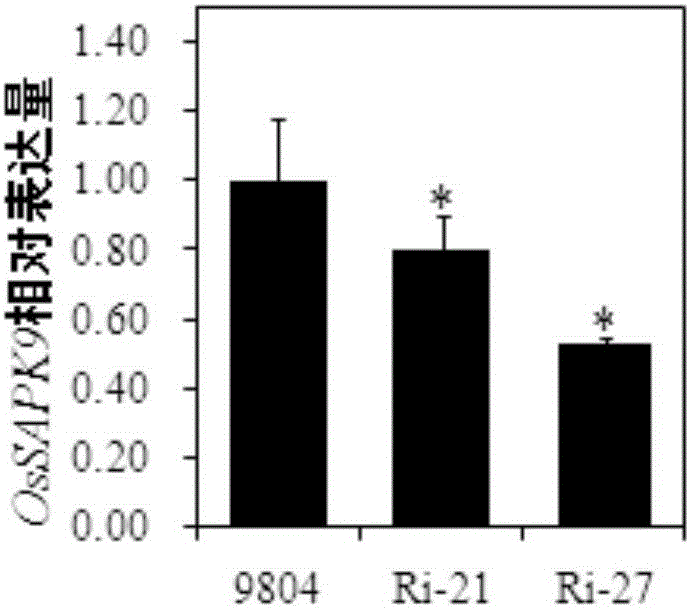
[0114] Example 3 Application of OsSAPK9 gene in improving rice bacterial blight
[0115] 1. Construction of OsSAPK9 gene overexpression vector
[0116] 1. Extract total RNA from 9804 rice leaves and reverse transcribed into cDNA.
[0117] 2. Using the cDNA obtained in step 1 as a template, use primer attB-F1 and primer attB-R1 for PCR amplification to obtain the amplified product.
[0118] attB-F1: 5′- GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTGC ATGGAGAGGGCGGCGG-3';
[0119] attB-R1: 5′- GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGT GACATGGCATATACGATCTCTCCG-3'.
[0120] 3. Through the BP reaction, the amplified product obtained in step 2 is introduced into the vector pDONR201 to obtain the positive entry cloning plasmid pDONR201-OsSAPK9 containing the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 of the sequence table.
[0121] BP reaction system: amplified product 2.7μL (50-100ng), vector pDONR201 1.0μL (30-50ng), 5×BPReaction Buffer 1.0μL, BP Enzyme mix 0.3μL.
[0122] BP reaction conditions: 25℃ warm bath fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com