Recovery method of mother liquor in preparation process of glucosamine sulfate and sodium chloride double salt
A technology of glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride, which is applied in the field of medicine and chemical industry, can solve problems such as unqualified glucosamine, product impurities exceeding standards, and difficult quality standards, and achieve stable quality and properties, low recovery costs, and good crystal forms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
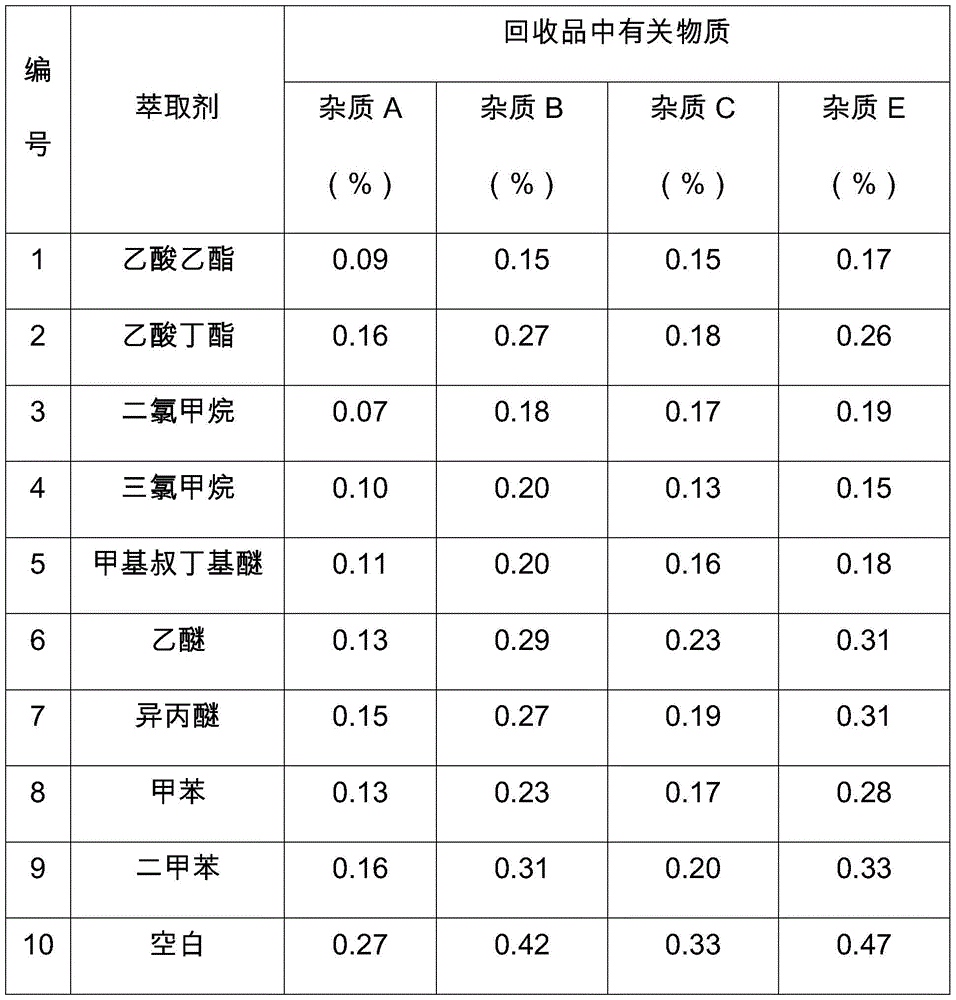
[0042] Embodiment 1: The influence of extractant on the removal of impurities
[0043] Mix the mother liquor at 55°C and distill part of the water under reduced pressure to a total volume of about 1L, with a solid content of 16.8%. Divide it into 10 equal parts, number them sequentially, and add ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, dichloromethane, and chloroform respectively. 150 mL each of 9 extractants, such as , methyl tert-butyl ether, diethyl ether, isopropyl ether, toluene, and xylene, were extracted in 3 times, and the 10th group was the blank group. After the above 10 groups were extracted respectively, the aqueous phase was taken to detect related substances.
[0044] Table 1 extraction agent to the removal situation of impurity
[0045]
[0046] Note: For impurities A, B, C, and E, refer to BP 2013 Quality Standard for Glucosamine Sulfate Sodium Chloride Double Salt.
[0047] As can be seen from the results shown in Table 1, the present invention uses extraction agent...
Embodiment 2
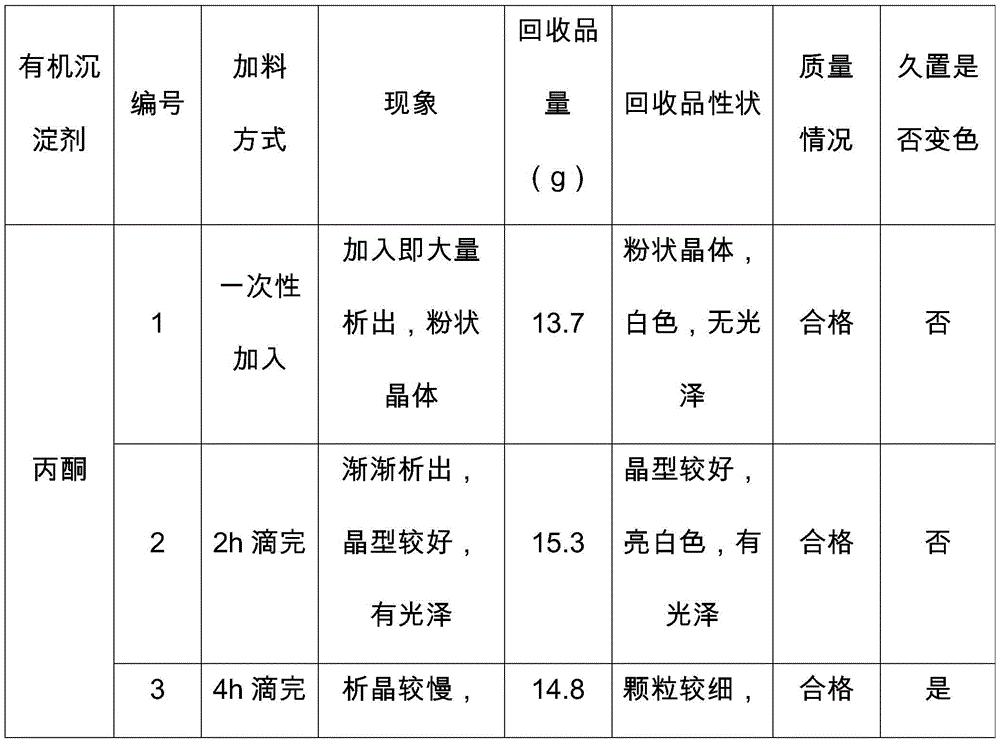
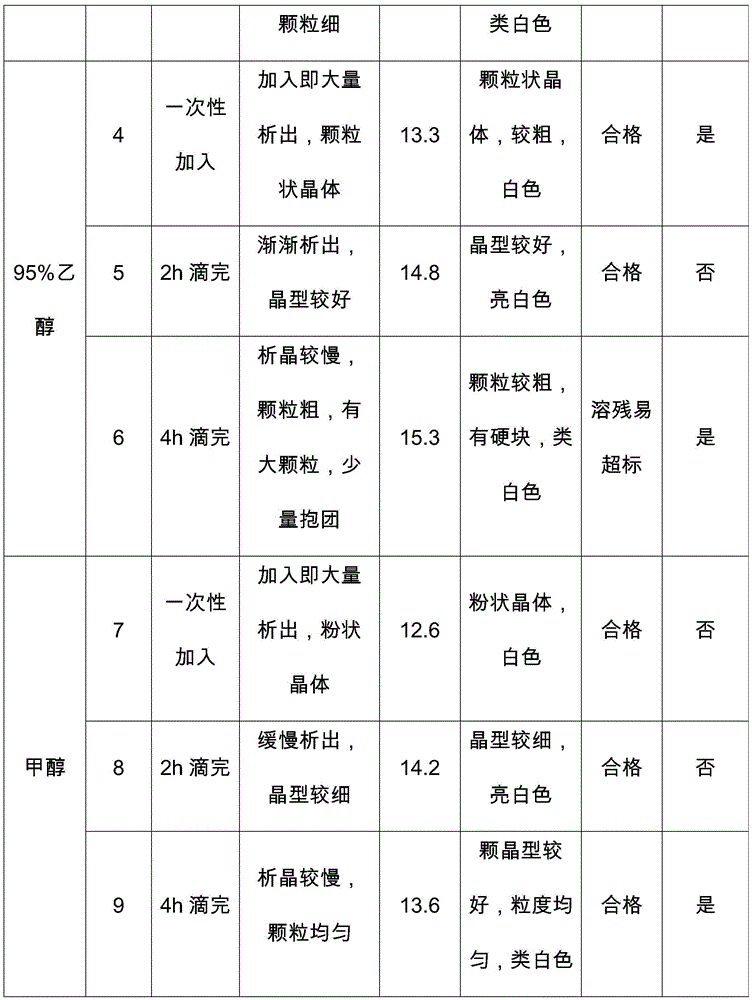
[0048] Embodiment 2: the impact of organic precipitant feeding mode on product
[0049] The mixed mother liquor was distilled under reduced pressure at 55°C to a total volume of about 900mL, with a solid content of 18.6%. Added 1.5L of dichloromethane, extracted three times, added 10g of activated carbon to the water phase, raised the temperature to 50°C for 0.5h, filtered, and weighed the filtrate. Detect the content of its glucosamine, sulfate ion and chloride ion, and calculate the respective amounts in the decolorizing solution to be 108.8g, 13.4g and 10.9g respectively. The extraction and decolorization solution was transferred to a reaction kettle, 24 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate was quantitatively added, and the temperature was raised to 50° C. for 1 h. After the reaction is complete, divide the feed solution into 9 parts, number them sequentially, control the temperature at 50° C., add 3 L of an organic precipitant (acetone, 95% ethanol or methanol) in the feeding met...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: organic precipitating agent dripping temperature influences on product
[0055] The mixed mother liquor was distilled under reduced pressure at 60°C to a total volume of about 800mL, with a solid content of 21.4%. Add 1.5L of ethyl acetate, extract three times, add 15g of activated carbon to the water phase, heat up to 55°C for 1h, filter, weigh the filtrate, and detect The contents of glucosamine, sulfate ion and chloride ion are calculated to be 107.2g, 12.8g and 10.7g respectively. The extraction and decolorization solution was transferred to a reaction kettle, 24 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate was quantitatively added, and the temperature was raised to 55° C. for 1 h. After the reaction is completed, divide the feed liquid into 4 parts, number them in turn, control the temperature at room temperature, 40°C, 50°C, and 60°C, add 3L of 95% ethanol dropwise, drop it in 2.5h, drop to room temperature for 1h, and continue to drop to Crystallize overnight at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com