A combined liquid chromatography separation method for large-scale plasmid purification
A purification method and liquid chromatography technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of not being able to recover pDNA with full load, increasing the sample volume, shortening the processing time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 : The basic method of alkaline lysis to lyse bacteria and concentrate by hollow fiber ultrafiltration
[0066] Prepare the following three liquids with purified water: P1 liquid: 50mM Tris-HC1+10mM EDTA, pH8.0; P2 liquid: 0.2M NaOH+1% SDS; P3 liquid: 3M KAC adjusted to pH5.5 with glacial acetic acid.
[0067] The plasmid transformed into Escherichia coli cultured in the fermenter was collected by centrifugal sedimentation, and the wet weight was weighed. Add 10ml of P1 solution to each gram of bacteria in a large scale glass or plastic bottle to evenly resuspend the bacteria, then add 20ml of P2 solution and stir quickly for 8-10 seconds to lyse the bacteria, let it stand for 6-8 minutes to form a light yellow gelatinous solution, pipette Add 15ml of P3 solution pre-cooled at 4-10°C to the ice bath (per gram of wet weight bacteria can also use the ratio of P1:P2:P3=15ml:15ml:15ml) and stir for 8-10 seconds and let it stand for 20 minutes. Floating large pie...
Embodiment 2
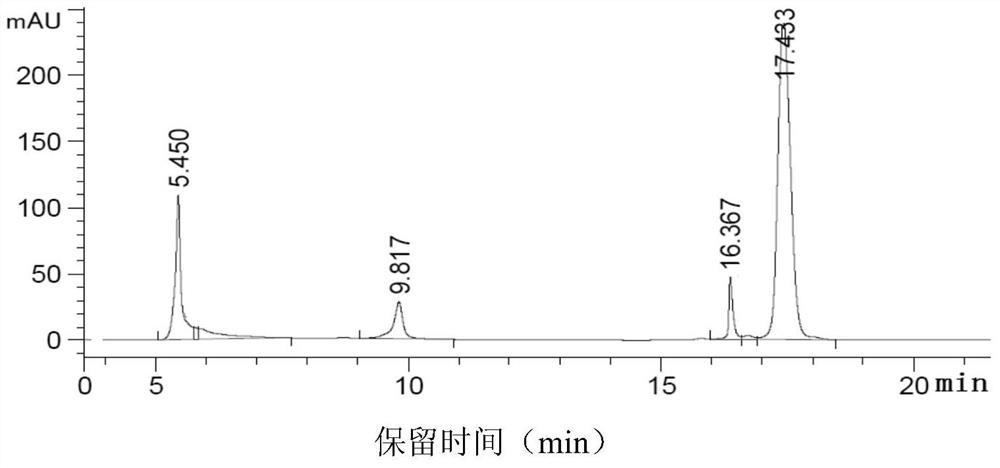
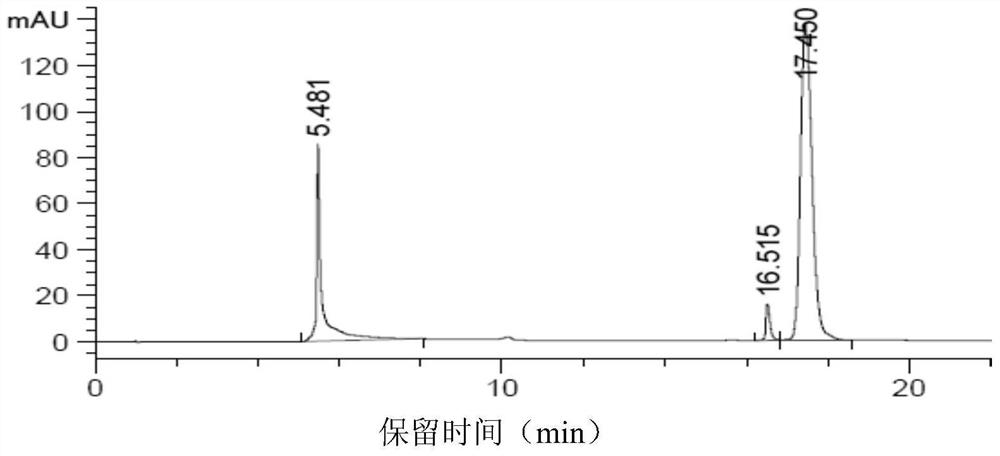
[0068] Example 2 : a method for measuring the pDNA content of each component in each step and analyzing the ratio of each component of nucleic acid
[0069] (1) Method for detecting plasmid content in lysate and concentrated lysate with small 6FF column
[0070] Use the 4.4ml Bestrose 6FF small column of Bergeron Company and prepare 1.0M KAC solution
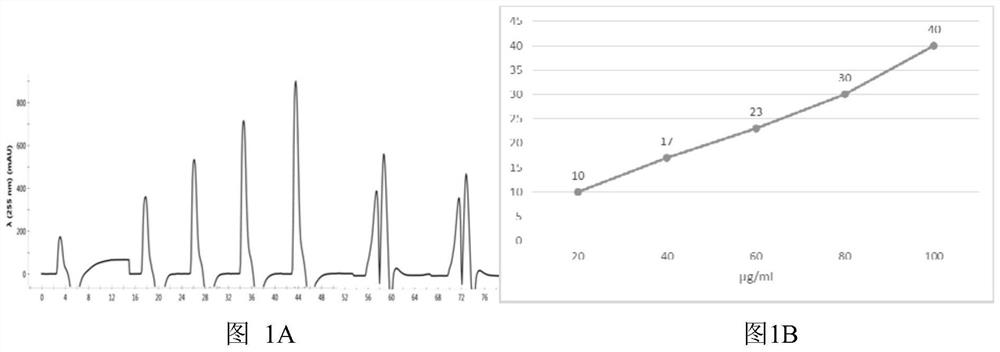
[0071] a) Make a plasmid concentration standard curve
[0072] Take the previously purified plasmid solution and use GE’s NanoVuePlus ultra-micro nucleic acid analyzer to determine the exact concentration, then use 1.0M KAC solution to make serial dilutions of 20μg / ml, 40μg / ml, 60μg / ml, 80μg / ml, and 100μg / ml Each solution is 1.2ml.
[0073] Use 1.0M KAC solution to equilibrate the 6FF small column to the baseline on the BioRad NGC medium-pressure chromatograph; take 1.0ml of the above-mentioned diluted solution and load the sample at a flow rate of 1.0ml / min, and wait 4-5 minutes after the peak appears on the computer screen...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 : The basic method of removing RNA from the lysate by gel filtration liquid chromatography to separate the pDNA fraction
[0083] On the NGC medium-pressure liquid chromatography separation device of BIO-RAD Company, 1 liter or 0.5 liter Bestrose 6FF gel column of Bogeron (Shanghai) Biotechnology Company was used, and TE (10-50mM Tris-HC1+10mM EDTA, pH 7.2) liquid equilibration, load the clarified lysate concentrated by hollow fiber ultrafiltration and filtered through a 0.45 μm filter. The loading amount was determined by preliminary experiments. After loading the sample, continue to wash with TE, collect the first peak of the macromolecule that comes down first, which is the pDNA component, and then discard the large peak of RNA that comes down. The peak area ratio of the two is usually between 1:8-12. After washing with TE solution until a flat baseline appears on the computer screen, perform the second and third loading to separate and collect pDNA frac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com