A method for removing complexed heavy metal ions in water
A technology of heavy metal ions and heavy metals, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, multi-stage water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increased burden, non-biodegradable pollutants, high cost, etc., and achieves wide application range and high removal efficiency High, simple method and effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Water containing complexed heavy metal ions (Ni 2+ :155mg / L; Zn 2+ :50mg / L)
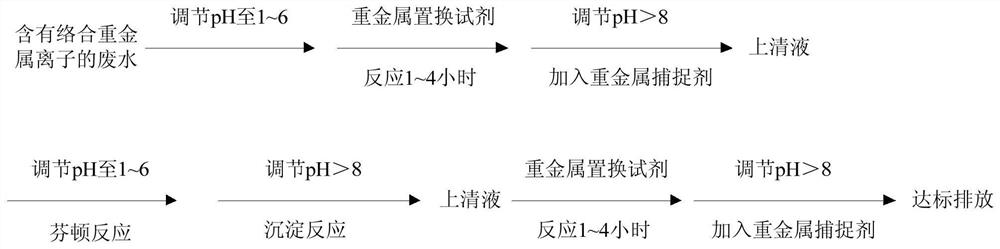
[0042] 1) Adjust the pH of the water body containing complexed heavy metal ions to 6 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent sodium sulfide (12g / L). The reaction time is 3 hours, adjust the pH to 9, and then add an anionic polyacrylamide (25g / L tons of water);
[0043] 2) carry out Fenton reaction after step 1) gained supernatant is adjusted pH to 2, namely add hydrogen peroxide 6L / ton of water (hydrogen peroxide content 30%) and ferrous ion 8kg / ton of water (ferrous sulfate), the reaction time is 2 hours, then adjust the pH to 8.5 for precipitation;
[0044] 3) Adjust the pH of the supernatant obtained in step 2) to 5 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent sodium sulfide 6g / L. After the reaction time is 3 hours, adjust the pH to 9, and then add the heavy metal scavenger anionic polyacrylamide 12g / ton water, to obtain the heavy metal ion content in the supernatant ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Water containing complexed heavy metal ions (Ni 2+ :88mg / L; Zn 2+ :55mg / L; Pb 2+ :20mg / L)
[0047] 1) Adjust the pH of the water containing complexed heavy metal ions to 1 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent sodium sulfite 5g / L. The reaction time is 2 hours, adjust the pH to 10, and then add the heavy metal scavenger neutral polyacrylamide 20g / ton of water;
[0048] 4) carry out Fenton reaction after step 1) gained supernatant is adjusted pH to 1, namely add hydrogen peroxide 10L / ton of water (hydrogen peroxide content 30%) and ferrous ion 3kg / ton of water (ferrous sulfate), the reaction time is 3 hours, then adjust the pH to 8.5 for precipitation;
[0049] 5) Adjust the pH of the supernatant obtained in step 2) to 4 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent sodium sulfite 10g / L. The reaction time is 4 hours, adjust the pH to 9, and then add the heavy metal scavenger polyaluminum chloride 100g / ton of water to obtain The content of heavy met...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Water containing complexed heavy metal ions (Ni 2+ :205mg / L; Zn 2+ :89mg / L; Pb 2+ :18mg / L; Cu 2+ :50mg / L)
[0052] 1) Adjust the pH of the water containing complexed heavy metal ions to 5 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent ferric chloride 25g / L. The reaction time is 3 hours, then adjust the pH to 8.5, and then add 50g / ton of heavy metal scavenger cationic polyacrylamide water;
[0053] 2) After adjusting the pH of the supernatant obtained in step 1) to 3, carry out the Fenton reaction, that is, add 20L / ton of hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide concentration is 30%) and 25kg / ton of ferrous ion water (ferrous sulfate), and the reaction time For 4 hours, then adjust the pH to 9 for precipitation;
[0054] 3) Adjust the pH of the supernatant obtained in step 2) to 3 and react with the heavy metal replacement reagent ferric chloride 15g / L. The reaction time is 3 hours, then adjust the pH to 9, and then add the heavy metal scavenger polyaluminium ferric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com