Compound bacteria capable of rapidly degrading 17-beta-estradiol as well as preparation method and application of compound bacteria
A technology of rapid degradation and compound bacteria, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of late start of research, less research on microbial degradation characteristics and degradation mechanism of environmental estrogens, etc., and achieve the effect of high efficiency degradation, good synergistic effect, and high efficiency degradation performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Acquisition and preservation of bacteria degrading 17β-estradiol
[0032] Sludge samples from pharmaceutical factories and sewage treatment plants were collected as microbial sources, refrigerated and transported back to the laboratory. And the samples were cultured with only carbon source. Dissolve 15 mg of 17β-estradiol in 30 mL of methanol to prepare a 17β-estradiol mother solution with a concentration of 500 mg / L. Take 1mL of 17β-estradiol mother liquor and add it to the Erlenmeyer flask containing 100mL of inorganic salt medium, so that the final concentration of 17β-estradiol in the inorganic salt medium is 5mg / L (the composition of inorganic salt medium is g / L) : Na 2 HPO 4 4.260; KH 2 PO 4 2.650; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.200; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.500; CaCl 2 0.020. Adjust the pH to 7.0 with 0.1mol / L NaOH and 0.1mol / L HCl, and add 1mL of trace elements. Trace element composition (g / L): NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.024; CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.190; H 3 BO 3 0.006; Z...
Embodiment 2
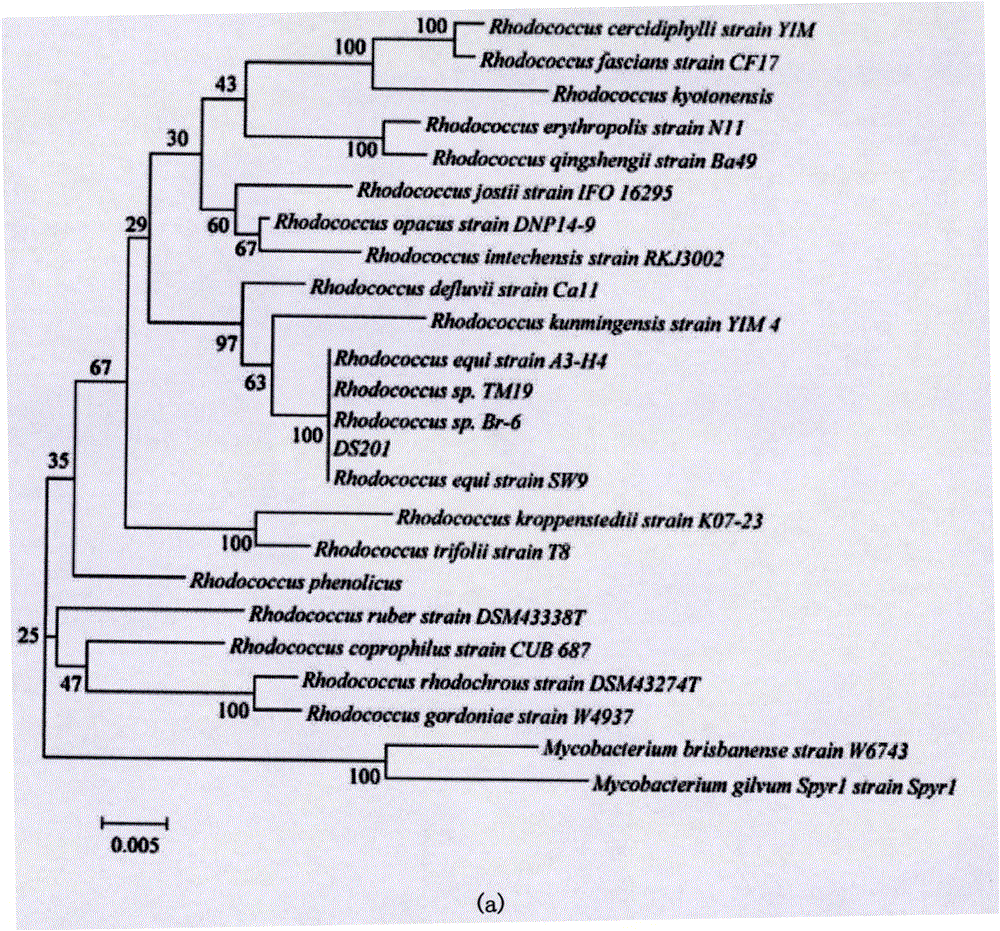
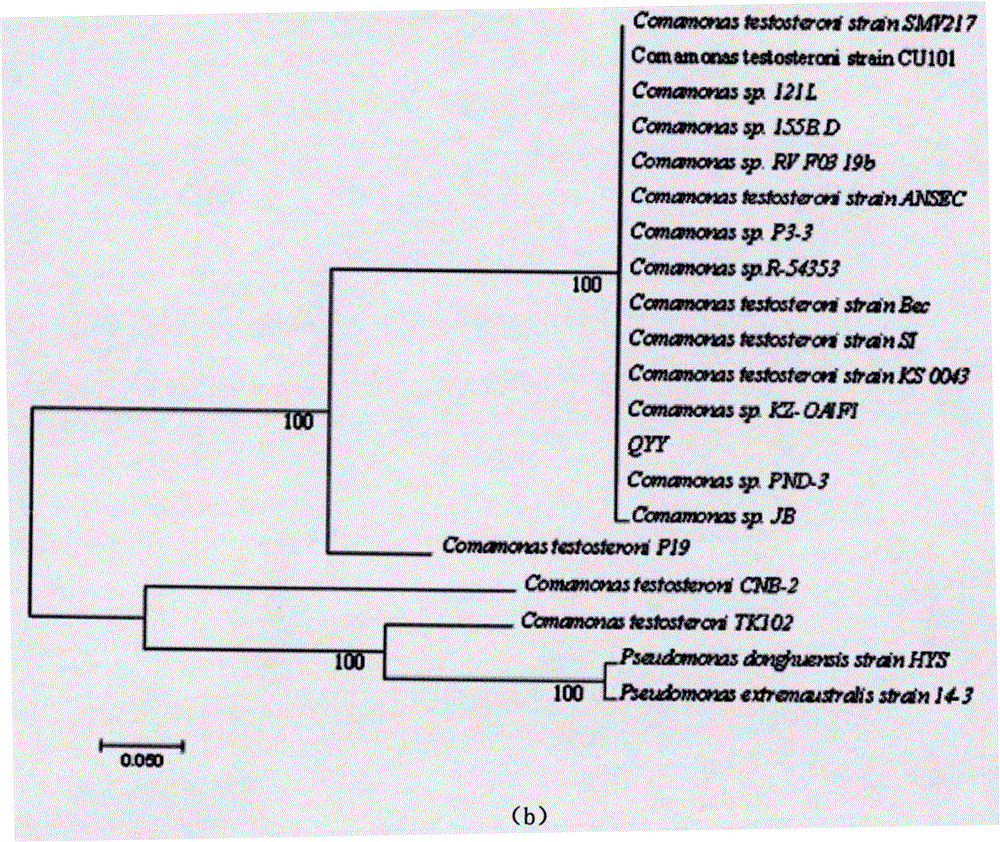
[0035] Example 2 Identification of bacteria degrading 17β-estradiol
[0036] The DNA was amplified by PCR amplification technique using universal primers for bacteria. The sequencing results were searched for homology comparison with the 16S rDNA gene sequence in the GenBank database using the BLAST tool in NCBI. The comparison results show that the 16S rDNA gene sequence of Rhodococcus DSH has high homology with the 16S rDNA gene sequences of multiple strains of Rhodococcus and Rhodococcus equi in the genus Rhodococcus (Rhodococcus), combined with the morphology of Rhodococcus DSH Characteristics and physiological and biochemical indicators, strain DSH was preliminarily identified as Rhodococcus, named Rhodococcus (Rhodococcus sp.) DSH. The 16S rDNA gene sequence of strain QYY is close to the genetic distance of Comamonas testosteroni, combined with the morphological characteristics and physiological and biochemical indicators of strain QYY, it was identified as Comamonas te...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3 Composite bacteria are to the degradation ability of 17β-estradiol
[0038] Dilute the prepared composite bacterial solution to OD with phosphate buffer solution 600 When the value is 1.0, the bacterial suspension is prepared for use. Take out 200 μL of composite bacteria liquid and inoculate it into 17β-estradiol as the only carbon source, and inoculate it into inorganic salt medium with a concentration of 50 mg / L, and culture it continuously for 7 days in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 30°C and 120 rpm, and take samples once a day . After the inorganic salt medium was pretreated, the ability of the complex bacteria to degrade 17β-estradiol was detected by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The detector is UV (DualλAbsorbance Detector, Water2487), and the chromatographic column is Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 column (150×4.6mm, 3.5mm). The mobile phase volume ratio is acetonitrile: water = 1:1, the detector wavelength is 275 nm, the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com