Rice OsGRDP1 protein related to disease resistance of plants and its encoding gene and application
A disease resistance, plant technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as not yet established
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of rice OsGRDP1 protein and its coding gene
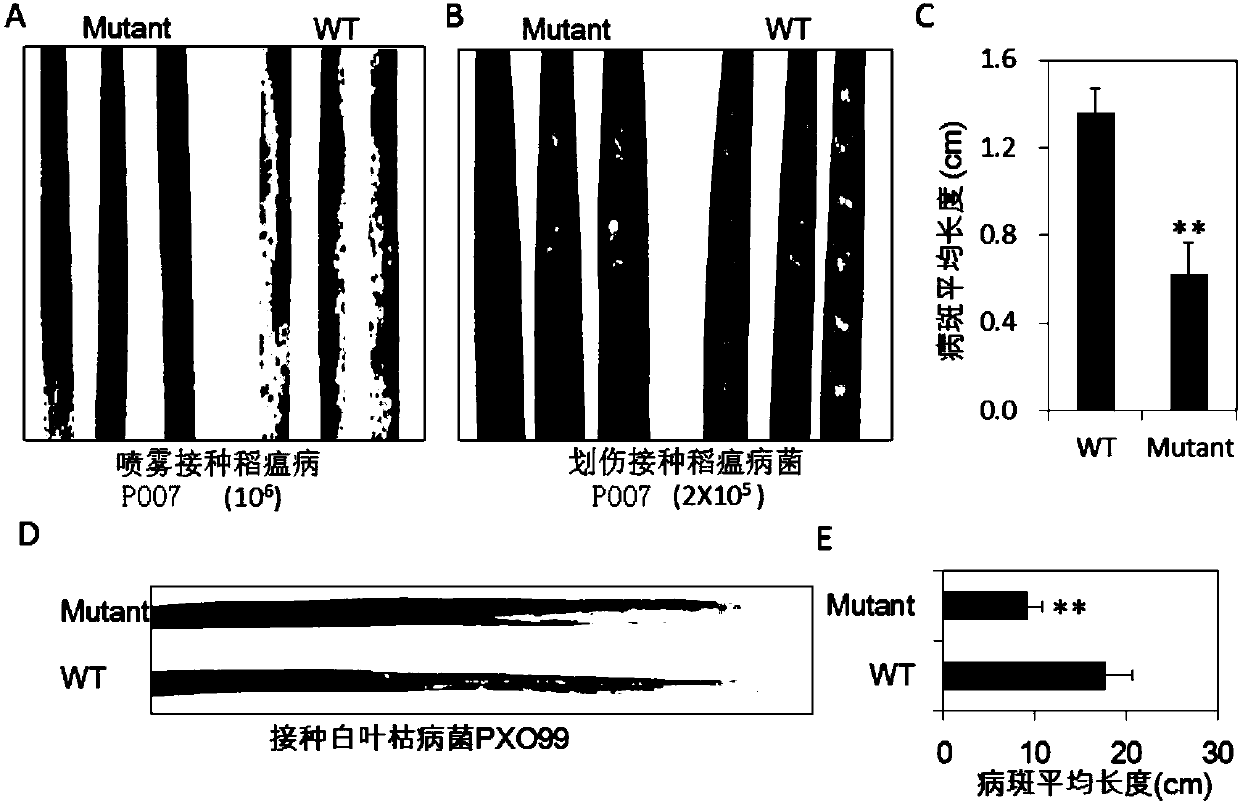
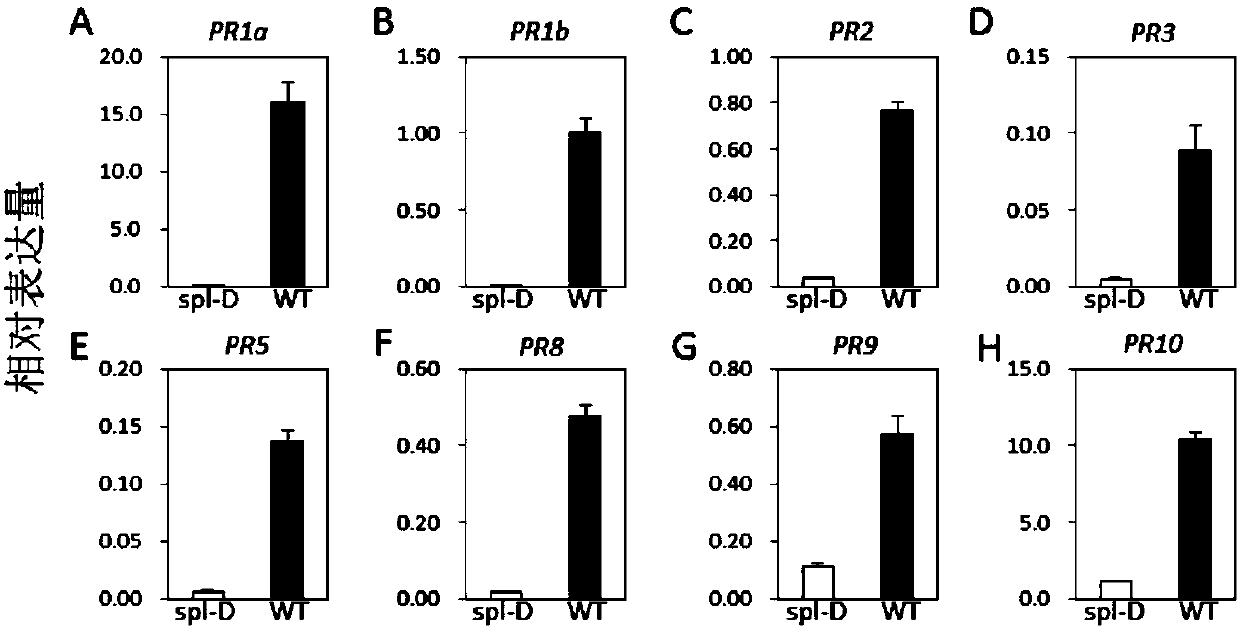
[0077] 1. Acquisition of mutant spl-D and detection of disease resistance traits
[0078] 1. The acquisition of mutant spl-D and its phenotype
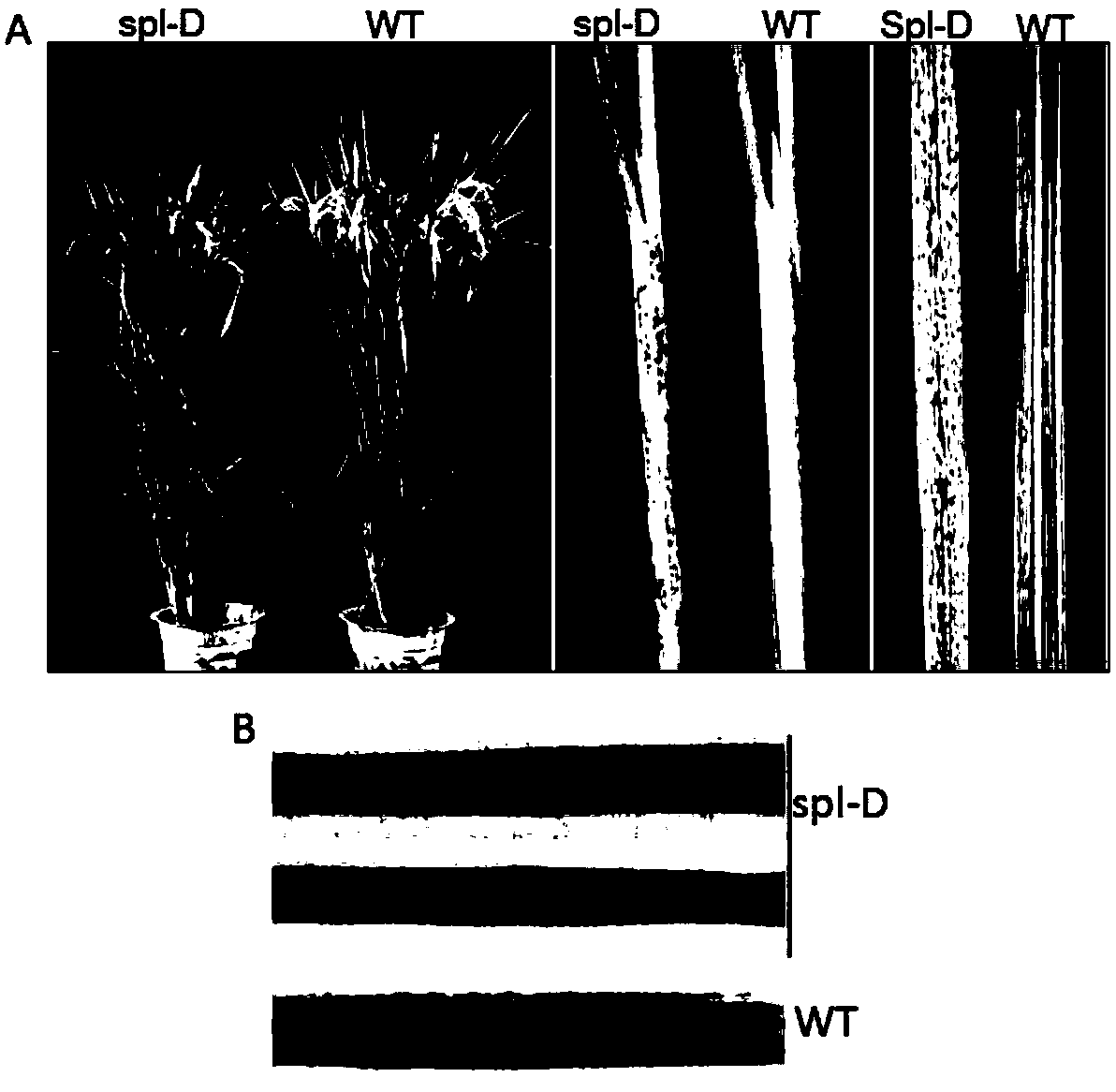
[0079] Mutant spl-D was screened from the offspring of T-DNA transformed rice variety Aichi Asahi. Compared with the wild-type rice variety Aichi Asahi, the mutant spl-D spontaneously produces lesion-like spots, and the phenotype of the mutant is as follows: figure 1 Shown in A. Among them, WT is the wild-type rice variety Aichi Asahi, and spl-D is the mutant rice. Under long-day conditions (Beijing, May-October, about 12-14 hours of sunshine), there is almost no difference between the mutant and the wild type at the rice seedling stage. As the growth proceeds, after entering the tillering stage, lesion-like spots appear successively from the lower leaves to the upper leaves, and the lesion-like spots can extend to the leaf sheaths; under short-day...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Example 2, the subcellular localization of OsGRDP1 protein
[0103] 1. Using the PCR method, GFP-GRDP1-F (5'-ATA ggtacc ATGGACGGGGAGCAAGAG-3', the underlined part is the Kpn I site) as the forward primer, GFP-GRDP1-R (5'-TAT ggatcc GGTGCTCGCGTTG-3', the underlined part is the Bam HI site) was used as a reverse primer to amplify the open reading frame sequence of the OsGRDP1 gene from the cDNA of the rice variety Aichi Asahi. After the PCR product was recovered, it was connected into the pMD-18T vector (TaKaRa). After the sequencing was correct, it was digested with Kpn I and BamHI, and the digested product was connected into the plant subcellular localization expression vector pCG1301 (purchased from Protin (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) to obtain the recombinant expression vector pCG1301-OsGRDP1-GFP containing the OsGRDP1 gene. The structure of the recombinant expression vector pCG1301-OsGRDP1-GFP is described as: a recombinant plasmid obtained by inserting positions 1-2970 ...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3, Obtaining and phenotypic identification of OsGRDP1 gene overexpression plants
[0106] The gene involved in this example is the OsGRDP1 gene of the rice variety Aichi Asahi obtained in Example 1, its nucleotide sequence is sequence 1 in the sequence listing, and the protein (OsGRDP1) shown in sequence 2 in the coding sequence listing . Sequence 1 consists of 2973 nucleotides, and Sequence 2 consists of 930 amino acids.
[0107] 1. Obtaining and identification of OsGRDP1 gene overexpression plants
[0108] 1. Construction of recombinant expression vector pCAMBIA1301-Ubi-OsGRDP1
[0109] (1) Utilize PCR method, adopt primer 5'-ata gagctc GTGCAGCGTGACCCGGT-3' (the underlined part is the Sac I site) and 5'-ata ggatcc AAGTAACACCAAACAACAGGGT-3' (the underlined part is the BamHI site), using the binary vector pUbiGUSPlus (Prutin Biotechnology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) as a template to amplify the ubiquitin promoter region. After the amplified product was recovered...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com