Molybdenum disulfide-based nanometer material for efficiently producing hydrogen by decomposing water through photocatalysis and preparation method thereof
A molybdenum disulfide-based, nanomaterial technology, which is applied in the field of catalysis, can solve the problems of limited research on precious metal nanoparticles/molybdenum disulfide composite materials, independent light absorption and interface engineering, and difficulty in improving at the same time, so as to achieve wide application of propulsion technology. , the effect of promoting electron transfer and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
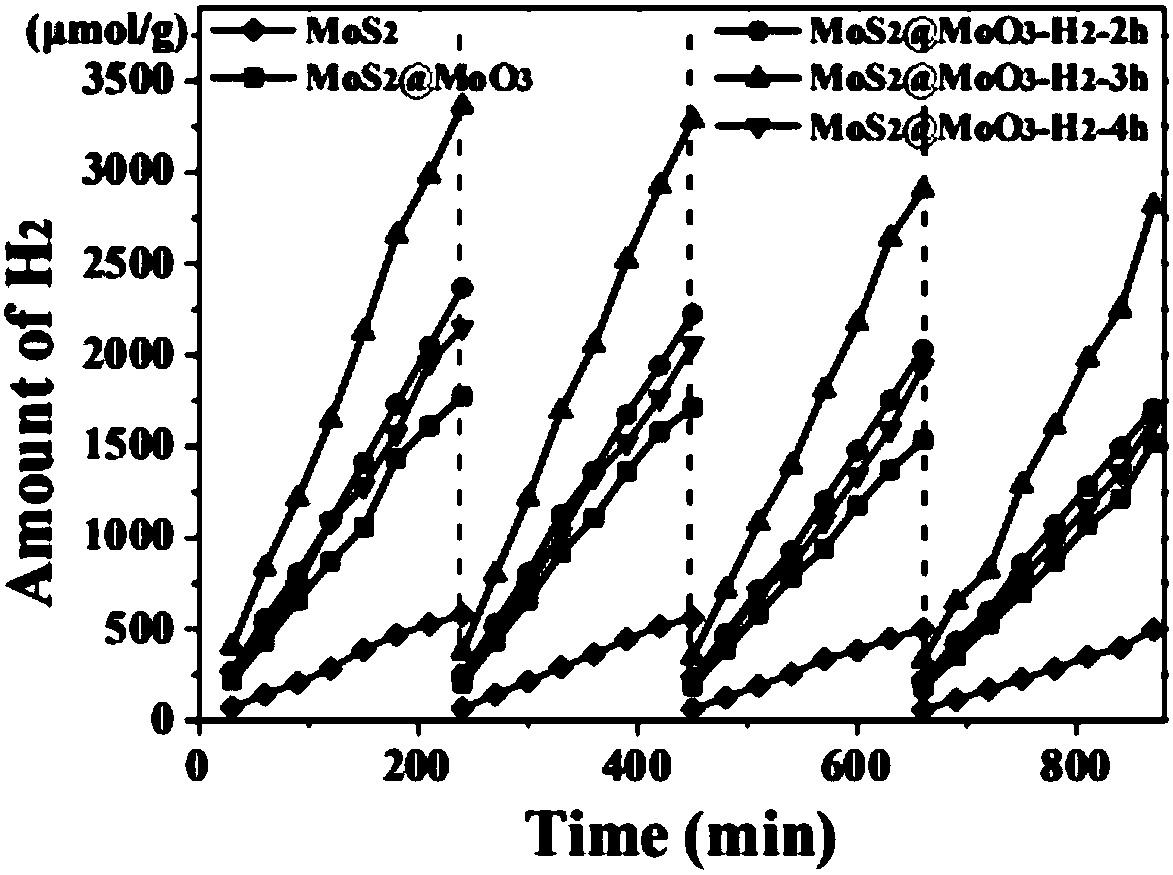
[0020] Polyvinyl alcohol (7wt%) was dissolved in dimethylformamide and stirred overnight at 60°C, and then 1.5g of ammonium molybdate was added to obtain a uniform electrospinning solution. A syringe with a needle tip diameter of 0.5mm and a volume of 20ml was used, the electric field voltage was set to 16KV, and the flow rate was controlled at 0.7ml / h for electrospinning, and then calcined in air at 280°C for 3h to obtain molybdenum trioxide nanomaterials. Take 2.0mmol sodium molybdate and 4.0mmol cysteine dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution A, take 0.5g of molybdenum oxide nanomaterials dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution B, add solution B drop by drop to solution A and ultrasonically 20min, and then carry out a hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 12h. After the reaction is finished, it is centrifuged and washed at 4500 rpm, and then dried at 65° C. to obtain a molybdenum disulfide / molybdenum trioxide nanocomposite material.
[0021] Characterizatio...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Polyvinyl alcohol (7wt%) was dissolved in dimethylformamide and stirred overnight at 55°C, and then 2g of ammonium molybdate was added to obtain a homogeneous electrospinning solution. A syringe with a needle tip diameter of 0.5mm and a volume of 20ml was used, the electric field voltage was set to 17KV, and the flow rate was controlled at 0.8ml / h for electrospinning, and then calcined in air at 300°C for 2h to obtain molybdenum trioxide nanomaterials. Take 2.5mmol sodium molybdate and 4.0mmol cysteine dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution A, take 0.6g of molybdenum oxide nanomaterials dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution B, add solution B drop by drop to solution A and sonicate 25min, and then conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 190°C for 9h. After the reaction is finished, it is centrifuged and washed at 5000 rpm, and then dried at 60° C. to obtain a molybdenum disulfide / molybdenum trioxide nanocomposite material.
[0024] Characterization: Take...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Polyvinyl alcohol (7wt%) was dissolved in dimethylformamide and stirred overnight at 65°C, and then 1 g of ammonium molybdate was added to obtain a uniform electrospinning solution. A syringe with a needle tip diameter of 0.5mm and a volume of 20ml was used, the electric field voltage was set to 17KV, and the flow rate was controlled at 0.9ml / h for electrospinning, and then calcined in air at 320°C for 1.5h to obtain molybdenum trioxide nanomaterials. Take 3.0mmol sodium molybdate and 4.5mmol cysteine dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution A, take 0.8g of molybdenum oxide nanomaterials dissolved in deionized water to obtain solution B, add solution B drop by drop to solution A and sonicate 30min, and then carry out a hydrothermal reaction at 200°C for 16h. After the reaction is finished, it is centrifuged and washed at 5500 rpm, and then dried at 70° C. to obtain a molybdenum disulfide / molybdenum trioxide nanocomposite material.
[0027] Characterization: Ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com