Meloidogyne graminicola translation elongation factor Mg-eFF1A and application thereof to control of plant diseases
A technique for translating elongation factors and root-knot nematodes, applied in angiosperms/flowering plants, applications, nematicides, etc., can solve the problems of undiscovered nematode-related molecular patterns and undiscovered receptors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Mg-eEF1A clone
[0043] According to the transcriptome data of M. graminearum, the full-length cDNA sequence of Mg-eEF1A gene was spliced. Subsequently, primers Mg-eEF1A-gDNA-F / Mg-eEF1A-gDNA-R covering the full-length sequence were designed to amplify the genome sequence.
[0044] SEQ ID NO.4 (Primer Mg-eEF1A-gDNA-F)
[0045] ATGGGAAAAGAAAAGATTC
[0046] SEQ ID NO.5 (Primer Mg-eEF1A-gDNA-R)
[0047] TTATTTCTTCTTTCCAGCAG
[0048] The amplified Mg-eEF1A gene has a full length of 1650 bp (shown in SEQ ID NO.1), contains 6 short introns, and encodes 465 amino acids (shown in SEQ ID NO.2).
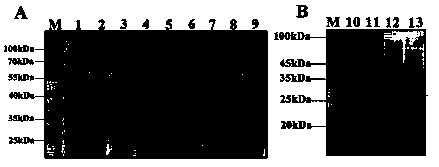
[0049] Through homologous comparison, it was found that Mg-eEF1A is very conserved in nematodes ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Yeast two-hybrid
[0051] 1. Experimental method
[0052] (1) Collect the 2nd instar larvae before root-knot nematode infection, use Trizol regent to extract the total RNA of nematodes, and use DNase 1 to remove residual DNA. The specific operation process is as follows:
[0053] Collect root-knot nematode graminaceae in a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube, use a suitable grinding rod to crush the insect body in a liquid nitrogen environment, and add 1 ml of Trizol regent to mix. Let stand at room temperature for 5 min to completely dissociate ribosomes. Add 200 μl of chloroform to the above lysate, shake vigorously for 15 seconds, repeat 3 times, and let stand at room temperature for 2 minutes. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 15 min, carefully pipette the upper layer into a new centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix by inverting up and down, and place at room temperature for 30 min. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 15 min, remove the supernat...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Co-immunoprecipitation
[0067] 1. Experimental method
[0068] OsCERK1Δsp and Mg-eEF1A without the signal peptide region were obtained by PCR and cloned into the rice protoplast transient expression vector pUbi to obtain pUbi:OsCERK1Δsp:HA and pUbi:Mg-eEF1A:EGFP. At the same time, a plant expression vector pUbi:EGFP was constructed as a negative control. pUbi:OsCERK1Δsp:HA was co-expressed with pUbi:Mg-eEF1A:EGFP and pUbi:EGFP respectively in rice protoplasts. After 48 hours, the protoplast cells were collected and the total protein was extracted. The extraction method of the total protein was carried out according to 2.3.7. The method of co-immunoprecipitation was carried out according to the instructions of EZview Red Anti-HA Affinity Gel (sigma), and the process was as follows: first, EZview Red Anti-HA Affinity Gel was added to the total protein, and incubated overnight at 4°C; then, washed with the protein extract 4-5 times, collect the precipitate; a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com