Method for treating pyridine pesticide wastewater by aid of biological-electrochemical coupling technologies
A technology for the treatment of pesticide wastewater, which is applied in the field of bio-electrochemical coupling technology to treat pyridine pesticide wastewater, and can solve the problems that the removal rate of COD and total nitrogen is difficult to meet the takeover requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
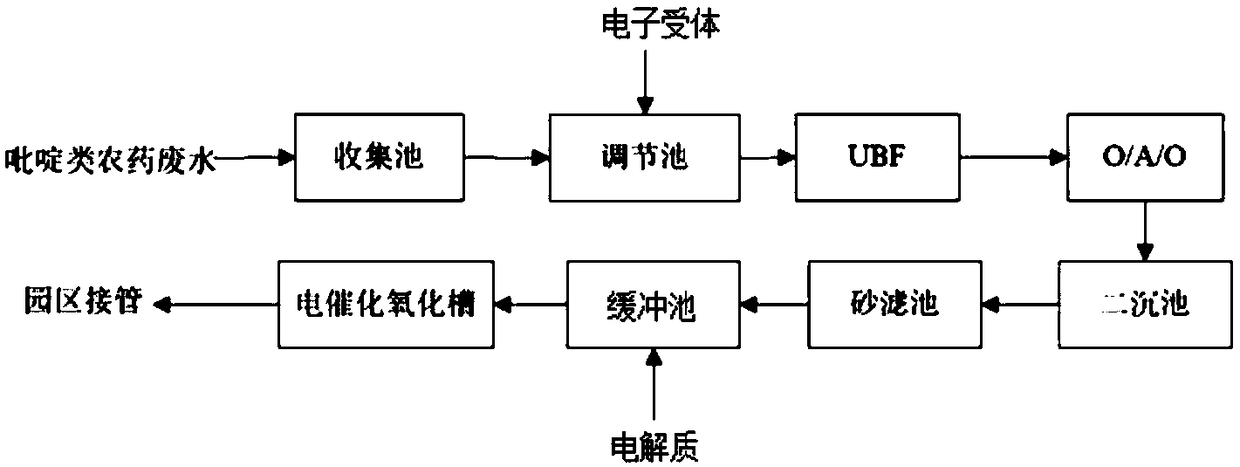
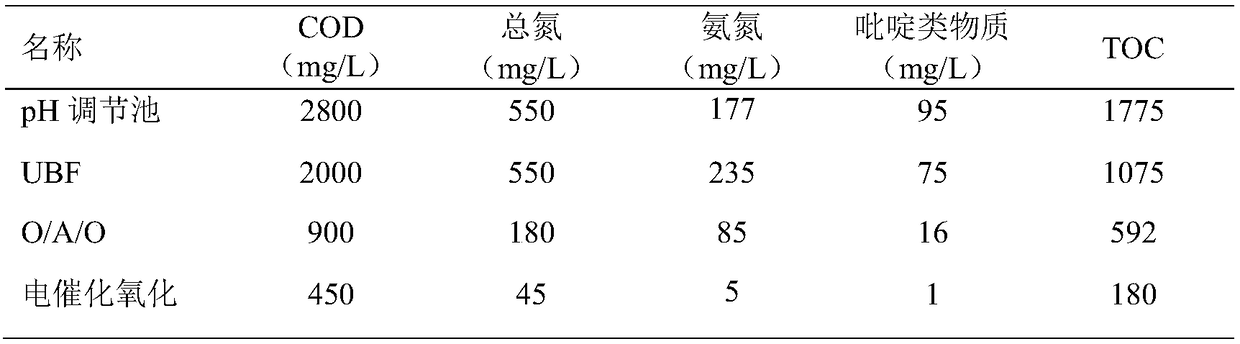
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for treating pyridine pesticide wastewater by bio-electrochemical coupling technology, wherein the pyridine pesticide wastewater is the pyridine pesticide wastewater from the first workshop of a pesticide enterprise in Binhai, Jiangsu, and is treated at an ambient temperature of 20°C. Proceed as follows:
[0047] (1) Pyridine wastewater enters the collection pool of the terminal sewage station after steaming and resin adsorption in the workshop;
[0048] (2) The waste water from the collection pond is pumped into the biochemical adjustment pond, the pH value is adjusted to 7 with sodium carbonate, and 50 mg / L sodium nitrate is added simultaneously to carry out homogenization and equalization;
[0049] (3) waste water in step (2) enters the microbial treatment section of UBF+O / A / O, UBF anaerobic residence time 60h, O section residence time 60h, A section residence time 20h, secondary O section with 100% The r...
Embodiment 2
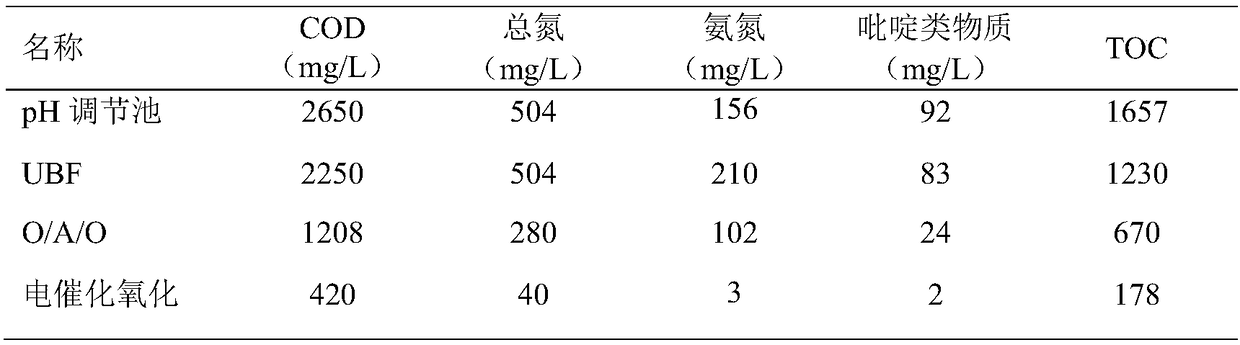
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for treating pyridine pesticide wastewater by bio-electrochemical coupling technology, wherein the pyridine pesticide wastewater is picoline pesticide wastewater, and at an ambient temperature of 15°C, the treatment steps are as follows:
[0063] (1) Pyridine waste water is pretreated by stripping in the workshop and then enters the collection pool of the terminal sewage station;
[0064] (2) Pump the waste water from the collection pond into the biochemical adjustment pond, adjust the pH value to 7.5 with sodium carbonate, and add a mixture of 60 mg / L sodium nitrate and sodium nitrite at a mass ratio of 1:1 at the same time for homogenization and equalization;
[0065] (3) waste water in step (2) is entered into the microbial treatment section of UBF+O / A / O, UBF anaerobic residence time 72h, O section residence time 72h, A section residence time 16h, secondary O section with 200% The reflux ratio returns to s...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Such as figure 1 As shown, this example provides a method for treating pyridine pesticide wastewater by bio-electrochemical coupling technology, wherein the pyridine pesticide wastewater is 3-cyanopyridine pesticide intermediate wastewater, and the treatment steps are as follows at an ambient temperature of 10°C:
[0074] (1) Pyridine wastewater enters the collection pool of the terminal sewage station after being adsorbed by resin in the workshop;
[0075] (2) Pump the waste water from the collection pond into the biochemical adjustment pond, adjust the pH value to 8 with sodium carbonate, and add 30 mg / L sodium nitrite simultaneously to carry out homogenization and equalization;
[0076] (3) waste water in step (2) is entered into the microbial treatment section of UBF+O / A / O, UBF anaerobic residence time 36h, O section residence time 84h, A section residence time 36h, secondary O section with 400% The reflux ratio returns to section A, and the effluent flows to the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com