Non-noble metal catalytic electrode, film electrode and preparation method of non-noble metal catalytic electrode
A non-precious metal, catalytic electrode technology, used in battery electrodes, circuits, fuel cells, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming preparation methods, catalyst loss, etc., achieve excellent conductivity, simplify electrode manufacturing steps, and promote the effect of industrialization development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
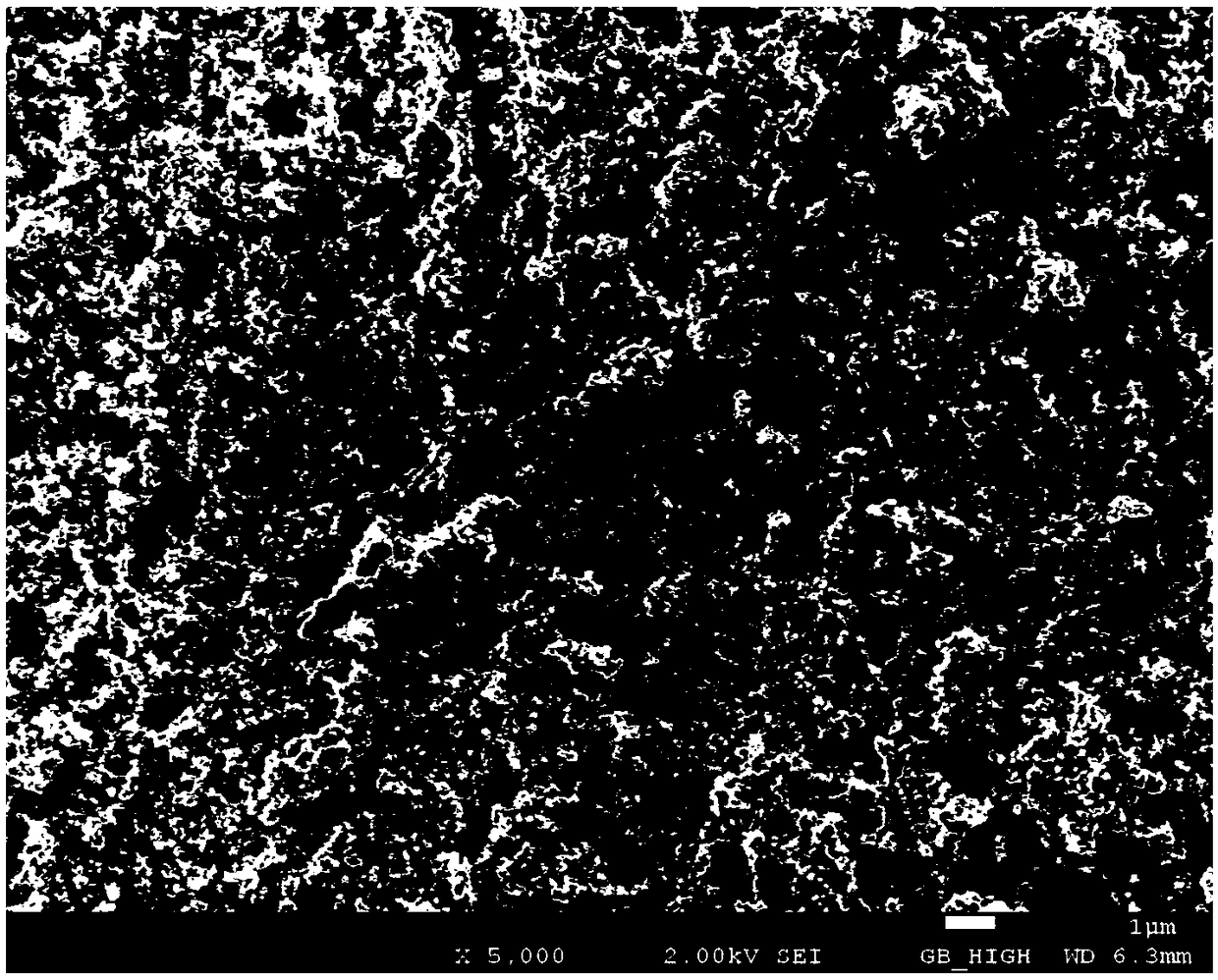
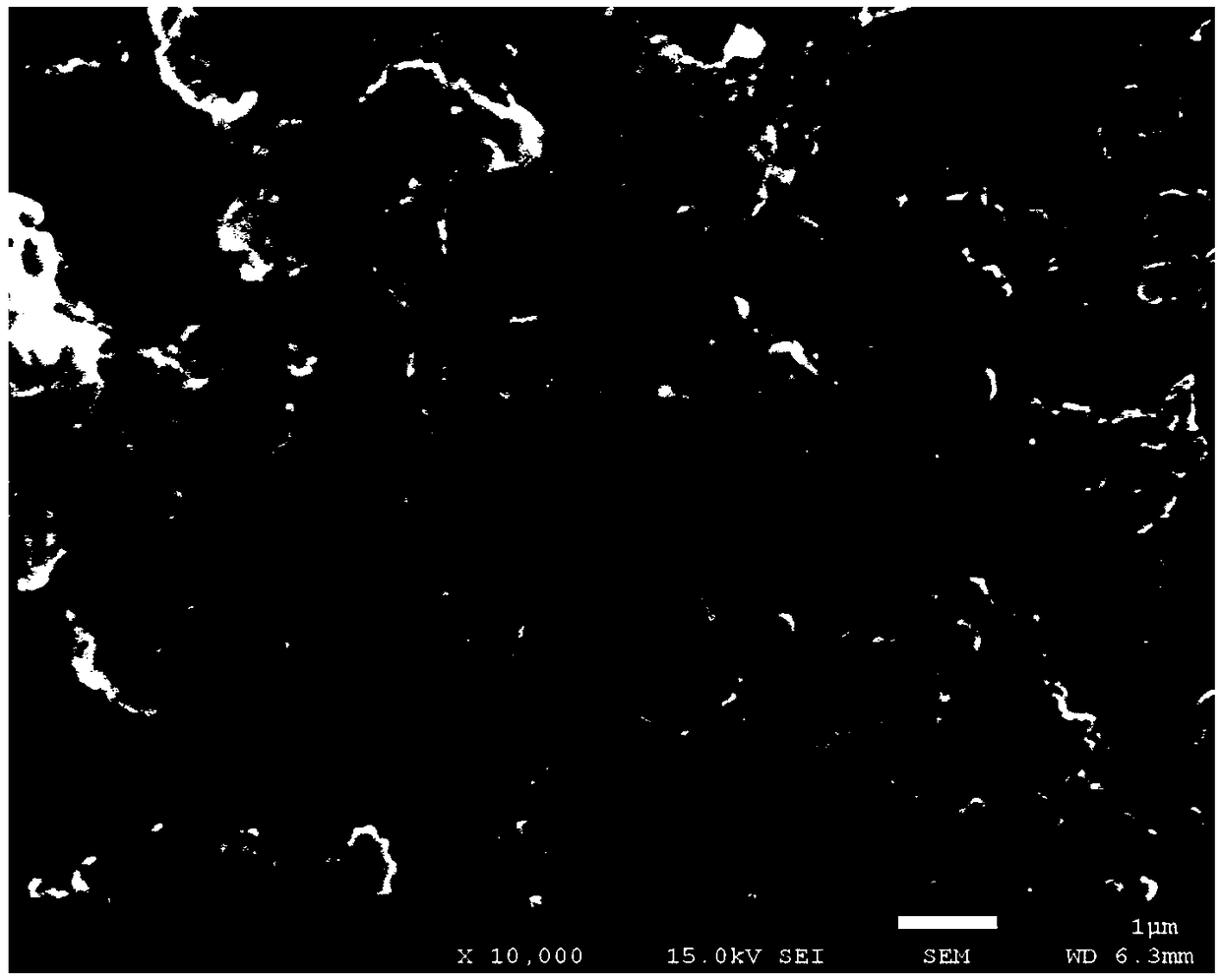
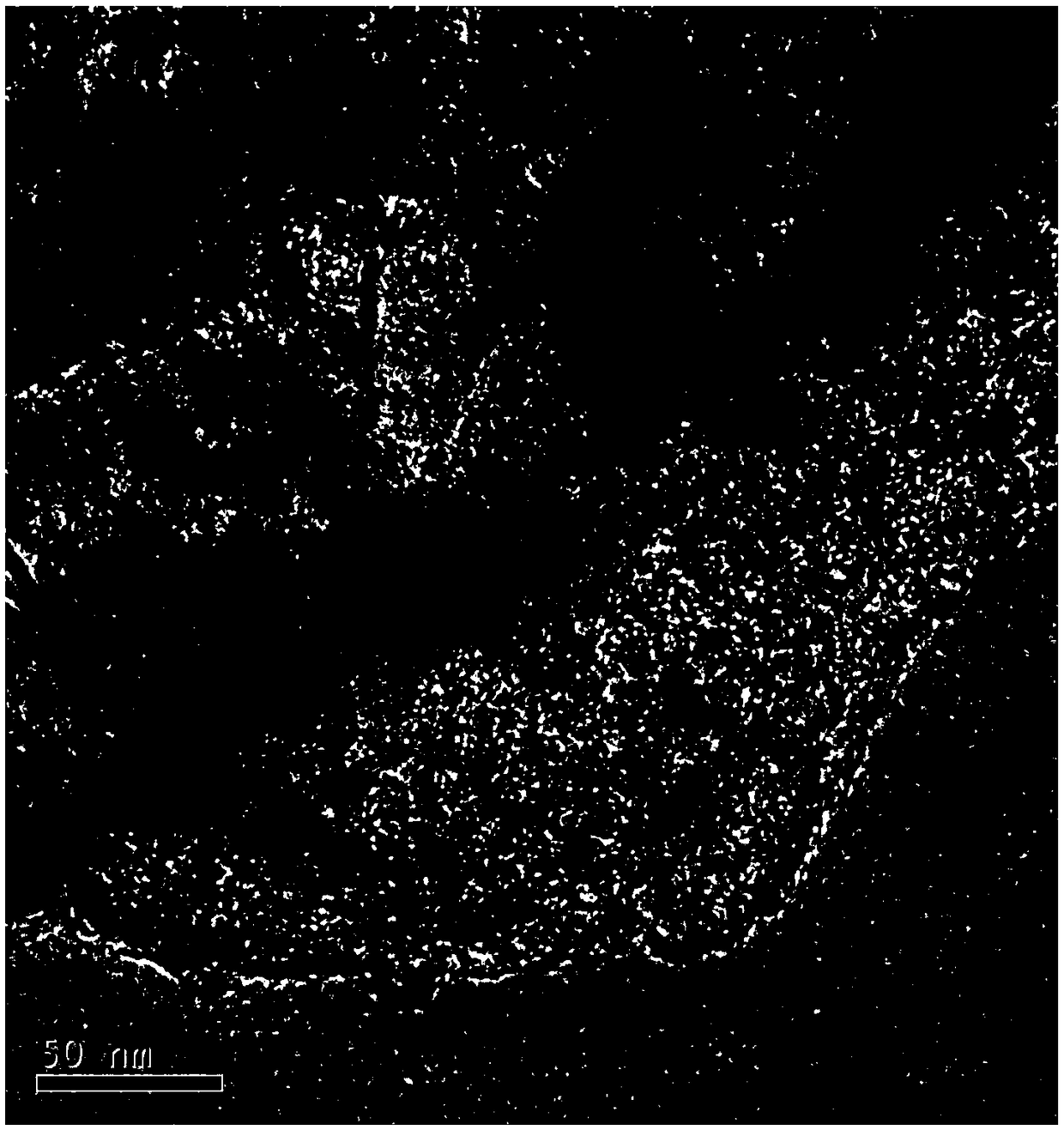
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Preparation of Carbon Paper Supported Cobalt-Molybdenum-Doped Highly Nitrided Carbon Catalytic (MoCo-N-C) Electrodes
[0039] 20.0 g of sodium chloride was dissolved in 100 ml of deionized water, then 9.0 g of pentaethylenehexamine was added dropwise to it, and after stirring for one hour, 15.0 g of MCM-41 was added and ultrasonically dispersed for two hours to obtain MCM- 41 of the ultrafine slurry. Dissolve 2.2 g of cobalt chloride (CoCl) in 30 ml of ethanol 2 ·6H 2 O) and 1.6 g of ammonium molybdate ((NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 O 24 ·4H 2 0), mixed evenly and added to the above MCM-41 slurry, and stirred overnight. The viscous paste of the mixture after rotary evaporation at 50°C to remove most of the solvent was spread evenly on a carbon paper diffusion layer of 80 mm × 50 mm, and freeze-dried to remove the remaining solvent. The carbon paper was then placed in a tube furnace for temperature-programmed heat treatment with high-purity nitrogen: from room temperature to 30...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Preparation of Carbon Paper Supported Cobalt-N-Doped Highly Nitrided Carbon Catalytic (Co-N-C) Electrodes
[0043] In a typical example of preparing a cobalt nitrogen doped non-noble metal catalytic electrode, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride (CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O) was used as the cobalt source, 4.4 g of Pentaethylenehexamine was used as the nitrogen source and carbon source material, and 0.5 g of graphene was used as the carbon source material. First, pentaethylene hexamine was dissolved in 50 ml of sodium chloride (12.0 g) aqueous solution, stirred for half an hour to mix evenly, then 2.5 g of pre-ground and dried MCM41 was added to ultrasonically disperse for half an hour, and stirred for half an hour; It was added to the above solution, fully dispersed with ultrasonic stirring, and an aqueous solution of cobalt chloride (50 ml) was added dropwise and stirred overnight. The water was removed by drying at 50°C on a rotary evaporator, and the black powder was collected by freeze-d...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Preparation of carbon paper-supported cobalt-nitrogen double-doped non-noble metal carbon catalytic (Co-N-C) electrodes
[0046] In a typical example of preparing cobalt-nitrogen double-doped non-noble metal catalytic electrodes, pentaethylenehexamine was used as carbon and nitrogen source, cobalt nitrate (Co(NO) 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) was used as a cobalt source. First, dissolve 1.9 g of pentaethylene hexamine in 50 ml of water and stir for 0.5 hours to mix evenly; then add 2.3 g of pre-ground and dried MCM-41, ultrasonically shake and stir for 2 hours to make it evenly dispersed and keep stirring; thereafter Dissolve 2.3 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in 50 ml of water, add 1.5 g of cobalt nitrate and 1.6 g of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO) 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O), ultrasonically vibrate and stir for one hour to make the three evenly mixed; then slowly drop the aqueous solution containing cobalt nitrate, zinc nitrate and PVP into the slurry containing pentaethylenehexamine, and stir at ro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com