Application of a lipase in splitting n-acetyl-dl-methionine methyl ester
A technology of methionine methyl ester and lipase, which is applied in the field of N-acetyl-L-methionine methyl ester enantiomer, can solve the problem of high cost of enzyme extraction and purification, low animal lipase activity and limited source of raw materials and other problems, to achieve the effect of high chemical selectivity, non-polluting energy consumption, and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
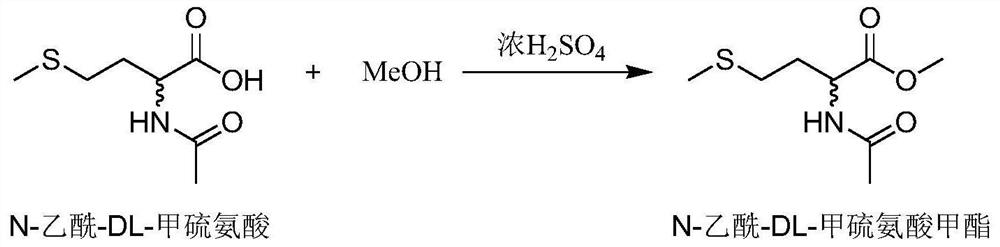
[0027] Embodiment 1 chemical synthesis substrate N-acetyl-DL-methionine methyl ester
[0028] Get 5g of N-acetyl-DL-methionine and 5mL of methanol (analytically pure, excess methanol) into a 250mL round bottom flask, add 20mL of toluene as a reaction solvent, then add 125uL of concentrated sulfuric acid (mass concentration 98%) as catalyst. React for 6-8h under the conditions of 80° C. and 600 rpm with a magnetic stirrer in an oil bath. The reaction solution obtained after the reaction was finished, was first washed with saturated Na 2 CO 3 Wash to remove the unreacted acid therein, then extract with an equal volume of ethyl acetate, separate the organic phase and the water phase with a separatory funnel, extract the water phase twice with ethyl acetate, combine the organic phases, and wash with pure water for two times, washed twice with saturated NaCl, the organic phase obtained after washing was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and after removing water, the organi...
Embodiment 2
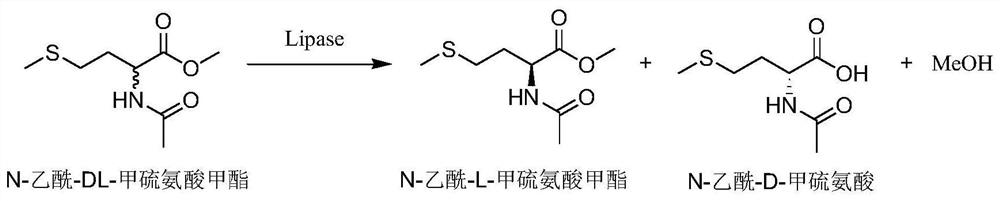
[0029] Example 2 Enzyme-catalyzed resolution of lipase screening for N-acetyl-DL-methionine methyl ester
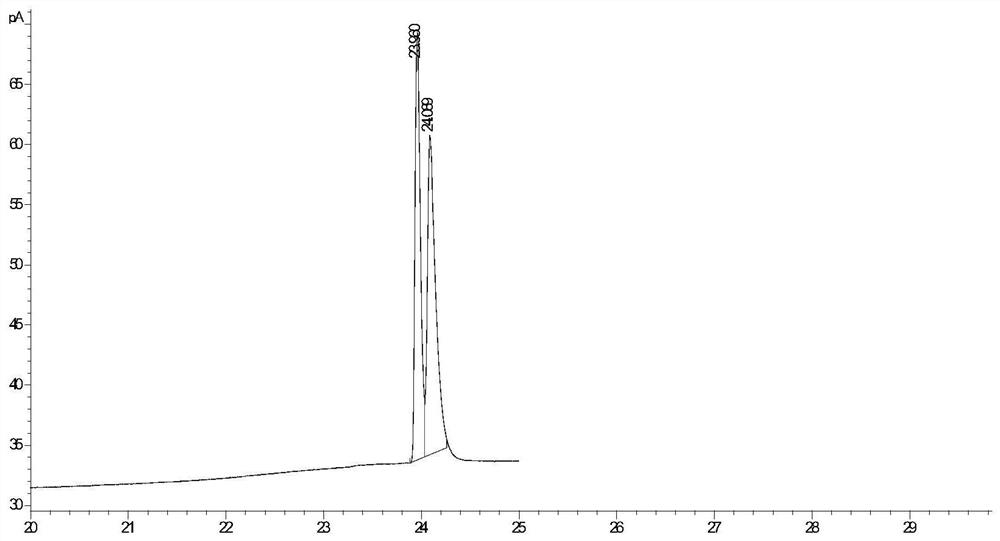
[0030] Weigh 0.01g of lyophilized wet bacterial powder of proteins with lipase hydrolysis activity from different sources screened in Table 1 into a 2mL EP tube, add 1mL of PB (pH 7.0, 0.2mM) as a reaction solvent, and then add 0.01 g substrate N-acetyl-DL-methionine methyl ester, without adding bacteria as a blank control, placed in a 35°C, 800rpm constant temperature mixer for 10min. After the reaction, the reaction solution was acidified with 2mM HCl, then 1mL of ethyl acetate was added, vortexed for 2min, fully extracted, and centrifuged (1200rpm, 3min) to obtain an organic phase. Take 700 μL ethyl acetate layer and detect the stereoselectivity and enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis activity of the bacteria by gas chromatography. The results are shown in Table 1. The microorganisms with an enantiomeric excess value of >99% and a conversion rate of 51.2% were screened. strai...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3 lipase protein induction condition
[0035] The Escherichia coli BL21 (F1) obtained in Example 2 was inoculated in LB medium, and cultivated at 37° C. 600 to 0.5 (about 2 hours of culture), add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.02mM, and culture at 30°C for 10-12 hours. Centrifuge 300mL of the bacterial solution at 8000rpm at 4°C for 10min to collect the bacterial cells, then wash the bacterial cells with PBS buffer twice at 8000rpm for 10min to collect the wet bacterial cells. The collected wet bacteria were freeze-dried with a freeze dryer to obtain lipase F1 crude enzyme powder, which was stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. LB medium composition: tryptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 5g / L, solvent is water, pH is natural.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com