Dendrobium officinale powder preparation method
A technology of dendrobium powder and iron sheet, which is applied in the field of preparation of dendrobium powder, can solve the problems of limited extraction of dendrobium fiber and waste of raw materials of dendrobium, and achieve the effects of improving uniformity and stability, increasing efficiency, and improving properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
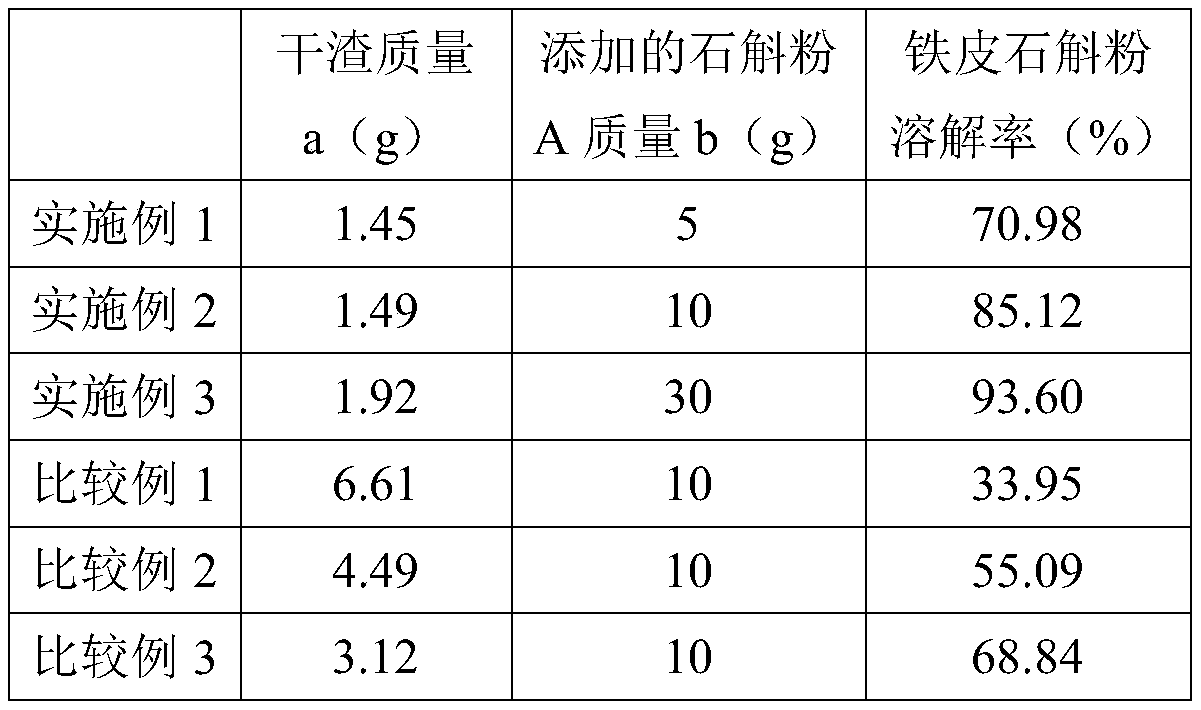
[0032] (1) Material pretreatment: Dry the fresh strips of Dendrobium at 80°C for 5 hours to obtain dry strips of Dendrobium with a moisture content of 5.2%, then grind the dried strips of Dendrobium, and sieve to select Dendrobium powder with a particle size of less than 200 mesh A;
[0033] (2) Shearing and stirring treatment: add 5 g of the dendrobium powder A obtained in step (1) into 1000 g of water, shear and stir at 40° C. for 1 hour, fully swell the fibers, and obtain the initial extract B and wet residue C after filtration;
[0034] (3) freeze-drying treatment: the wet residue C obtained in step (2) was freeze-dried for 24 hours at -30° C. to obtain dry powder D. Freeze-drying treatment can improve the wall-breaking rate of dendrobium fibers and remove free water and Combining water to form a loose and porous structure is more conducive to subsequent processing;
[0035] (4) Enzymolysis treatment: add cellulase, hemicellulase and pectinase to the dry powder D obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Material pretreatment: Dry the fresh strips of Dendrobium at 90°C for 6 hours to obtain dry strips of Dendrobium with a moisture content of 4.8%, then grind the dried strips of Dendrobium, and sieve to select Dendrobium powder with a particle size of less than 250 mesh A;
[0046] (2) Shear stirring treatment: add 10 g of the dendrobium powder A obtained in step (1) into 1000 g of water, shear and stir at 50° C. for 2 hours, fully swell the fibers, and obtain the initial extract B and wet residue C after filtration;
[0047] (3) Freeze-drying treatment: the wet residue C obtained in step (2) was freeze-dried for 48 hours at -40° C. to obtain dry powder D. Freeze-drying treatment can improve the wall-breaking rate of dendrobium fibers and remove free water and Combining water to form a loose and porous structure is more conducive to subsequent processing;
[0048] (4) Enzymolysis treatment: add cellulase, hemicellulase and pectinase to the dry powder D obtained in ste...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Material pretreatment: Dry the fresh dendrobium strips at 100°C for 8 hours to obtain dry dendrobium strips with a moisture content of 3.7%, then grind the dry strips of dendrobium into powder, and sieve to select dendrobium powder with a particle size of less than 300 mesh A;
[0059] (2) Shearing and stirring treatment: add 30 g of dendrobium powder A obtained in step (1) into 1000 g of water, shear and stir at 60° C. for 3 hours, fully swell the fibers, and obtain initial extract B and wet residue C after filtration;
[0060] (3) freeze-drying treatment: the wet residue C obtained in step (2) was freeze-dried for 108 hours at -50° C. to obtain dry powder D. Freeze-drying treatment can improve the wall-breaking rate of dendrobium fibers and remove free water and Combining water to form a loose and porous structure is more conducive to subsequent processing;
[0061] (4) Enzymolysis treatment: add cellulase, hemicellulase and pectinase to the dry powder D obtained...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com