A method for purification and separation of bacterial cellulose
A bacterial cellulose, purification and separation technology, applied in cellulose pulp post-treatment, fiber raw material treatment, papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as inability to use in-situ composite bacterial cellulose, destroy structure and performance, affect application, etc., achieve shortening The effect of purification time, short time consumption and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A method for purifying and separating bacterial cellulose, comprising the following steps:
[0022] Step 1): Weigh 1.212g of Tris (Tris) powder to prepare 1000mL of 0.1M Tris solution, use HCl solution to adjust the pH to 6.5, add lysozyme powder to prepare a lysozyme with a mass volume concentration of 0.5g / L Enzyme solution; prepare 1000mL of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution with a mass volume concentration of 1.0g / L; mix the above-mentioned lysozyme solution and EDTA solution in equal volumes to obtain a lysozyme-EDTA mixed solution;
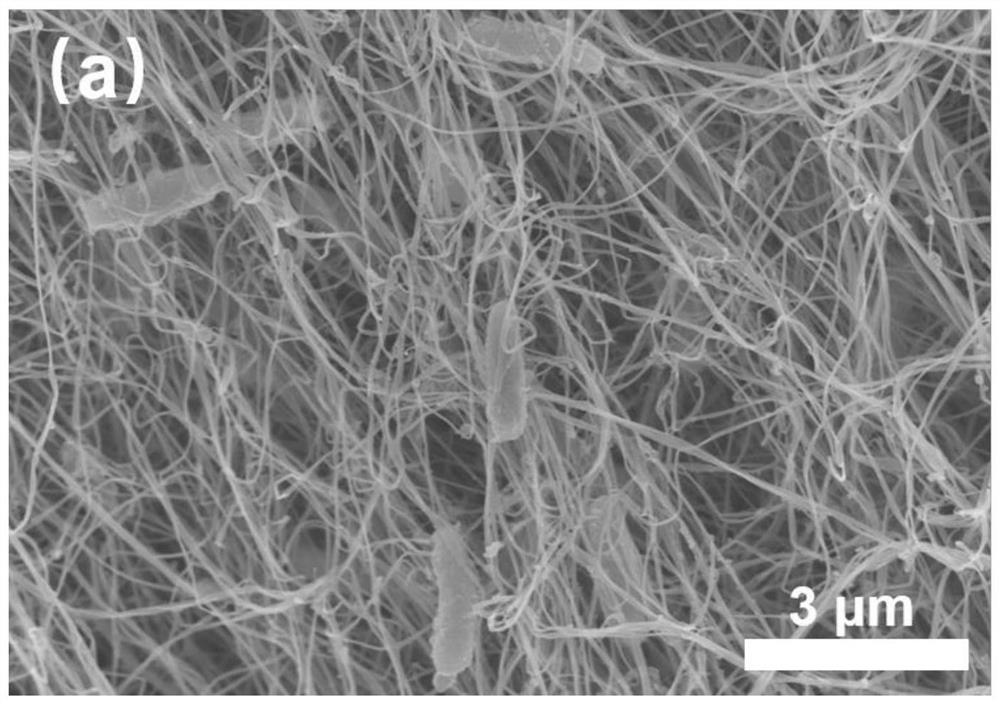
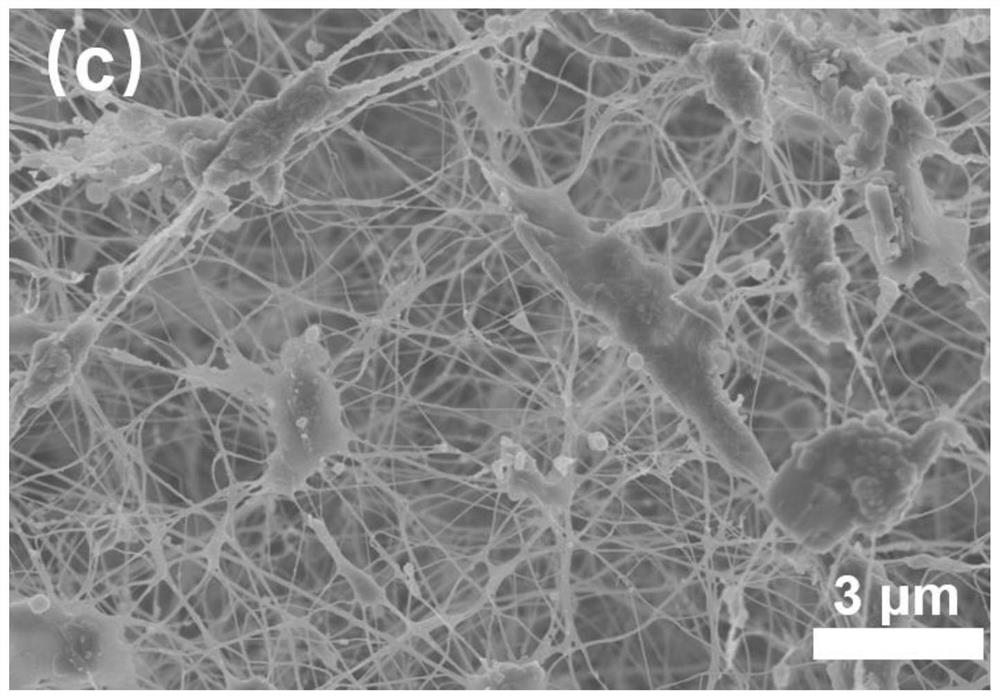
[0023] Step 2): The bacterial cellulose hydrogel cultured for 3 days (as shown in Fig. 1(a)) was taken out and soaked in deionized water for 12 hours. Replace the deionized water and repeat it several times until the culture medium inside the bacterial cellulose is replaced by deionization, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel appears white and opaque;
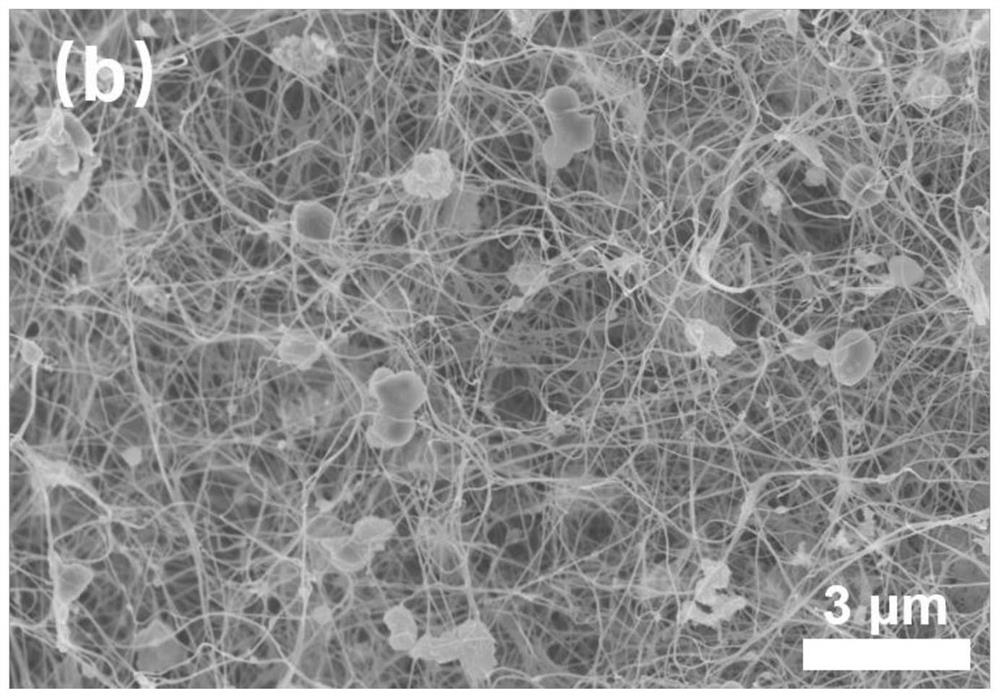
[0024] Step 3): soak the bacterial cellulose hydrogel treated in s...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for purifying and separating bacterial cellulose, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Step 1): Weigh 1.212g of Tris (Tris) powder to prepare 1000mL of 0.1M Tris solution, use HCl solution to adjust the pH to 6.5, add lysozyme powder to prepare a lysozyme with a mass volume concentration of 0.5g / L Enzyme solution; preparing a trypsin solution with a mass concentration of 2.5%, uniformly mixing the above-mentioned lysozyme solution and trypsin solution in equal volumes to obtain a lysozyme-trypsin mixed solution;
[0030] Step 2): The bacterial cellulose hydrogel cultured for 4 days was taken out and soaked in deionized water for 10 hours. Replace the deionized water and repeat it several times until the culture medium inside the bacterial cellulose is replaced by deionization, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel appears white and opaque;
[0031] Step 3): The bacterial cellulose hydrogel after step 2) is soaked in the lysozyme-trypsin- Trypsin mixed solu...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A method for purifying and separating bacterial cellulose, comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step 1): prepare the lysozyme-EDTA mixed solution according to the method of Example 1, and set aside;
[0037] Step 2): The bacterial cellulose cultured for 5 days was taken out and soaked in deionized water for 12 hours. Replace the deionized water and repeat it several times until the culture medium inside the bacterial cellulose is replaced by deionization, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel appears white and opaque;
[0038] Step 3): The bacterial cellulose hydrogel treated in step 2) is soaked in the lysozyme prepared in step 1) according to the mass volume concentration of bacterial cellulose and lysozyme-EDTA mixed solution of 0.25g / mL - in the mixed solution of EDTA; and oscillate on a shaking table, the speed is 200r / min, the temperature is 40°C, and the soaking time is 12h,
[0039] Step 4): soak the bacterial cellulose hydrogel obtained in step 3) in Span-80...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com