Method for preparing marsh gas through lignocellulose hydrolysate
A technology of lignocellulose and hydrolyzate, applied in waste fuel, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of the influence of microbial activity, the influence of methane production process, and the load should not be too high, so as to reduce the loss of methane, broaden the selectivity, and improve the reaction rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: a kind of method that lignocellulose hydrolyzate prepares biogas, it comprises the steps:
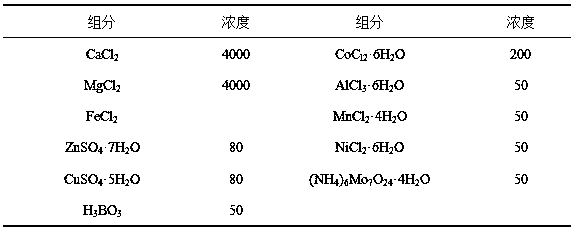
[0028] (1) Acidification of the hydrolyzate. Add 0.3L of corncob hydrolyzate into a 0.5L continuous stirring reactor. The hydrolyzate is obtained from Shandong Longli Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and its main components are glucose (3.13 g / L), xylose (9.87 g / L), Arabic Sugar (2.51 g / L), xylooligosaccharide (3.72 g / L), furfural (1.9 g / L), add the inoculum according to the ratio of 0.5:1 between the inoculum and the volatile solids of the substrate, and the inoculum is double sedimentation pool sludge, and add 30 mg / L activated carbon, after stirring evenly, seal it and place it in a water bath heating device at 38°C. An air bag is connected to the reactor bottle stopper to balance the pressure of the reaction device. Stir once every 2 hours, sample and measure the concentration of organic acids and soluble COD in the fermented liquid every day, and obtain the fermented ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: The similarities between this example and Example 1 will not be repeated. The difference is that the ratio of the inoculum to the substrate in the (1) acidification step of the hydrolyzed solution in Example 1 is changed to 1:1, The rest of the operations were the same, the concentration of organic acid in the final fermentation broth was 0.33 g / L, and no methane was produced in the process. The methanogenic process is the same as in Example 1 (2), the organic load is increased from 2 g COD / L to 8 g COD / L, the methane yield is 280-314 mL / g COD, and the methane content is 75.6-80.9% , COD removal rate is 85.0-94.9%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: The similarities between this example and Example 1 will not be repeated, the difference is: the ratio of the inoculum to the substrate in the (1) acidification step of the hydrolyzed solution in Example 1 is changed to 2:1, The rest of the operations were the same, the concentration of organic acid in the final fermentation broth was 0.35 g / L, and no methane was produced in the process. The methanogenic process is the same as the steps in Example 1 (2), the organic load is increased from 2 gCOD / L to 8 gCOD / L, the methane yield is 282 - 318 mL / g COD, the methane content is 76.1-81.0%, and the COD The removal rate is 85.6-95.3%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com