Fluoroacetic acid dehalogenase mutant and application thereof
A technology of acetate dehalogenase and mutants, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem that fluoroacetic dehalogenase cannot be used to catalyze brominated substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1 Construction of Fluoroacetic Dehalogenase Mutant Library
[0069] The primer sequences designed for the construction of the mutant library for mutations at positions 155, 156, and 219 of the fluoroacetic dehalogenase FAcD-RPA1163 (sourced as Rhodopseudomonas palustris) sequence (ie, SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence listing) are shown in the table 3 shows:
[0070] table 3
[0071]
[0072] Wherein, N represents any nucleotide in A, G, C, T, M represents A or C, and K represents G or T; it is selected according to the coding nucleotide of the amino acid to be mutated into at the site , For example, NNK in the A166-forward primer can represent AAG (lysine), AAT (aspartic acid), AGG (arginine) or AGT (serine), etc. The nucleotides corresponding to specific amino acids can be found in Table 2.
[0073] According to the method disclosed in the literature J.Am.Chem.Soc., 2017, 139(32), 11241-11247, the plasmid template pET28a-FAcD-RPA1163 was constructed, and the t...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2 High-throughput screening mutant library
[0080] Screen according to the following experimental steps:
[0081] The transformant obtained in Example 1 was inoculated into a 96-well plate for culture, and induced overnight at 30° C. with IPTG. Afterwards, the bacteria were harvested, cracked with bugbuster protein extraction reagent, and centrifuged to obtain the total enzyme solution.
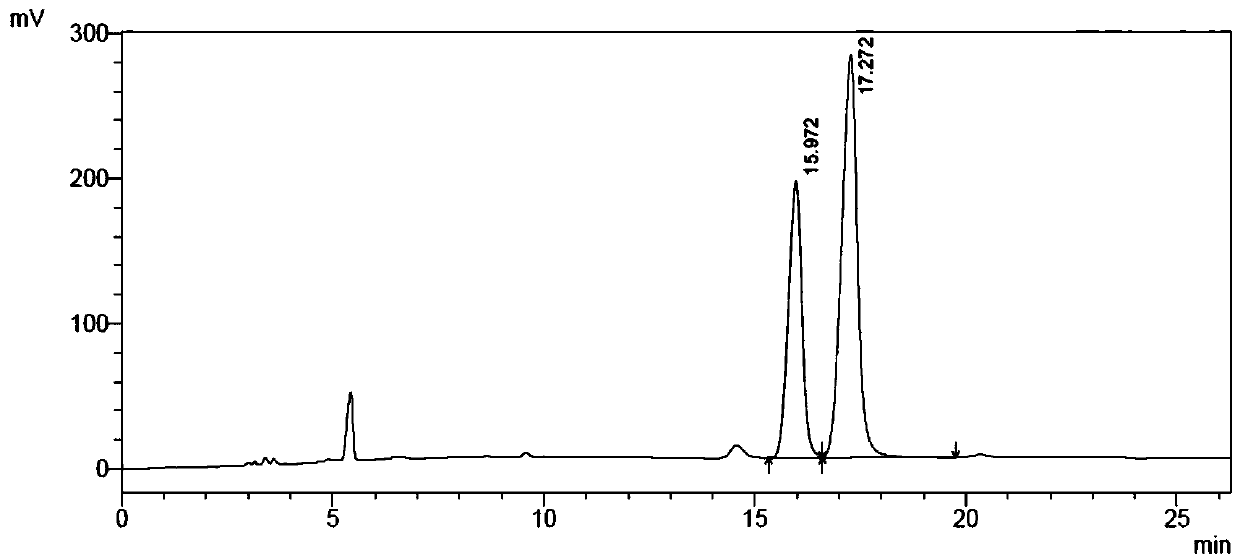
[0082] Weigh 250mg of racemized 2-bromobutyric acid substrate, dissolve it in 45mL 1mM Tris solution, place it on ice, adjust the pH between 8.0 and 8.5 with dilute NaOH, and adjust the volume to 50ml to prepare 2-bromobutyric acid The substrate concentration was 30 mM substrate solution. Add 100 μl of substrate solution (final concentration: 25 mM) and 20 μL of the above-mentioned total enzyme solution to each reaction. After reacting for a period of time, take 20 μl of the reaction solution to a 96-well microtiter plate, and add 30 μl of saturated Hg (SCN) in sequence. ...
Embodiment 3
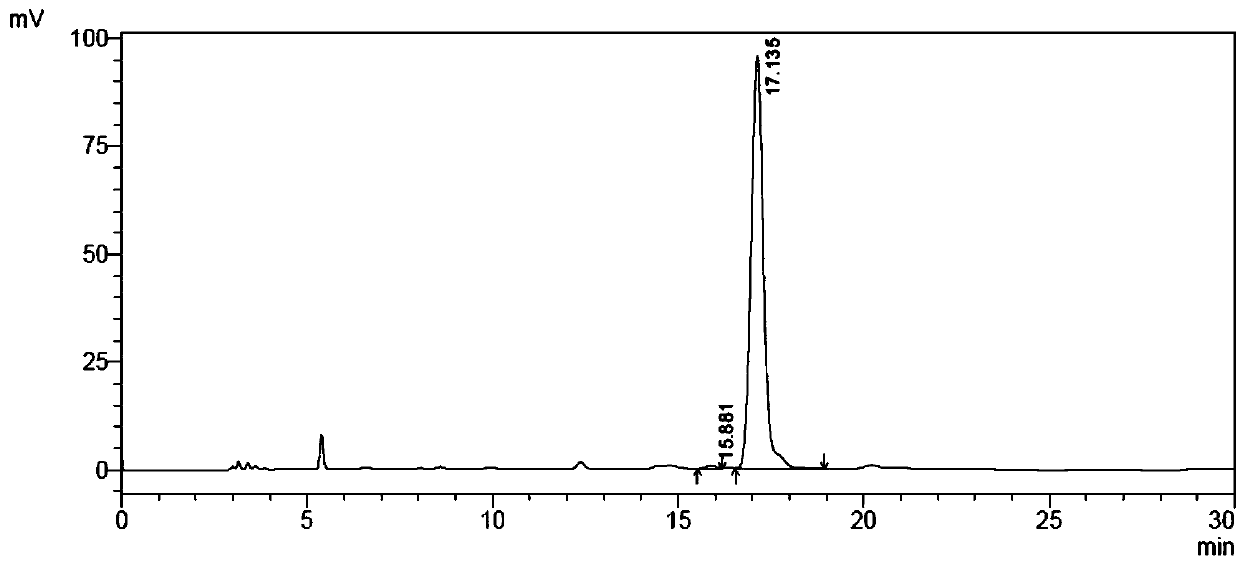
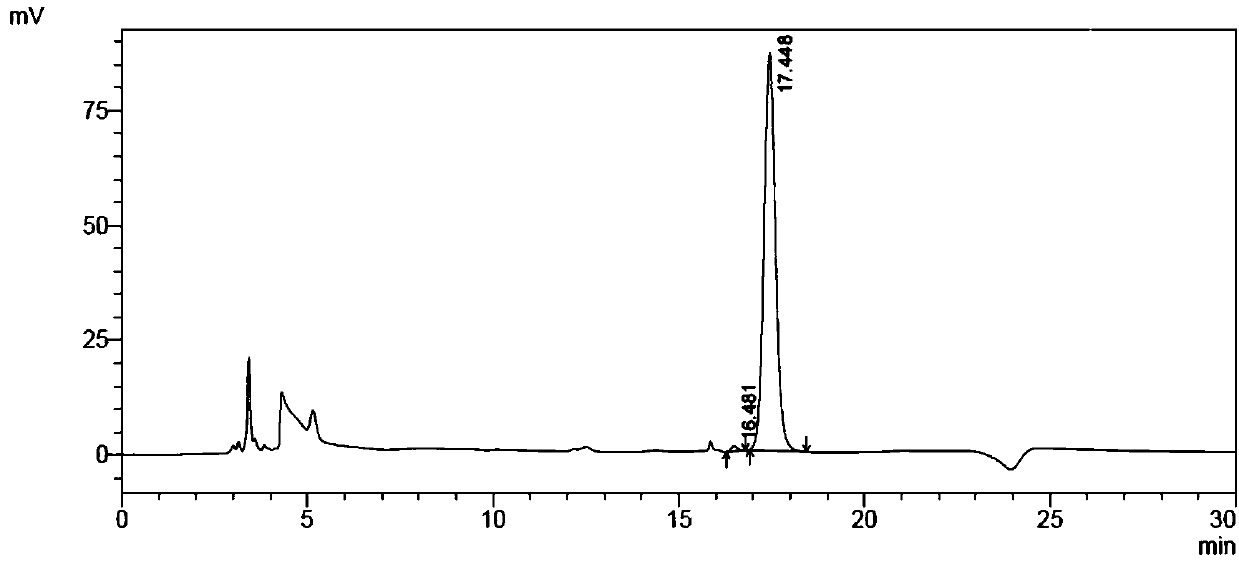
[0096] Example 3 Catalytic preparation of (R)-2-bromobutyric acid by fluoroacetic acid dehalogenase mutant
[0097] Add 50mL tap water into the reaction bottle, add 10g 2-bromobutyric acid substrate, stir and dissolve, adjust the pH to 7.0 with 30% NaOH solution, add 20mL of the mutant crude enzyme solution prepared according to the method of Example 2 (that is, weigh 4g The thallus described in Example 2 was added to 20 mL of 100 mM pH7.0 disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer, stirred evenly, and homogeneously crushed under high pressure to obtain mutant crude enzyme liquid. Mutation with fluoroacetic acid dehalogenase Take body 3 as an example, its concentration is 10U / ml), dilute the reaction system to 100mL with tap water. During the reaction process, 2mol / L sodium carbonate solution was used to control the pH at about 7.0, and after 8 hours of reaction in a water bath at 30°C, samples were taken to detect the conversion rate of the 2-bromobutyric ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com