Complex antibacterial acrylic fiber
An acrylic fiber, compound antibacterial technology, applied in the field of special synthetic fiber preparation, can solve the problems of easy shedding of antibacterial components, poor water resistance, weakened antibacterial effect, etc., to achieve enhanced water resistance, increased adhesion fastness, and improved water resistance and stability. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
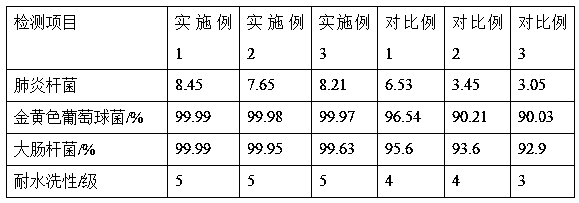
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The preparation method of composite acrylic fiber base material comprises the steps:
[0029] (1) Take the nutrient solution in the fermenter, add 1-4% yeast powder into the fermenter, stir and mix, and ferment at a constant temperature of 28-32°C for 12-20 days. During the fermentation process, every Add pretreated loofah with 6-10% of the total mass of materials in the fermenter every 3-5 days. After the fermentation is completed, heat and sterilize at 90-100°C for 12-20 minutes to obtain the fermented material. Take the fermented material according to the mass ratio of 20-20 30:3~7:1 Add the reagent, mix the hexacyclite passing through the 120 mesh sieve for 30~55min, move it into the ultrasonic oscillator, and oscillate ultrasonically for 25~40min at the ultrasonic frequency of 45~50kHz to obtain the dispersion, take the dispersion Suction filtration, collect the filter residue and treat it in a freeze dryer at -20~-10°C for 4~8 hours to obtain a freeze-dried materi...
Embodiment 1
[0037] Nutrient solution: in parts by weight, mix 1 part of agar, 8 parts of bagasse powder, 10 parts of wort juice, 2 parts of yeast extract, 2 parts of glucose, 2 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1 part of casein, and 700 parts of water, That is the nutrient solution.
[0038] Regulator: At 30°C, take fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether and add 12% triethanolamine solution in a mass ratio of 3:15 to mix to obtain a mixed solution. Take the mixed solution and add hydroxyethyl cellulose in a mass ratio of 10:1:2 Mixing element and polylactic acid to obtain regulator.
[0039] Additives: At 20°C, take casein and add hexamethylenetetramine and water in a mass ratio of 7:1:30 to mix, heat up to 65°C, keep stirring for 25 minutes, heat up to 70°C, add caprolactam with 25% casein mass Mix and stir for 35 minutes, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain the reaction material. At 30°C, take the reaction material and add carbamate in a mass ratio of 12:1 and mix to o...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Nutrient solution: in parts by weight, mix 3 parts of agar, 10 parts of bagasse powder, 15 parts of wort juice, 4 parts of yeast extract, 4 parts of glucose, 4 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 4 parts of casein, and 900 parts of water, That is the nutrient solution.
[0054] Regulator: At 40°C, take fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether at a mass ratio of 7:15 and add triethanolamine solution with a mass fraction of 12% for mixing to obtain a mixed solution. Take the mixed solution and add hydroxyethyl cellulose at a mass ratio of 10:4:5 Mixing element and polylactic acid to obtain regulator.
[0055] Additives: At 40°C, take casein and add hexamethylenetetramine and water in a mass ratio of 10:1:40 to mix, heat up to 75°C, keep stirring for 50 minutes, heat up to 85°C, add caprolactam with 40% casein mass Mix and stir for 60 minutes, cool naturally to room temperature to obtain the reaction material, at 45°C, take the reaction material and add carbamate at a mas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com