Biological ink for 3D printing of artificial skin
A technology of bio-ink and artificial skin, applied in drug delivery, medical science, capsule delivery, etc., can solve the problems of immune rejection, bacterial contamination, incomplete differentiation of exogenous stem cells, etc., and achieve the goal of reducing immune rejection Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] A preparation method for bioink for 3D printing artificial skin, has the following steps:
[0050] S1: Enzymatic solution configuration: D-Hanks solution was used to prepare 2g / L neutral protease solution, trypsin with a mass fraction of 0.25%, and EDTA with a mass fraction of 0.02%, and stored at 4°C after filter sterilization.
[0051] S2: Preparation of type IV collagen culture bottle: Dissolve human type IV collagen in 0.1% acetic acid solution, filter and sterilize, and store at 4°C for later use. Spread 1-2ml of the prepared type IV collagen in a culture bottle overnight, discard the supernatant, rinse 3-4 times with PBS solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L, dry in a 40°C drying oven, and irradiate with ultraviolet light 2h disinfection standby.
[0052] S3: Extraction of epidermal stem cells: take normal skin slices from the body, wash them with PBS solution containing double antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin) for 5-6 times, and remove the subcutaneous...
Embodiment 1
[0078] A kind of bio-ink for 3D printing artificial skin, the preparation of its C component and decellularized matrix scaffold comprises the following steps:
[0079] ①Dissolve gelatin in PBS buffer to form a 10wt% solution; dissolve sodium alginate in PBS buffer to form a 2wt% solution; use NaOH to neutralize residual acetic acid, adjust the pH value to 7.2, and batch in a 60°C oven Sterilize.
[0080] ② Weigh a certain amount of type I Sigma collagen powder, add acetic acid to a final concentration of 30 mg / mL, stir, and put it in a 4°C refrigerator overnight after stirring.
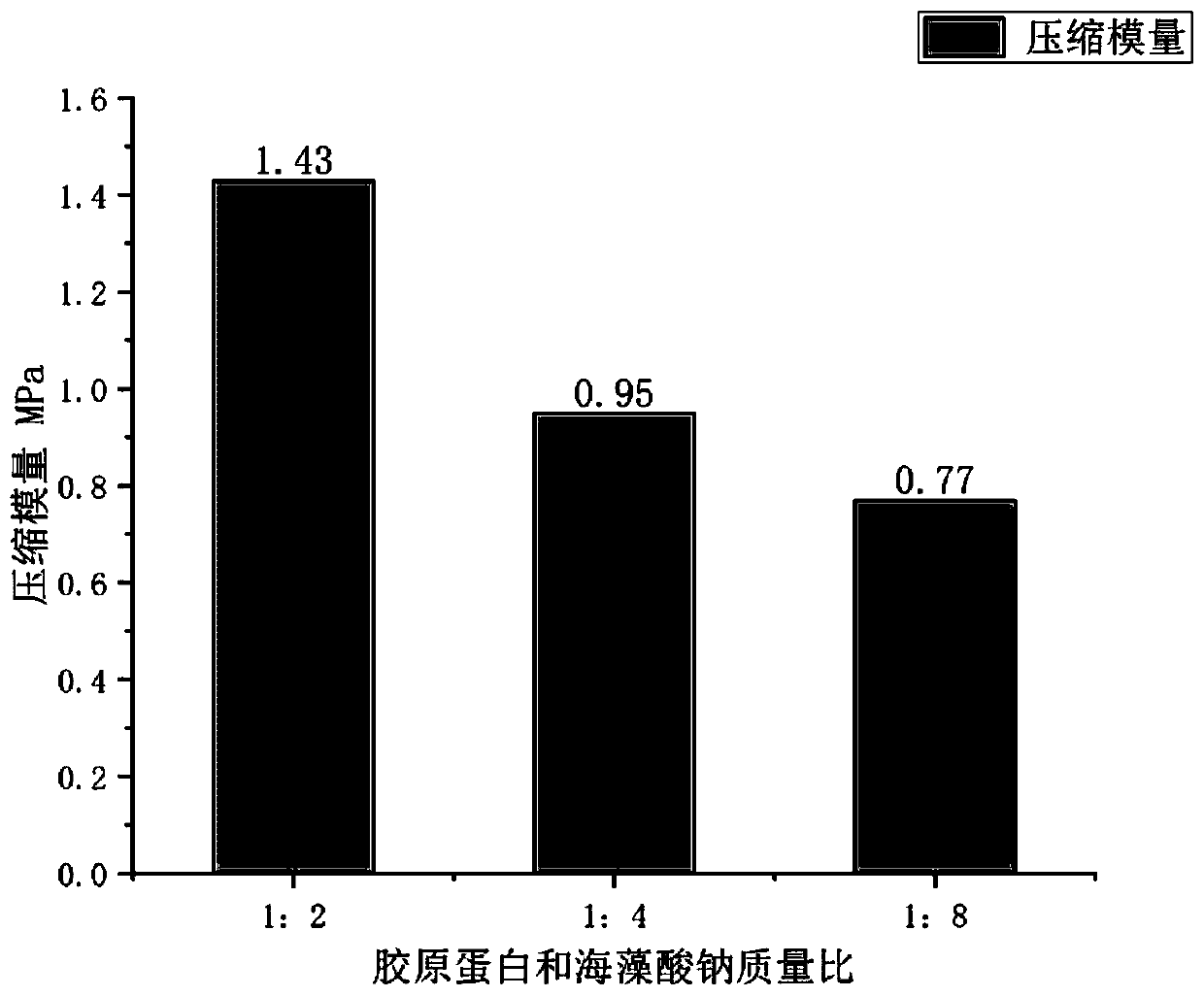
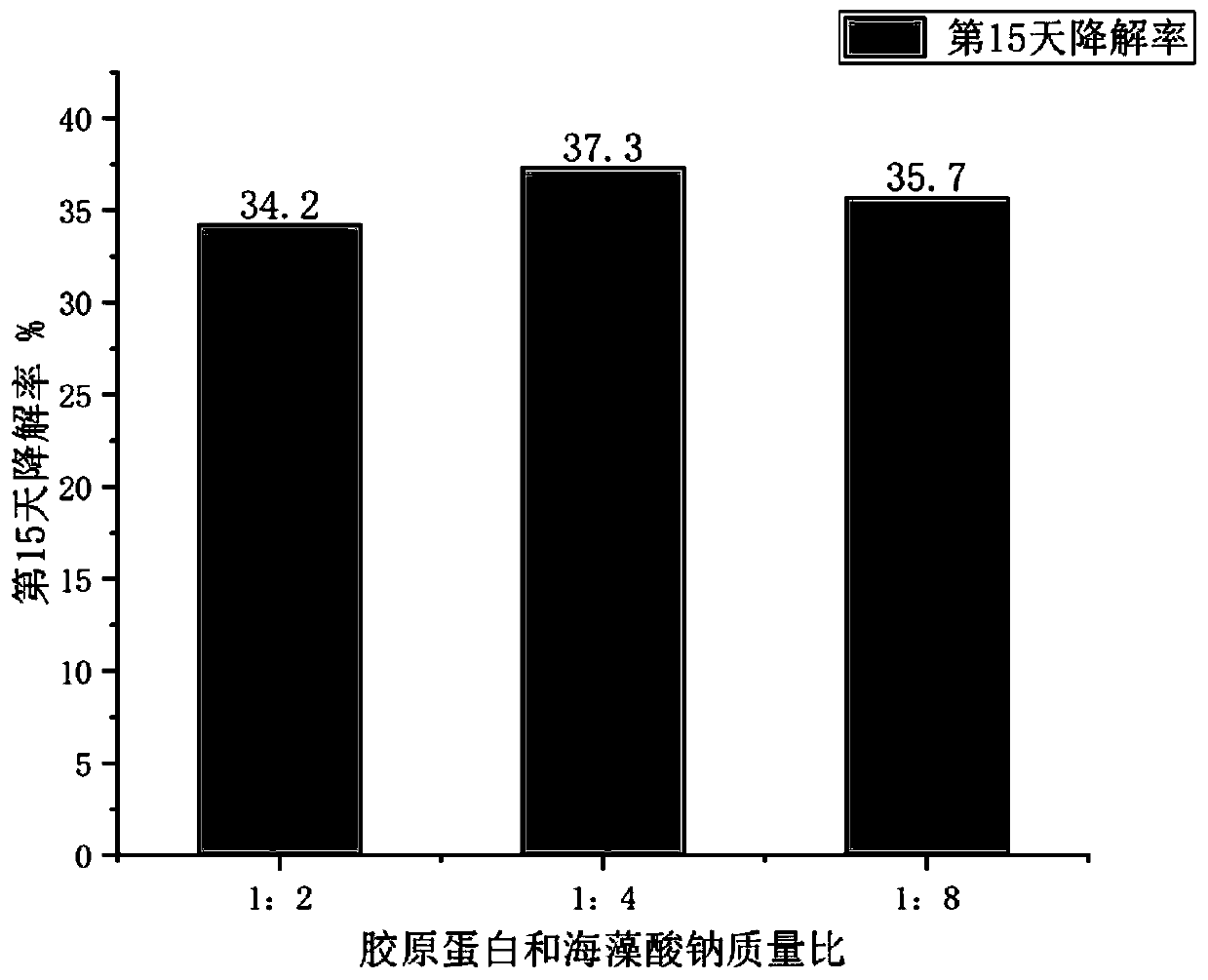
[0081] ③ According to the mass ratio of gelatin solution: collagen solution: sodium alginate solution is 1:1:2, mix evenly and carry out high temperature sterilization.
[0082] ④ Use 3D modeling software to reconstruct the image of the constructed 3D model to generate an STL file, import it into the 3D bioprinter for layering and setting of printing parameters, and then start printing.
[0083] ⑤ A...
Embodiment 2
[0085] A kind of bio-ink for 3D printing artificial skin, the preparation of its C component and decellularized matrix scaffold comprises the following steps:
[0086] ① Dissolve gelatin in PBS buffer to form a 10% solution, dissolve sodium alginate in PBS buffer to form a 2% solution, neutralize residual acetic acid with NaOH, adjust the pH value to 7.2, and batch in an oven at 60°C Sterilize.
[0087] ② Weigh a certain amount of type I Sigma collagen powder, add acetic acid to a final concentration of 30 mg / mL, stir, and put it in a 4°C refrigerator overnight after stirring.
[0088] ③ According to the mass ratio of gelatin solution: collagen solution: sodium alginate solution is 1:1:4, mix evenly and carry out high temperature sterilization.
[0089] ④ Use 3D modeling software to reconstruct the image of the constructed 3D model to generate an STL file, import it into the 3D bioprinter for layering and setting of printing parameters, and then start printing.
[0090] ⑤ Af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com