Non-animal-derived LMW (low molecular weight) heparin, preparation method therefor and application of non-animal-derived LMW heparin
A low-molecular-weight heparin, animal-derived technology, used in medical preparations, drug combinations, and pharmaceutical formulations containing active ingredients, can solve the problem of inability to achieve efficient preparation of non-animal-derived products, fine structure, large difference in weight-average molecular weight, and technology. problems such as poor stability, achieving major industrialization and clinical application prospects, easy separation, and quality controllable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
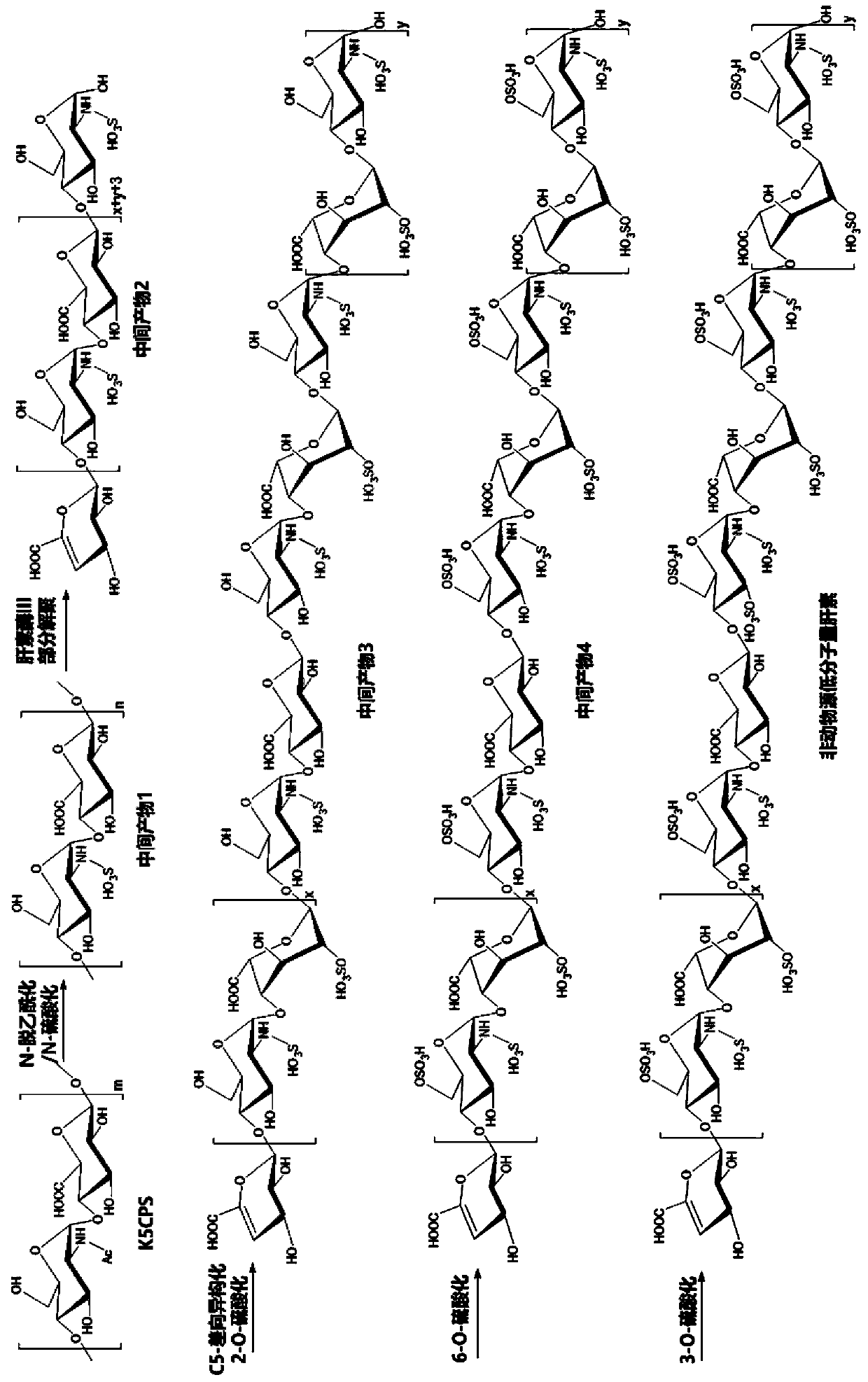
[0075] Example 1: Preparation of Escherichia coli K5 exopolysaccharide K5CPS
[0076] Escherichia coli K5 is cultured in a fermenter, the medium is glucose medium, and its composition is: 20g / L glucose, 10-300mg / L vitamin B1, 13.5g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 4.0g / L (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 , 1.4g / L MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 1.7g / L citric acid, 10.0mL / L trace elements, pH 7.0. Among them, the preparation of trace elements is as follows: 10.0g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 2.0g CaCl 2 , 2.2g ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.5g MnSO 4 4H 2 O, 1.0g CuSO 4 ·H 2 O, 0.1g (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O and 0.02g Na 2 B 4 o 7 10H 2 O was dissolved in 1 L of 2M HCl. Feed medium: 300~600g / L glucose, 20g / LMgSO 4 ·7H 2 O. 0.15-0.25g / L vitamin B1.
[0077] The fermentation conditions are as follows: the inoculum size is 4%, the pH is adjusted by 30% ammonia water, the temperature is 37° C., the rotation speed is 500 rpm, and the cultivation is carried out for 36 hours.
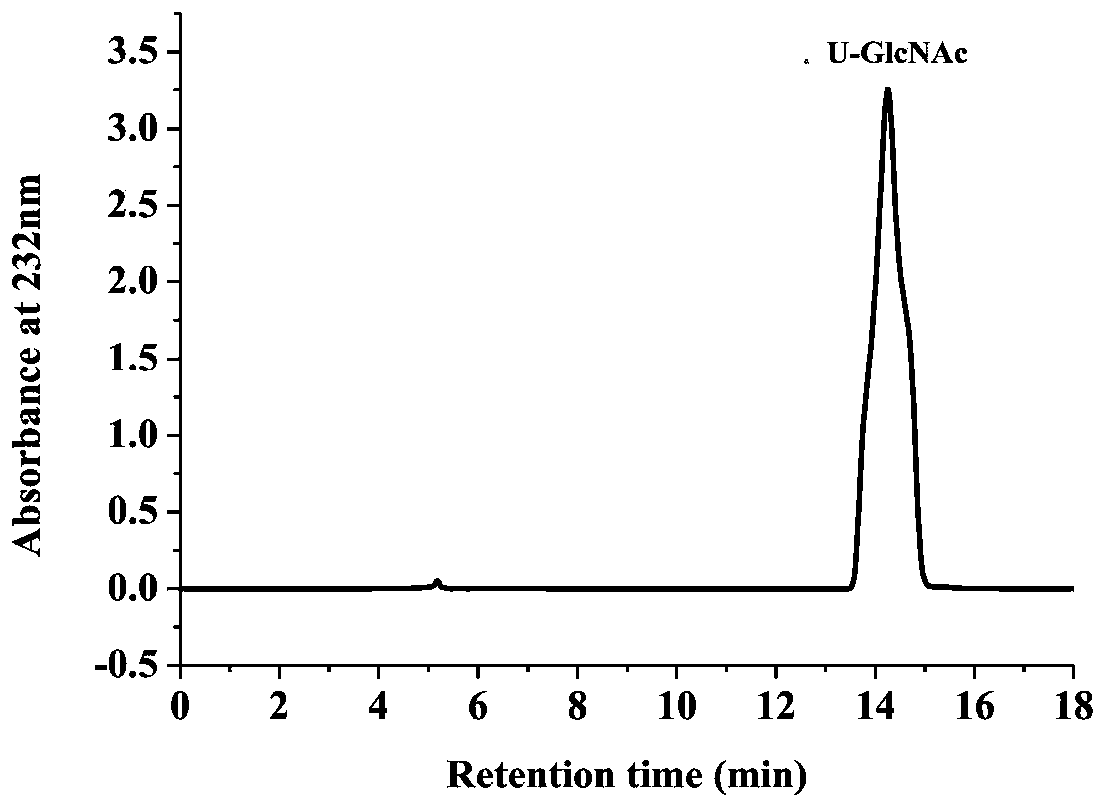
[0078] After the fermentation is completed, the fermenta...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Chemical N-deacetylation / N-sulfation modification of exopolysaccharide K5CPS
[0082] Dissolve 100 mg of the pure exopolysaccharide K5CPS prepared in Example 1 in 25 mL of 2M sodium hydroxide solution, react in a water bath at 60°C for 7 hours, cool to room temperature after completion, adjust the pH to 7.0-8.0 with 2M hydrochloric acid, and then Add 0.3g of sodium carbonate and 0.3g of sulfur trioxide-trimethylamine mixture, and react at 47°C for 12h, then add an equal amount of sodium carbonate and sulfur trioxide-trimethylamine mixture, and continue to react at 47°C for 12h. After the reaction, cool to room temperature, adjust the pH to 7.0 with hydrochloric acid, dialyze with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500Da to remove salt, and freeze-dry the dialysate to obtain the N-deacetylated / N-sulfated exopolysaccharide K5CPS derivative. Pure intermediate 1.
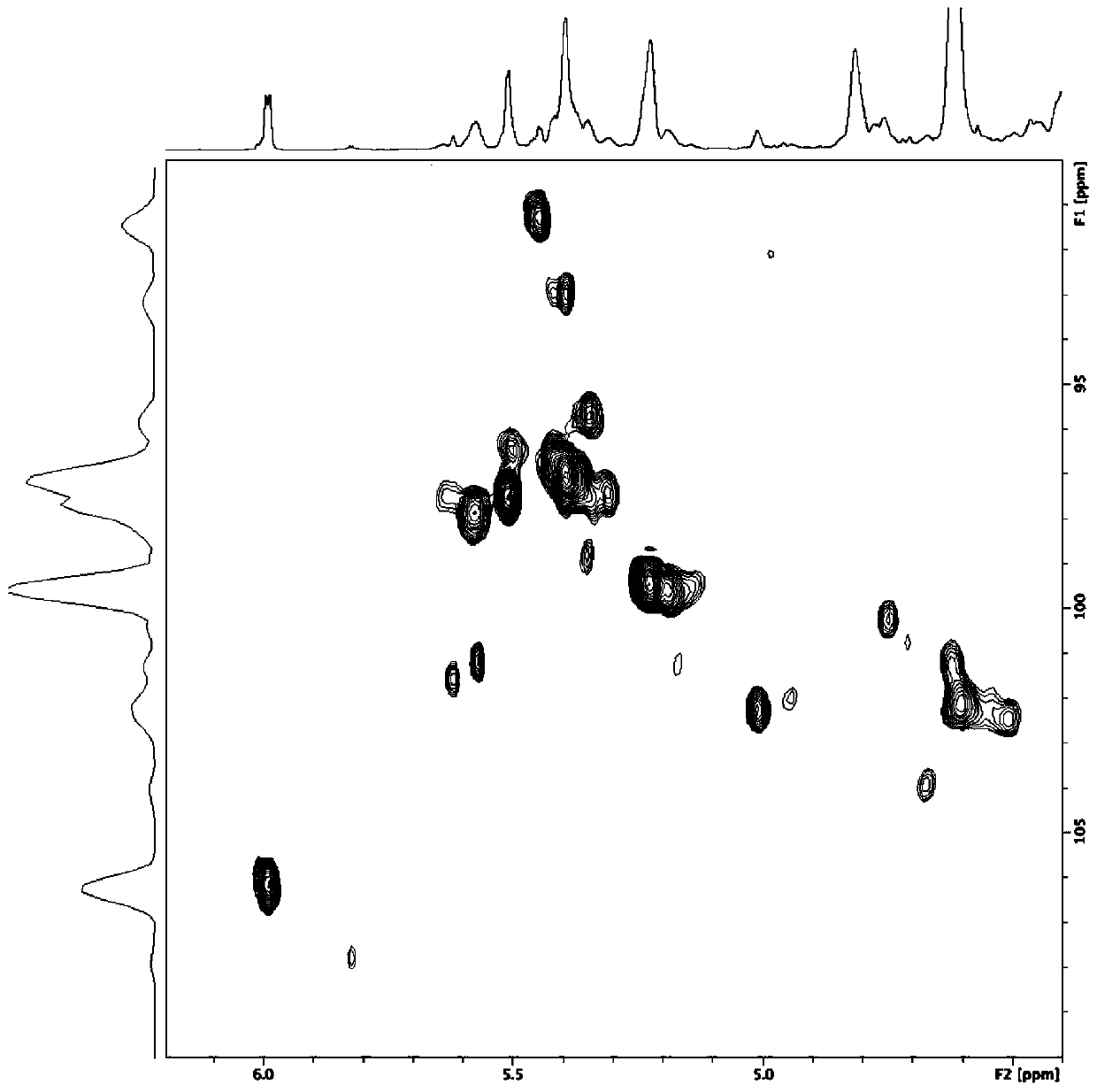
[0083] The resulting intermediate product 1 was fully cut with heparanase I, II, I...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3: Heparanase III partial depolymerization of intermediate 1
[0085] Escherichia coli expressing heparanase III was constructed according to literature (Carbohydr Polym, 2017, 173:276-285). The engineered strains were cultured in LB medium with a resistance of 50 μg / mL ampicillin, cultured at 37°C until OD 600 0.6 ~ 0.8, 0.2mM IPTG induced 18 ~ 20h at 22 ℃. After the cultivation, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 15min to collect the thalli, crush and filter on ice, and then use Ni Sepharose 6B affinity column chromatography to purify. The purity of the obtained recombinant heparanase III is greater than 80%.
[0086] Weigh the intermediate product 1 that 100mg embodiment 2 makes and dissolve in 50mL buffer solution (50mM Tris-HCl, 10mM CaCl 2 , the solvent is water, the pH is 7.0), add 36 μL of heparanase III solution with a total activity of 371mIU, depolymerize in a constant temperature water bath at 37°C for 30 minutes, and deactivate the enzyme in a boiling wate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com