Xylose utilization yeast and application thereof
A technology of xylose and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in genetic engineering and biological fields, can solve the problems of high production cost and inability to produce on a large scale, and achieve the effect of reducing waste, reducing production cost and eliminating inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Construction of xylose utilization metabolic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
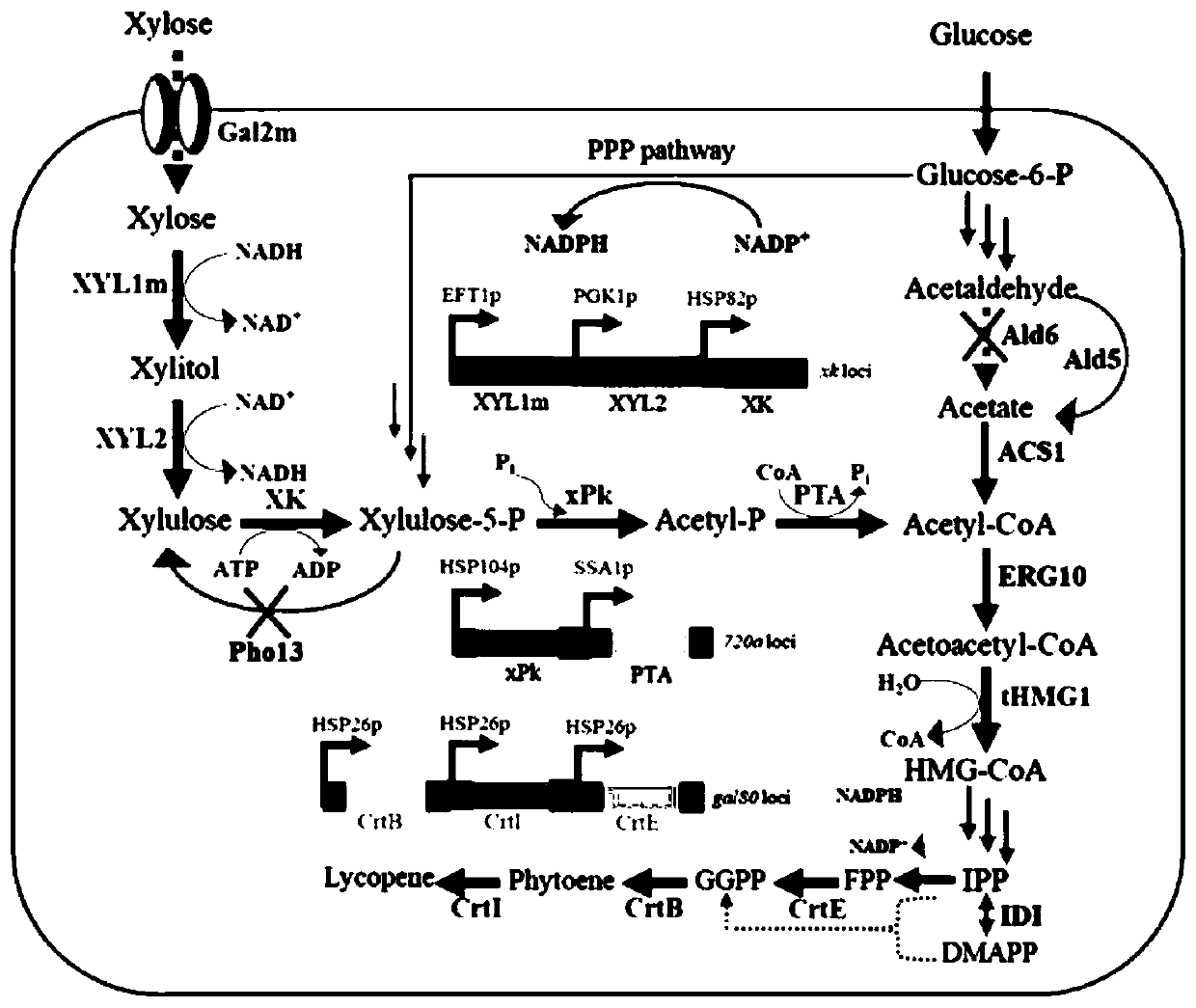
[0028] Since Saccharomyces cerevisiae itself cannot metabolize xylose, in order to use xylose to synthesize carotenoids, this example introduces xylose reductase gene XYL1 and xylitol dehydrogenase gene XLY2 from Scheffersomyces stipitis. Use the plasmid pHCas9-gRNA as a template (pHCas9-gRNA contains the guide sequence N 20 ), use the primers gRNA-XK-F / gRNA-R to amplify the functional modules, and construct the genome integration plasmid pHCas9-XK. Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome as a template, primers EFT1-F-2, EFT1-F / EFT1-R, PGK-F / PGK-R, HSP82-F / HSP82-R were used to amplify EFT1, PGK1, and HSP82 promoters respectively; Scheffersomyces stipitis genome was used as a template, and primers XYL1-F / XYL1-R, XYL1-R-2, XYL2-F / XYL2-R, XYL2-R-2 were used to amplify XYL1 (Gene ID: 4839234), XYL2 (Gene ID :4852013) gene. Using overlapping PCR, build the EFT1-XYL1-PGK1-XYL2-HS...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2 pentose phosphate ketolysis (PK) pathway construction
[0036] In the above-mentioned Example 1, after introducing the xylose metabolism pathway into Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although the engineered bacteria can already utilize xylose, the content of the target product is still relatively low. In order to improve the product yield, the pentose phosphate ketolysis (PK) pathway was introduced in this example. Use the plasmid pHCas9-gRNA as a template (pHCas9-gRNA contains the guide sequence N 20 ), use the primers gRNA-720a-F / gRNA-R to amplify the functional modules, and construct the genome integration plasmid pHCas9-720a. Using the Leuconostoc mesenteroides genome as a template, use primers xpk-F / xpk-R, xpk-R-2 to amplify the xPK gene (GenBank: TJY30451.1); using the Clostridium butyricum genome as a template, use primers pta-F / pta-R , pta-R-2, 720-R amplified PTA gene (GenBank: EEP53689.1). Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome as a template, prime...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Pho13 gene knockout
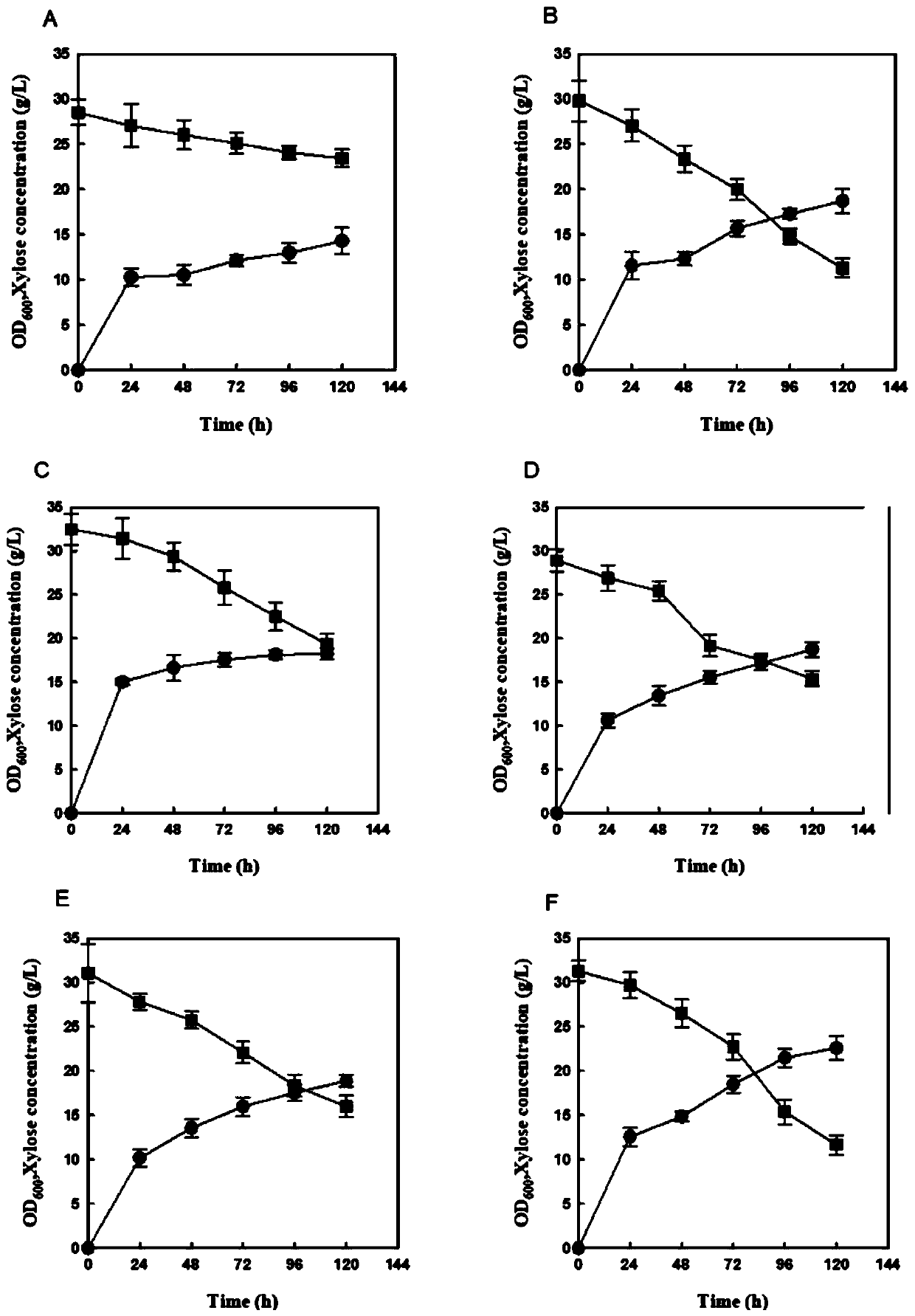
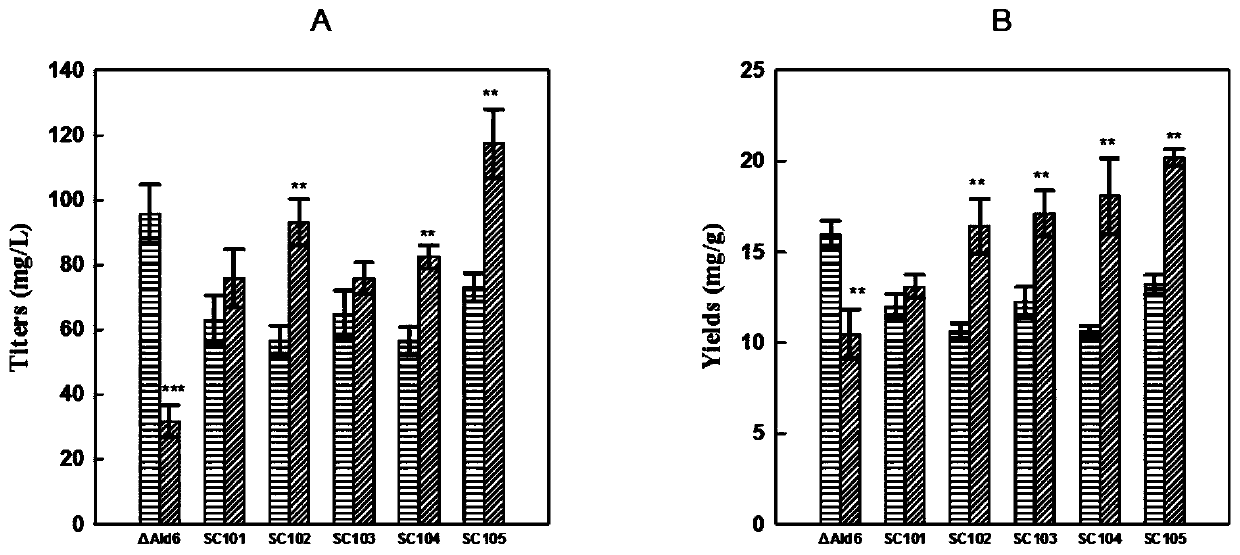
[0042] After the above-mentioned Example 2, the xylose utilization rate of the engineered bacteria is still relatively slow. In order to improve the xylose utilization efficiency, the Pho13 gene (Gene ID: 851362) is knocked out in this example. Using the plasmid pHCas9-gRNA as a template, the primers gRNA-Pho13-F / gRNA-R were used to amplify the functional modules to construct the genome-integrated plasmid pHCas9-Pho13. Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome as a template, primers Pho13-UP-F / Pho13-UP-R, Pho13-DOWN-F / Pho13-DOWN-R were used to amplify the upstream and downstream homology arms of the Pho13 gene, and the Pho13 gene knockout was constructed by overlapping PCR. In addition to the module, the strain SC103 constructed in Example 2 was introduced together with pHCas9-Pho13, and the identification primer Pho13-check-F / Pho13-check-R was used for identification to obtain the engineering strain SC104. The obtained recombinant strai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com