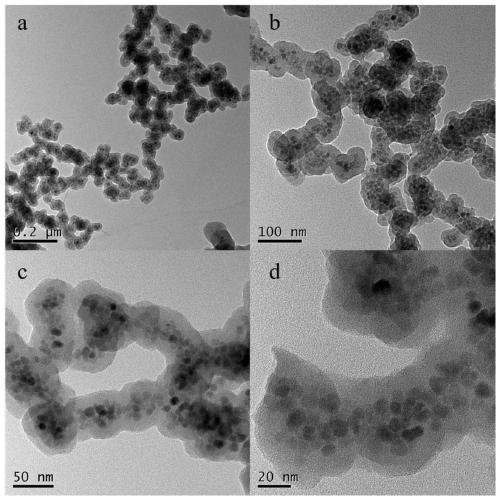
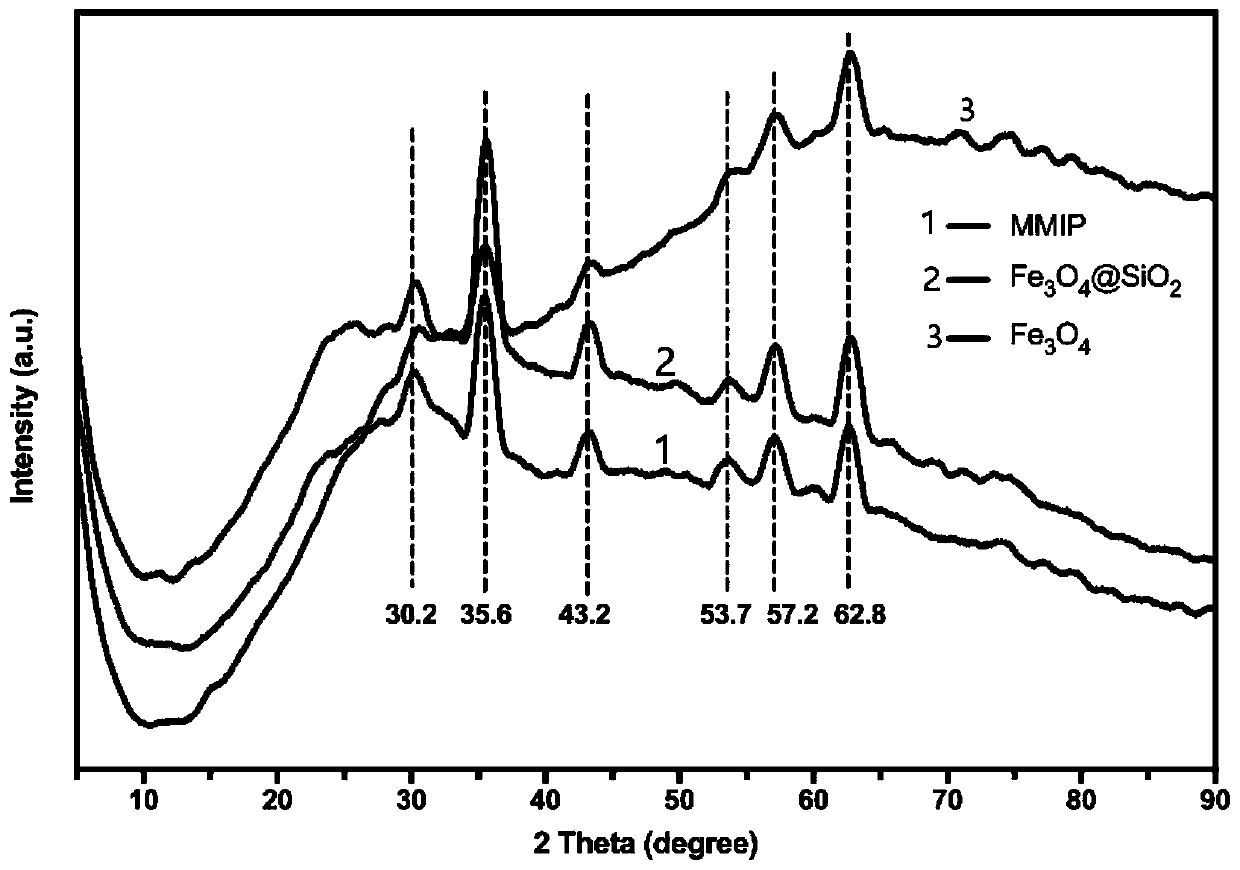
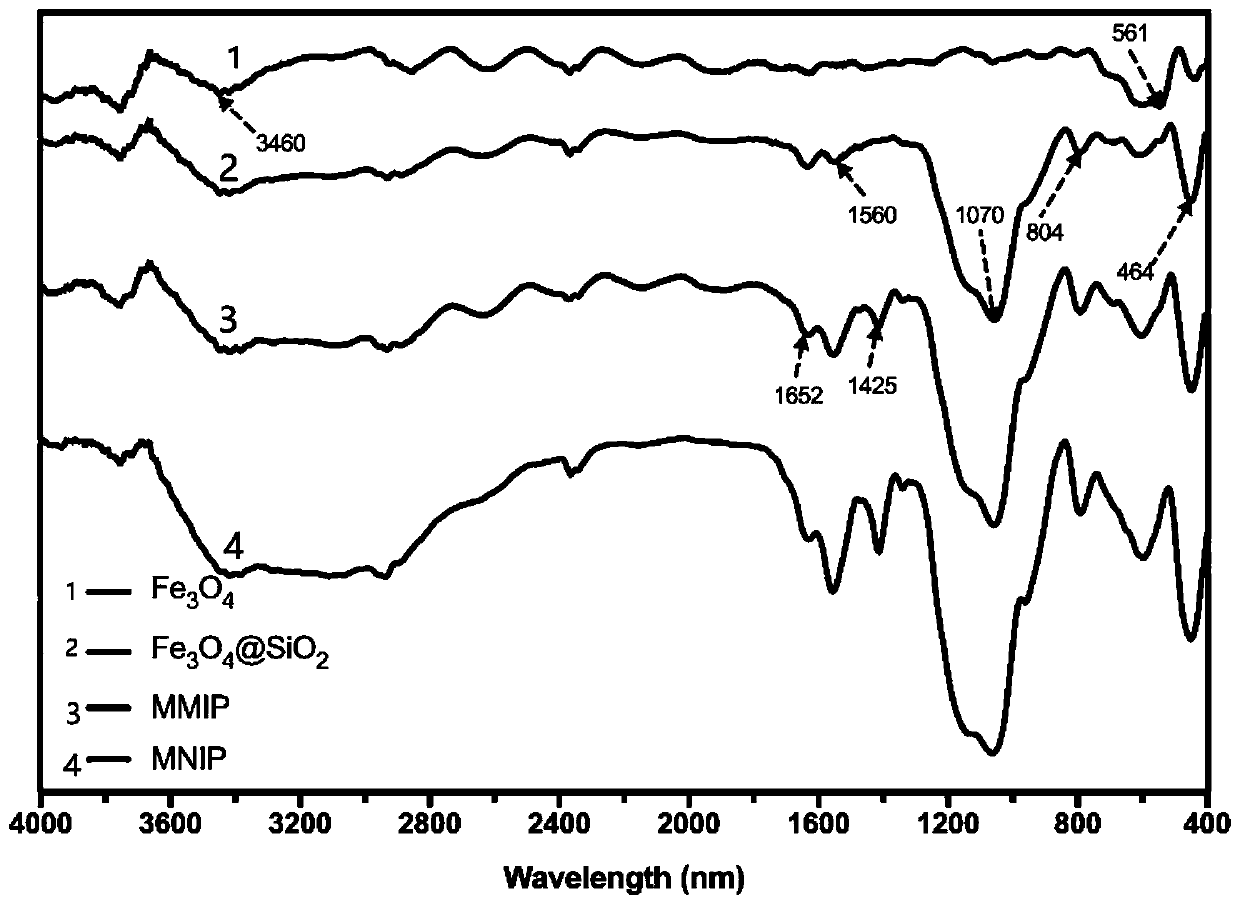
Preparation method of high-selectivity ceftriaxone sodium magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer
A magnetic molecular imprinting and ceftriaxone sodium technology, applied in the fields of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problem of unreliable detection of analytes, complex pretreatment process, and target To solve the problem of low concentration of substances, to achieve the effect of excellent magnetic response, good selectivity and high adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Preparation of superparamagnetic Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles
[0042] After dissolving the iron acetylacetonate in triethylene glycol, venting nitrogen to remove oxygen and stirring, react for 20-40 minutes at a temperature of 150-200℃ and a speed of 200-400rpm; then turn off the stirrer, insert the condenser, React for 20-40min at 250-300℃;
[0043] (2) The solution prepared in step (1) is continuously vented with nitrogen until it is cooled to room temperature, and the reaction product A is washed with ethyl acetate to completely remove the excess triethylene glycol and by-products; the washed precipitate is ultrasonically dispersed into ethanol In the preparation of Fe 3 O 4 Magnetic fluid
[0044] (3) Preparation of Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 Nanoparticles
[0045] Add the magnetic fluid and ammonia prepared in step (2) to the ethanol-water solution, stir for 20-40 min at a temperature of 20-40°C and a rotation speed of 200-400 rpm; then add tetraethoxysilane dropwise to the ethanol ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The steps of Example 2 and Example 1 are the same, but the difference lies in the ratio of ingredients in the reaction, which are specifically as follows:
[0059] In the step (1), the mass ratio of triethylene glycol to iron acetylacetonate is 16:1.
[0060] In the step (2), Fe 3 O 4 The concentration of the magnetic fluid is 3.5 mg / mL.
[0061] In the step (3), Fe 3 O 4 The mass ratio of magnetic fluid, ammonia, tetraethoxysilane, and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane is 1100:12:6:1.
[0062] In the step (5), ceftriaxone sodium, Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 The mass ratio of nanoparticles, azobisisobutyronitrile, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and methacrylic acid is 2500:700:250:7:1.
[0063] In the step (5), the volume ratio of the acetonitrile-methanol solution is 1.1:1.
[0064] The magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer of ceftriaxone sodium prepared in this embodiment has a particle size of about 80 nm and a magnetic saturation intensity of 20 emu / g.
Embodiment 3
[0066] The steps of Example 3 and Example 1 are the same, but the difference lies in the ratio of ingredients in the reaction, which are specifically as follows:
[0067] In the step (1), the mass ratio of triethylene glycol to iron acetylacetonate is 17:1.
[0068] In the step (2), Fe 3 O 4 The concentration of the magnetic fluid is 4 mg / mL.
[0069] In the step (3), Fe 3 O 4 The mass ratio of magnetic fluid, ammonia, tetraethoxysilane, and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane is 1200:14:7:1.
[0070] In the step (5), ceftriaxone sodium, Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 The mass ratio of nanoparticles, azobisisobutyronitrile, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and methacrylic acid is 3000:800:300:9:1.
[0071] In the step (5), the volume ratio of the acetonitrile-methanol solution is 1.2:1.
[0072] The magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer of ceftriaxone sodium prepared in this embodiment has a particle size of about 100 nm and a magnetic saturation intensity of 16 emu / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic saturation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com