Nucleic acid aptamer combined with nucleocapsid protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and application of nucleic acid aptamer
A nucleic acid aptamer and nucleocapsid protein technology, which is applied in the direction of viruses/phages, viruses, viral peptides, etc., can solve the problems of renal failure, rapid transmission, and imperfect detection methods of new coronaviruses, and achieve small molecular weight, Chemically stable, easy to store and label
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
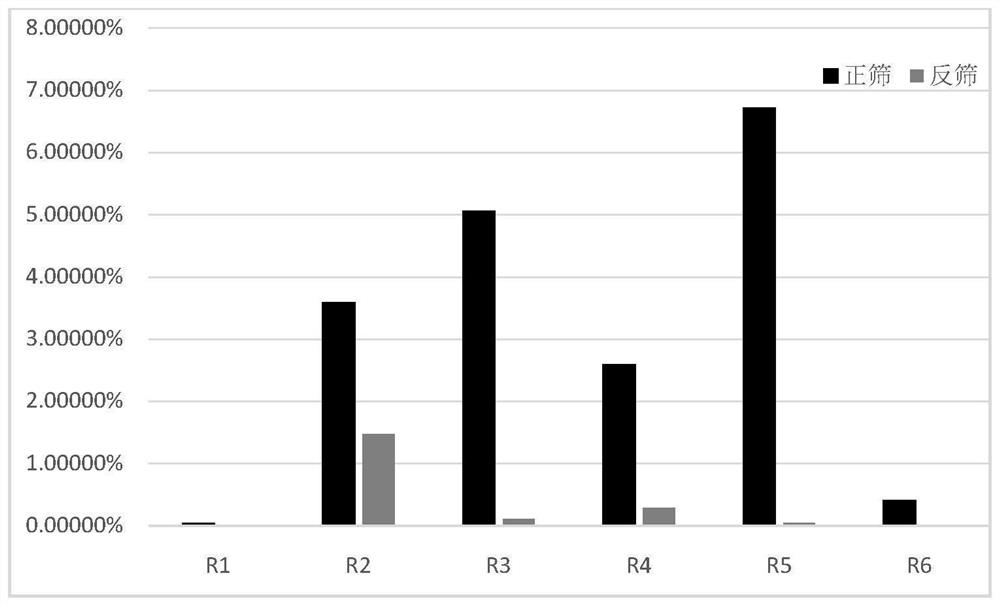
[0042] Screening of nucleic acid aptamers that specifically bind to the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein
[0043] 1. Synthesize the random single-stranded DNA library and primers shown in the following sequence:
[0044] Random single-stranded DNA library (denoted as lib13 library):
[0045] 5’~3’
[0046] TTCAGCACTCCACGCA-TAGCNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA
[0047] Wherein, "N" represents a sequence formed by linking arbitrary nucleotide bases, and the library is synthesized by Shenggong Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.;
[0048] The primer information is shown in Table 1, synthesized by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0049] Table 1 Primers and their sequences
[0050]
[0051] Remarks: ①In the primer name, S1 stands for forward primer, A2 stands for reverse primer, S1-FAM stands for fluorescently labeled forward primer, A2-ployA is a reverse primer with polyA tail attached, polyA is composed of 19 A (Adenylate) composed of...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2 Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) detection of the affinity between the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1-2 and the N protein
[0098] Sample solution: Take the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1-2 and dilute it with DPBS buffer to a concentration of 500 nM.
[0099] Other operations are the same as those in step 2.5 of Example 1 figure 2 The detection method of S1, the coupling amount of N protein is 1500Ru.
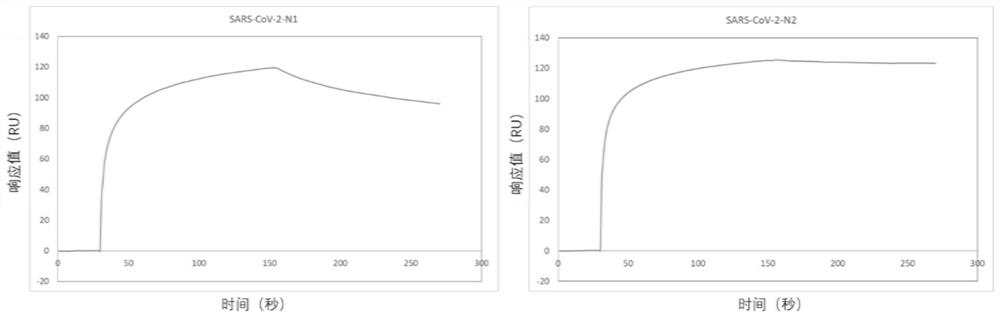
[0100] Test results such as image 3 As shown, image 3 It is the result of the binding force of the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2 to the N protein detected by SPR, where SARS-CoV-2-N1 is the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No.1 SARS-CoV-2-N2 is a nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No.2. Each curve is the curve after channel 2 minus channel 1.
[0101] by image 3 It can be seen that the nucleic acid aptamers shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2 have strong binding to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein detected by the SPR inst...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3 Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detects the binding sites of nucleic acid aptamers shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2 and N protein.
[0106] Solution preparation:
[0107] Sample 1: Take the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and dilute it with DPBS buffer to a concentration of 500 nM.
[0108] Sample 2: Take the nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and dilute it with DPBS buffer to a concentration of 500 nM.
[0109] Mixed solution: an equal volume mixed solution of 0.4M EDC aqueous solution and 0.1M NHS aqueous solution.
[0110] operating:
[0111] S1. Couple N protein to the second channel on the surface of the CM5 chip: first clean the chip with 50mM NaOH aqueous solution, inject 20μl at a flow rate of 10μl / min, and then inject 50μl of the activated chip with a mixed solution at a flow rate of 5μl / min; The protein was diluted with a pH=5.5, 10mM sodium acetate aqueous solution to a final concentration of 50μg / mL and then injected. The injection volume was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com