Composite material for removing lead ions in solution as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of composite materials and lead ions, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor hydrophilicity of molybdenum disulfide, etc., to improve poor hydrophilicity and high cost , the effect of low synthesis cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
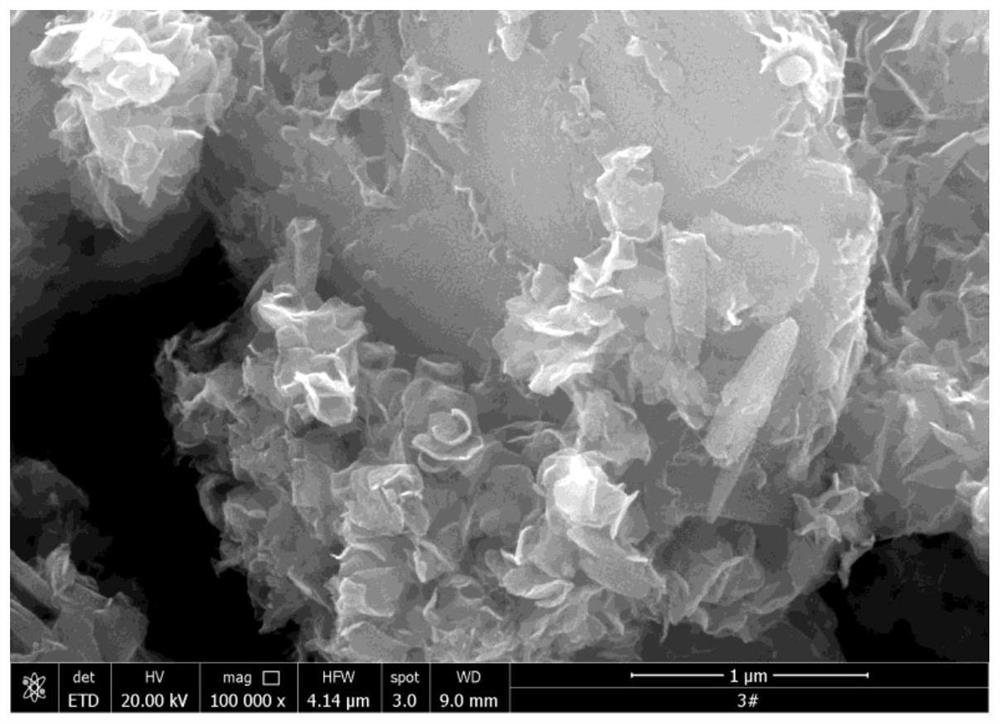
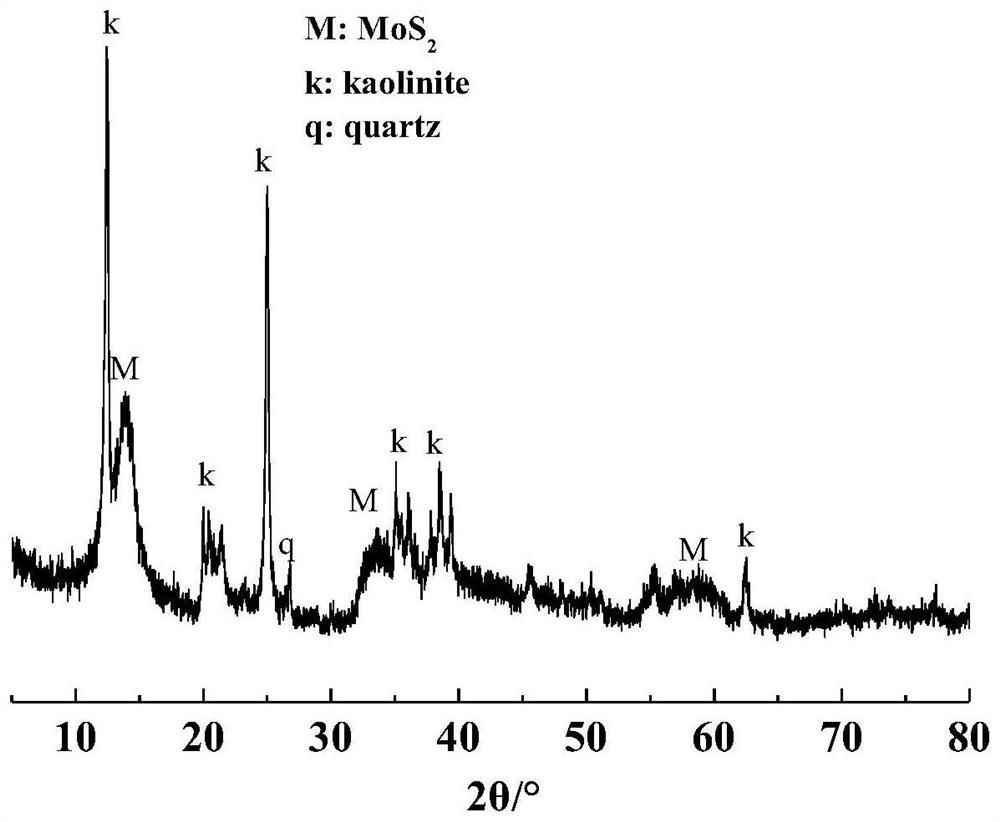
[0030] Weigh 1.24g of ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 1.07g of thiourea to dissolve in 60mL of deionized water, stir with a magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved; weigh 1g of kaolinite into the mixed solution, mix and stir for 30min to form a uniform suspension liquid; transfer the mixed suspension into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction kettle, raise the temperature to 210°C for 6 hours, and then naturally cool to room temperature; use a centrifuge to centrifuge the reaction product, and use deionized water and absolute ethanol alternately Wash the product more than three times; the washed product is placed in a vacuum drying oven at 80°C until the sample is completely dry, and it is ground for later use, code-named SK@MoS 2 .
[0031] figure 1 For the synthesis of SK@MoS in this example 2 The XRD pattern of the composite material. It can be seen from the figure that in addition to the characteristic diffraction peaks of the kaolinite substrate, the XRD pat...
Embodiment 2
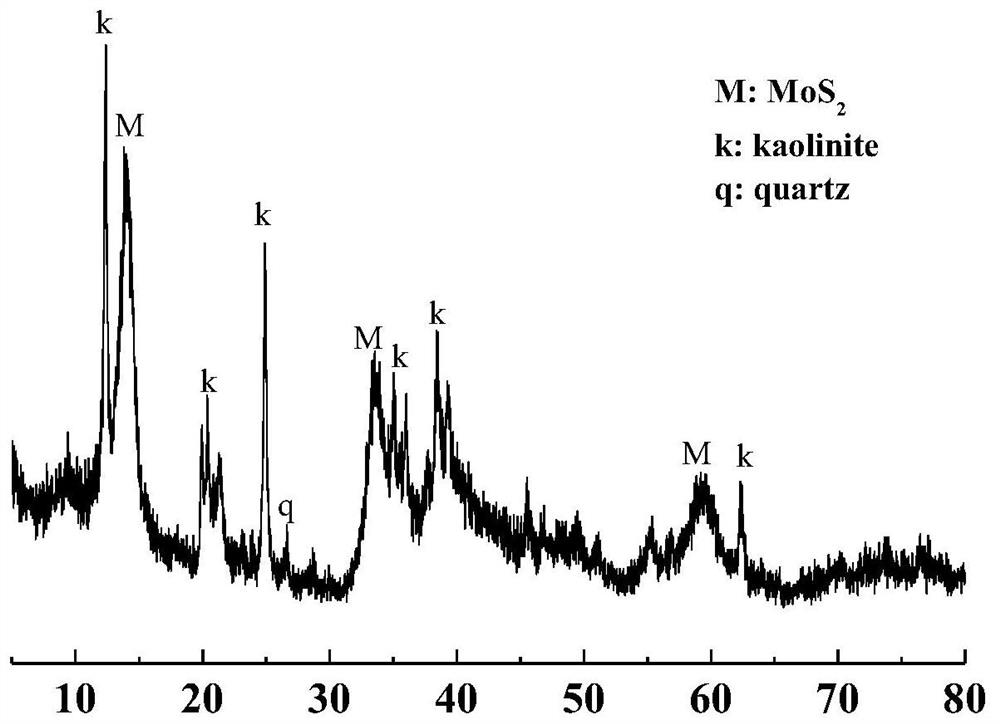
[0033] Weigh 2.48g of ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 2.14g of thiourea to dissolve in 60mL of deionized water, stir with a magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved; weigh 2g of kaolinite into the mixed solution, mix and stir for 30min to form a uniform suspension liquid; transfer the mixed suspension into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction kettle, raise the temperature to 220 ° C for 8 hours, and then naturally cool to room temperature; use a centrifuge to centrifuge the reaction product, and use deionized water and absolute ethanol alternately The product was washed more than three times; the washed product was placed in a vacuum drying oven at 80°C until the sample was completely dried, and ground for XRD testing.
[0034] image 3 For the synthesis of SK@MoS under the conditions of this example2 The XRD pattern of the composite material, it can be seen from the figure that the characteristic diffraction peaks of kaolinite and molybdenum disulfide appear on the...
Embodiment 3
[0036] To compare SK@MoS 2 Composite adsorption materials and single MoS 2 and kaolinite on Pb 2+ difference in adsorption performance. in Pb 2 + Add 0.08g of SK@MoS to the solution with concentration of 100mg / L, pH of 4.0 and volume of 50mL 2 、MoS 2 and kaolinite samples were placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred for 10min, 20min, 30min, 40min, 50min, and 60min, respectively, and then removed, and a centrifuge was used for solid-liquid separation to obtain supernatant and solid samples. Pb in the supernatant 2+ Concentration is detected to get Pb 2+ Concentration, using the residual method to calculate the effect of three adsorbents on Pb under different stirring time conditions 2+ the adsorption rate.
[0037] Figure 4 SK@MoS under different stirring time conditions in this example 2 、MoS 2 and kaolinite to Pb 2+ The graph of adsorption rate shows that when the stirring time is 10min, 20min, 30min, 40min, 50min, 60min, the 2 to Pb 2 + The adsorption rates ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com