Method for efficiently separating straw components by adopting novel eutectic solvent
A low eutectic solvent, a new type of technology, applied in the use of microorganism/enzyme cellulose treatment, textiles and papermaking, papermaking, etc., can solve the problems affecting high-value utilization, narrow utilization window, small molecular weight of lignin, etc., to achieve value-added The effect is obvious, the utilization rate of raw materials is high, and the effect of high-efficiency removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040]The method for efficiently separating straw components using a novel deep eutectic solvent comprises the following steps:
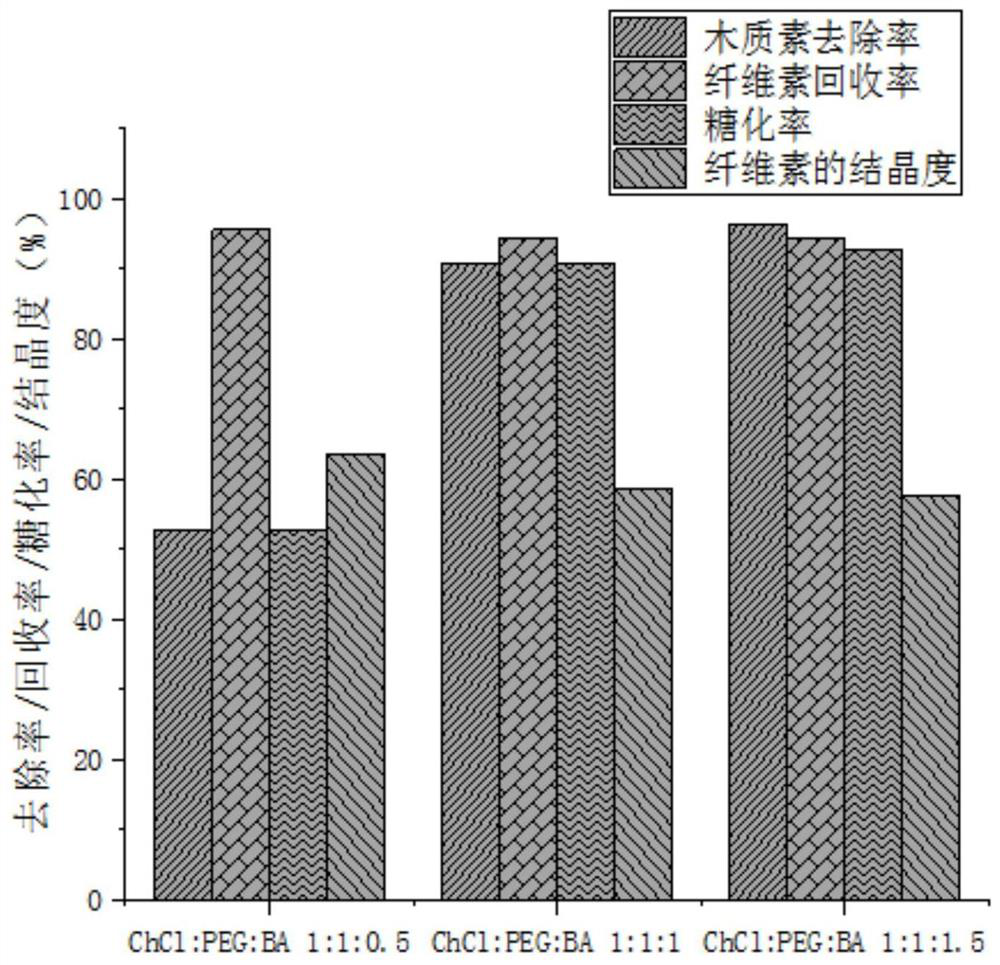
[0041] (1) Synthesis of novel deep eutectic solvent: choline chloride, polyethylene glycol-200 and boric acid are synthesized novel deep eutectic solvent as shown in Table 2, can be used directly without purification;
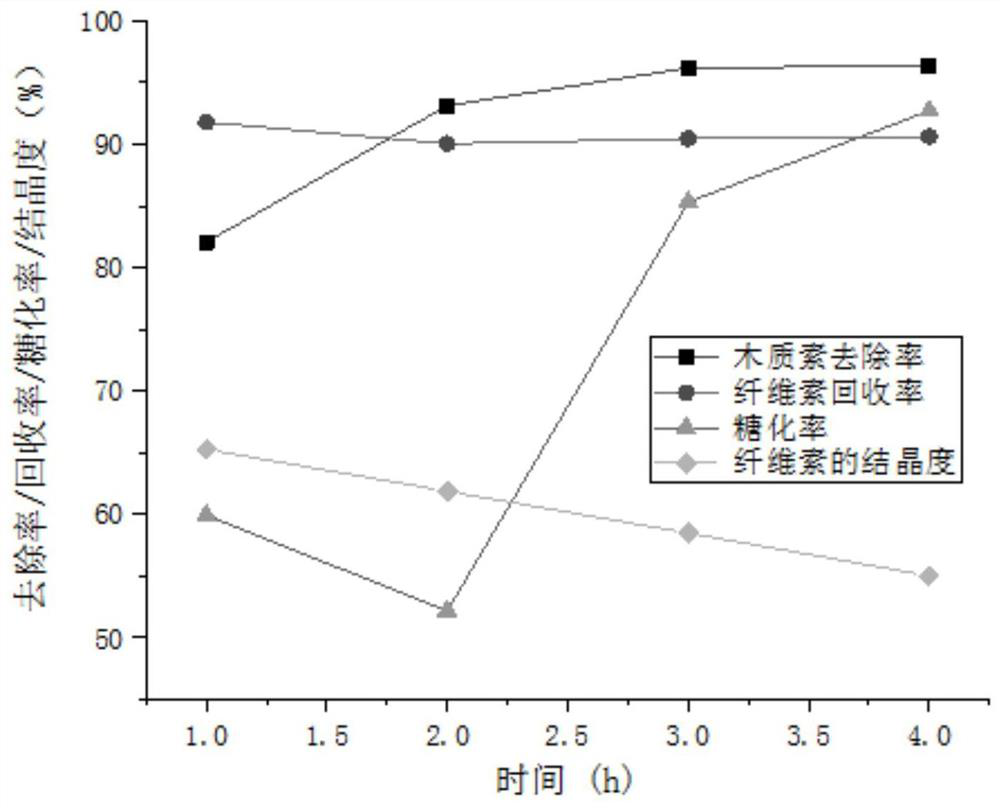
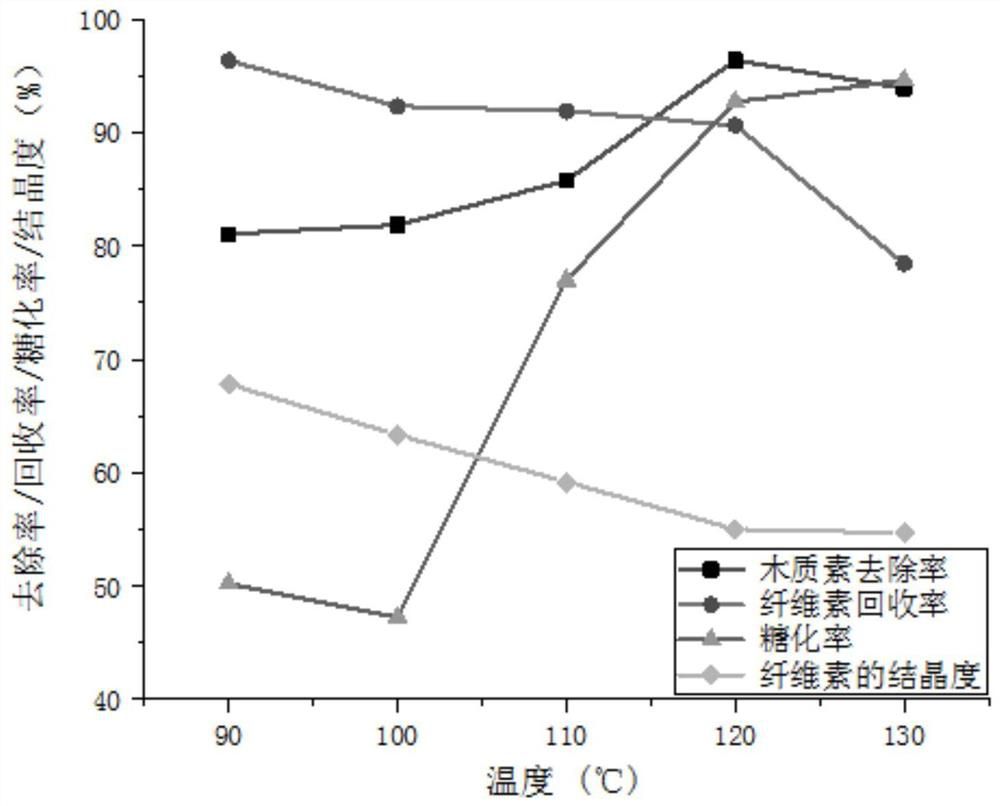
[0042] (2) Primary treatment of straw: first, mix straw and deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, and react at 120°C for 0.5h; then perform solid-liquid separation to obtain filtrate I and filter residue I, and use filter residue I Washing with ion water for 2-3 times, drying to absolute dryness to obtain the straw residue of primary treatment;
[0043] (3) Extraction of hemicellulose: add ethanol in the filtrate I of step (2) gained, wherein the volume ratio of ethanol and filtrate I is 5:1; The hemicellulose is obtained; the ethanol filtrate obtained by filtering is rotary evaporated and recycled;
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The method for efficiently separating straw components using a novel deep eutectic solvent comprises the following steps:
[0055] (1) Synthesis of a new type of deep eutectic solvent: mix choline chloride, polyethylene glycol-200 and boric acid at a molar ratio of 1:1:1.5, and react at 80°C for 1 hour to obtain a new type of deep eutectic solvent , can be used directly without purification;
[0056] (2) Primary treatment of straw: first, mix straw and deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, and react at 120°C for 0.5h; then perform solid-liquid separation to obtain filtrate I and filter residue I, and use filter residue I Washing with ion water for 2-3 times, drying to absolute dryness to obtain the straw residue of primary treatment;
[0057] (3) Extraction of hemicellulose: add ethanol in the filtrate I of step (2) gained, wherein the volume ratio of ethanol and filtrate I is 5:1; The hemicellulose is obtained; the ethanol filtrate obtained ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The method for efficiently separating straw components using a novel deep eutectic solvent comprises the following steps:
[0066] (1) Synthesis of a new type of deep eutectic solvent: mix choline chloride, polyethylene glycol-200 and boric acid at a molar ratio of 1:1:1.5, and react at 80°C for 1 hour to obtain a new type of deep eutectic solvent , can be used directly without purification;
[0067] (2) Primary treatment of straw: first, mix straw and deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, and react at 120°C for 0.5h; then perform solid-liquid separation to obtain filtrate I and filter residue I, and use filter residue I Washing with ion water for 2-3 times, drying to absolute dryness to obtain the straw residue of primary treatment;
[0068] (3) Extraction of hemicellulose: add ethanol in the filtrate I of step (2) gained, wherein the volume ratio of ethanol and filtrate I is 5:1; The hemicellulose is obtained; the ethanol filtrate obtained ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com