Method for producing biogas by co-fermentation of blue-green algae and bottom mud
A technology of co-fermentation and sediment, applied in the field of pollution control of rivers and lakes, can solve the problems of low efficiency of biogas production, achieve the effects of reducing electronic competition, increasing yield and output, and inhibiting system acidification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
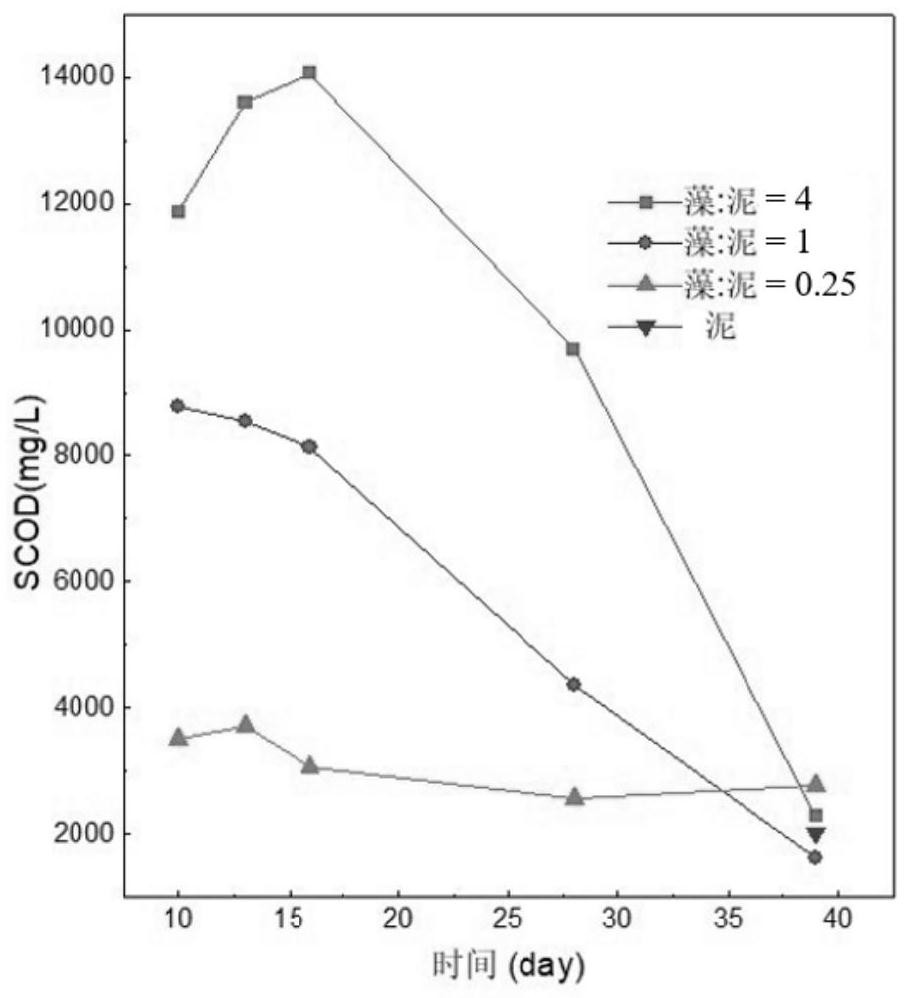
[0034] A method for producing biogas by co-fermentation of cyanobacteria and bottom mud according to the present invention includes adding 2% to 9% by weight of iron oxide into the mixture of bottom mud and cyanobacteria, mixing them evenly, and then carrying out anaerobic fermentation for 15-35 days, and then Produce biogas. Wherein, the blue-green algae and the bottom mud are mixed in different ratios of volatile solids (volatile solid, VS), and the ratio of the VS content of the bottom mud after mixing to the VS content of the blue-green algae is 0.25-4. The iron oxide used in the present invention can be rust powder, steel slag, hematite, etc., and its particle size is 0.05-1mm, preferably 0.05-0.1mm. The particle size of the iron oxide used in this embodiment is 0.05-0.1mm . The specific surface area is about 1500-3000cm 2 / g.
[0035] In the present invention, the bottom mud used is preferably grass-type bottom mud or algae-type bottom mud. The mass ratio of volatile...
Embodiment 2
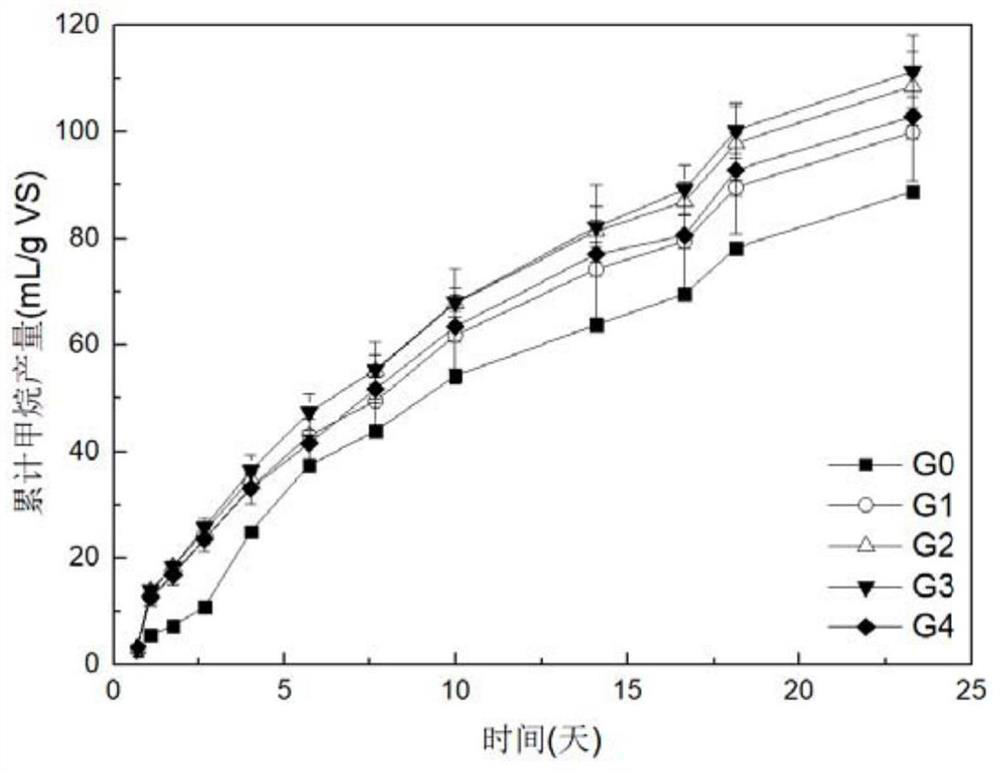
[0043] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that in this embodiment, the bottom mud used is algae type bottom mud. Such as Figure 4 As shown in a, the ratio of VS content of bottom mud and blue-green algae after mixing is 0.25, 1 and 4, and the addition amount of rust powder is 2% by weight. More than 90% of the total output of methane has been produced in 15 days of reaction. With the increase of the ratio of cyanobacteria, the methane production potential (Biochemical methane potential, BMP) is obviously increased, but the reaction lag period is also significantly increased, which may be the load of the hydrolysis process of cyanobacteria. High, slow gas production, microorganisms need to carry out coordinated multi-step hydrolysis to further decompose excess organic acids into small molecules. The algae-type sediment naturally enriches the microbial groups that decompose cyanobacteria, which is conducive to the anaero...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, and the difference is that in this embodiment, the bottom mud used for fermentation is a grass-type bottom mud, such as Figure 4 As shown in b, after the cyanobacteria and the bottom mud are mixed in this embodiment, the VS ratios are 0.25, 1 and 4, and the addition amount of the rust powder is 2% by weight. It is worth noting that the fermentation time required by the grass-type sediment is longer than that of the algae-type sediment, and the gas production of methane exceeds 98% of the total production at 35 days. Such as Figure 4 a and Figure 4 As shown in b, compared with the same ratio, the gas production lag period of the algae-type sediment is shorter, which may be caused by the lower microbial abundance of the hydrolyzed cyanobacteria in the grass-type sediment. Not only that, the stable and difficult-to-decompose cellulose and lignin substances in the grass-type sediment can be synergis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com