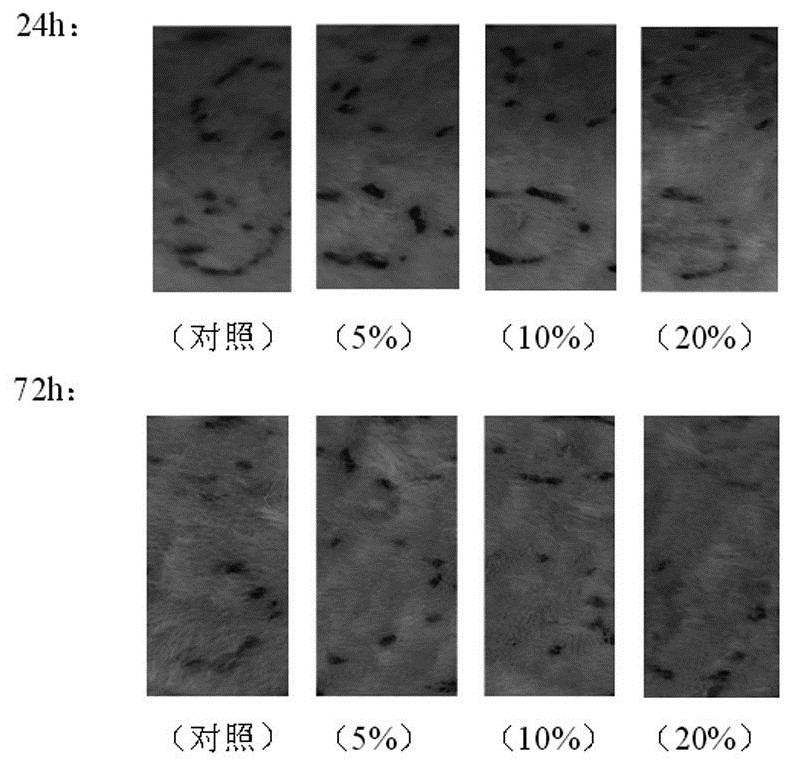
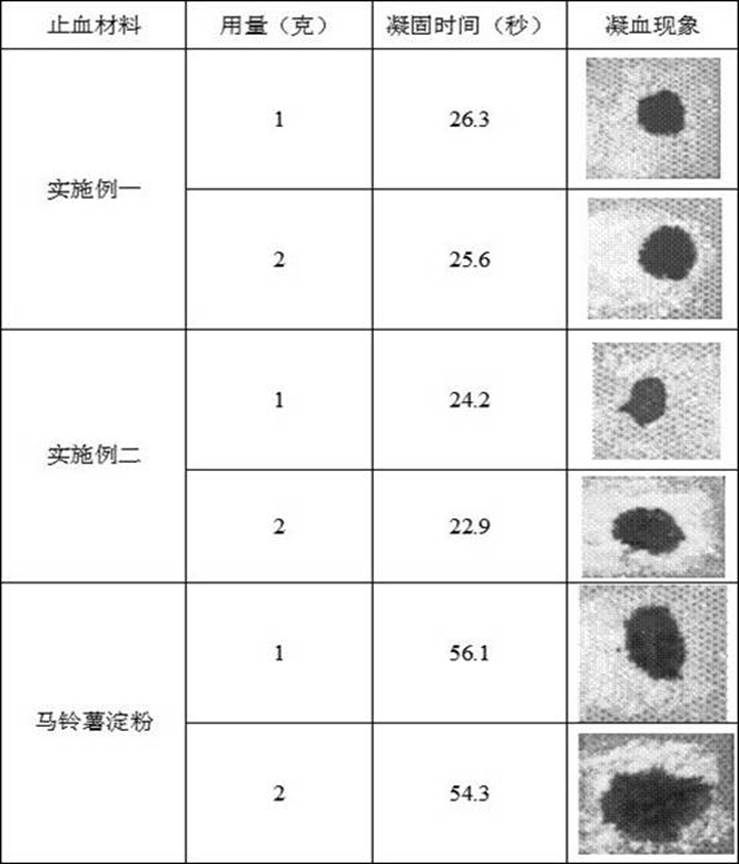
Preparation method of starch microsphere and human recombinant tissue factor lipid composite hemostatic material
A technology of starch microspheres and tissue factor, applied in drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulations, surgical adhesives, etc., can solve the problems of limited hemostatic effect of pure chitosan materials, long degradation time of cellulose materials, and increased risk of wound infection , to achieve the effect of increased specific surface area, improved water absorption performance, and shorter hemostasis time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] (1) Water phase preparation, add 1.5 g of potato starch into 8 mL of deionized aqueous solution, adjust the pH value to about 8.0 with NaOH solution, heat to 80 °C, wait for the starch to dissolve, and cool to room temperature.
[0022] (2) Oil phase preparation, take 1 g of Span60 into 20 mL of soybean oil, heat to 60 °C until completely dissolved, and cool to room temperature.
[0023] (3) For emulsification, slowly add the starch solution obtained in step (1) into the oil phase solution obtained in step (2), and stir thoroughly.
[0024] (4) Add 0.10 g of sodium trimetaphosphate to complete starch cross-linking and form starch microspheres.
[0025] (5) The solution in step (4) is centrifuged to separate the precipitate, washed with ethyl acetate and ethanol in sequence, and dried to obtain starch microspheres.
[0026] (6) Disperse 1.5 g of starch microspheres obtained in step (5) in 10 mL of anhydrous 1,4-dioxane solution, add 0.015 g of DSC, and 2 After protecti...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Add 20 g of potato starch into 100 mL of deionized aqueous solution, adjust the pH value to about 8 with NaOH solution, heat to 80°C until the starch is dissolved, and cool to room temperature.
[0030] (2) Add 15 g of Span60 to 240 mL of soybean oil, heat to 60°C until completely dissolved, and cool to room temperature.
[0031] (3) Slowly add the starch solution obtained in step (1) into the oil phase solution obtained in step (2), and stir thoroughly.
[0032] (4) Add 1 g of sodium trimetaphosphate and stir for 5 h to complete starch cross-linking and form starch microspheres.
[0033] (5) The solution in step (4) is centrifuged to separate the precipitate, washed with ethyl acetate and ethanol in sequence, and dried to obtain starch microspheres.
[0034] (6) Disperse 20 g of the starch microspheres obtained in step (5) in 100 mL of anhydrous 1,4-dioxane solution, add 0.2 g of DSC, and 2 After protection, 4°C, and magnetic stirring for 10 h, the surface of sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com