High-density fermentation culture medium of lactobacillus bulgaricus and fermentation process for high-density fermentation culture medium
A technology of high-density fermentation and fermentation process, which is applied in the field of high-density fermentation medium of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and its fermentation process, can solve the problems of the influence of the survival rate of live bacteria and the toxicity of physiological metabolism, so as to improve the survival rate of freeze-drying and reduce the production rate. cost, productivity improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Embodiment 1: configuration and fermentation process of Lactobacillus bulgaricus high-density fermentation medium
[0017] Lactobacillus bulgaricus high-density fermentation medium consists of the following components: glucose 18.0g, beef extract powder 5.0g, casein peptone 4.0g, yeast powder 4.0g, anhydrous sodium acetate 4g, potassium acetate 4.0g, magnesium sulfate 0.1g, Manganese sulfate 0.03g, L-cysteine hydrochloride 0.5g, sodium thiosulfate 0.05g and Tween-80 1.0g were successively dissolved in distilled water and fixed to 1000ml, and the pH of the culture medium was adjusted to 7.20. Sterilize at 121°C for 15 minutes.
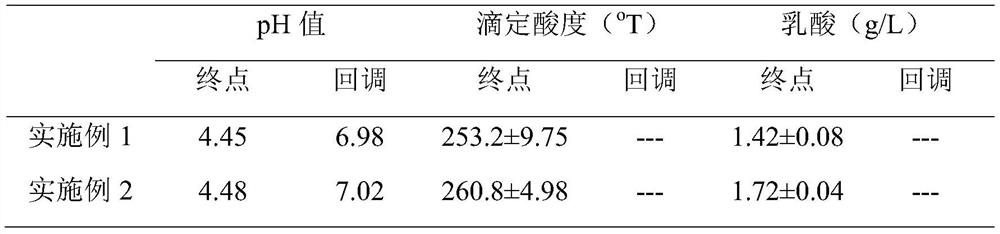
[0018] The specific strain of Lactobacillus bulgaricus selected is Lactobacillus bulgaricus NQ2508, which was purchased from Inner Mongolia Shuangqi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The high-density fermentation culture process of Lactobacillus bulgaricus is as follows: ①Fermentation stages: five-stage amplification fermentation process is adopted, an...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Embodiment 2: Lactobacillus bulgaricus high-density fermentation medium and fermentation process thereof
[0020] Lactobacillus bulgaricus high-density fermentation medium consists of the following components: glucose 10.0g, beef extract powder 4.0g, casein peptone 8g, yeast powder 6.0g, anhydrous sodium acetate 3.0g, potassium acetate 3.0g, magnesium sulfate 0.3g, Manganese sulfate 0.05g, L-cysteine hydrochloride 1.0g, sodium thiosulfate 0.01g and Tween-80 1.0g were successively dissolved in distilled water and fixed to 1000ml, and the pH of the culture medium was adjusted to 7.20. Sterilize at 121°C for 15 minutes. Among them, sodium thiosulfate can reduce the hypochlorite contained in water into non-toxic chloride ions, thereby eliminating the inhibitory effect of hypochlorous acid on the growth and metabolism of Lactobacillus bulgaricus.
[0021] The specific strain of Lactobacillus bulgaricus selected is Lactobacillus bulgaricus NQ2508, which was purchased from ...
Embodiment 3
[0022] Embodiment 3: the processing effect of sodium thiosulfate to residual chlorine in the medium
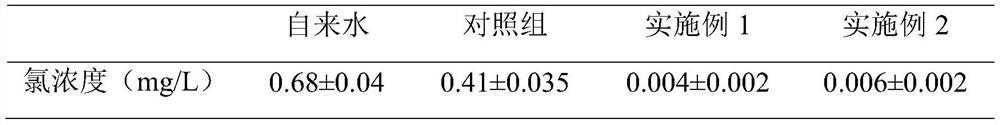
[0023] Taking the fermentation medium without adding sodium thiosulfate as a control, the residual chlorine concentration after the medium was prepared in drinking water was determined by iodometric method. The results showed that available chlorine in the medium was basically eliminated after adding sodium thiosulfate (Table 1). By improving the components of the medium, the influence of the inhibitor (hypochlorous acid) in the drinking water used in the fermentation process on the proliferation of the bacteria and the subsequent preparation process of the bacteria powder is solved.
[0024] Determination of available chlorine concentration in the medium of table 1
[0025]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com