Strain domestication and screening method based on micro-fluidic technology
A microfluidic technology and screening method technology, which can be used in microorganism-based methods, methods using microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: Escherichia coli domestication and screening
[0038] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0039] Material: Escherichia coli DH 5α
[0040] Reagents: LB solid medium: agar 20g, tryptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 10g, distilled water to volume 1L, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0041] LB liquid medium A: tryptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 10g, distilled water to volume 1L, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
[0042] LB liquid medium B: tryptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 30g, distilled water to volume 1L, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min.
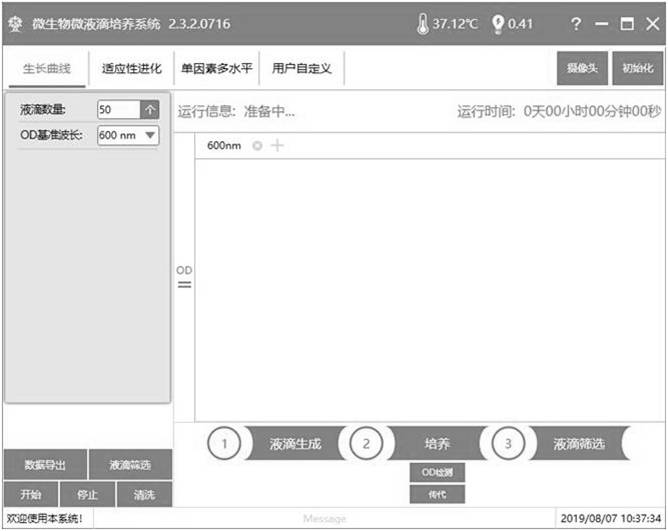
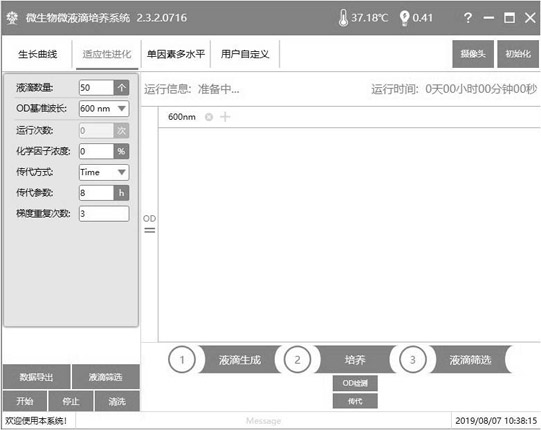
[0043]2. Experimental equipment: automatic high-throughput microbial droplet culture system (Microbial Microdroplet Culturesystem, MMC).
[0044] 3. Experimental steps:
[0045] 1) Inoculate Escherichia coli DH 5α on LB solid medium and culture it at 37°C. After the cultivation, pick a single colony and inoculate it in 5mL LB liquid medium A, and culture it at 37°C with shaking at 200 r...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Saccharomyces cerevisiae domestication and screening
[0059] Saccharomyces cerevisiae can convert sugars into ethanol, which is widely used in industry. However, the high concentration of ethanol produced in the production process will inhibit the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In order to obtain Saccharomyces cerevisiae that tolerates high concentrations of ethanol, it is necessary to domesticate Saccharomyces cerevisiae with ethanol resistance.
[0060] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0061] Material: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0062] Reagents: YPD solid medium: agar 20g, peptone 20g, yeast extract 10g, glucose 20g, distilled water to volume 1L, sterilized at 115°C for 15 min.
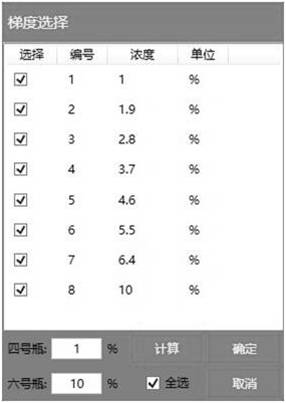
[0063] YPD liquid medium A: peptone 20g, yeast extract 10g, glucose 20g, distilled water to volume 1L, sterilized at 115°C for 15 min. Add ethanol to a volume fraction of 10%.
[0064] YPD liquid medium B: peptone 20g, yeast extract 10g, glucose 20g, distilled wat...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3 Domestication and Screening of Lactobacillus plantarum
[0087] Lactobacillus plantarum is a strain widely used in the food industry, and the product lactic acid in the fermentation process can inhibit the growth of the strain. In order to relieve the inhibitory effect of this product, it is necessary to domesticate Lactobacillus plantarum for lactic acid resistance.
[0088] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0089] Material: Lactobacillus plantarum
[0090] Reagents: MRS solid medium: agar 20g, peptone 10g, beef extract 10g, yeast extract 5g, diammonium hydrogen citrate 2g, glucose 20g, Tween 80 1mL, sodium acetate 5g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2g, magnesium sulfate 0.58 g, manganese sulfate 0.25g, distilled water to volume 1L, pH6.2~6.6, sterilized at 115℃ for 15min.
[0091] MRS liquid medium A: peptone 10g, beef extract 10g, yeast extract 5g, diammonium hydrogen citrate 2g, glucose 20g, Tween 80 1mL, sodium acetate 5g, dipotassium hydrogen phos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com