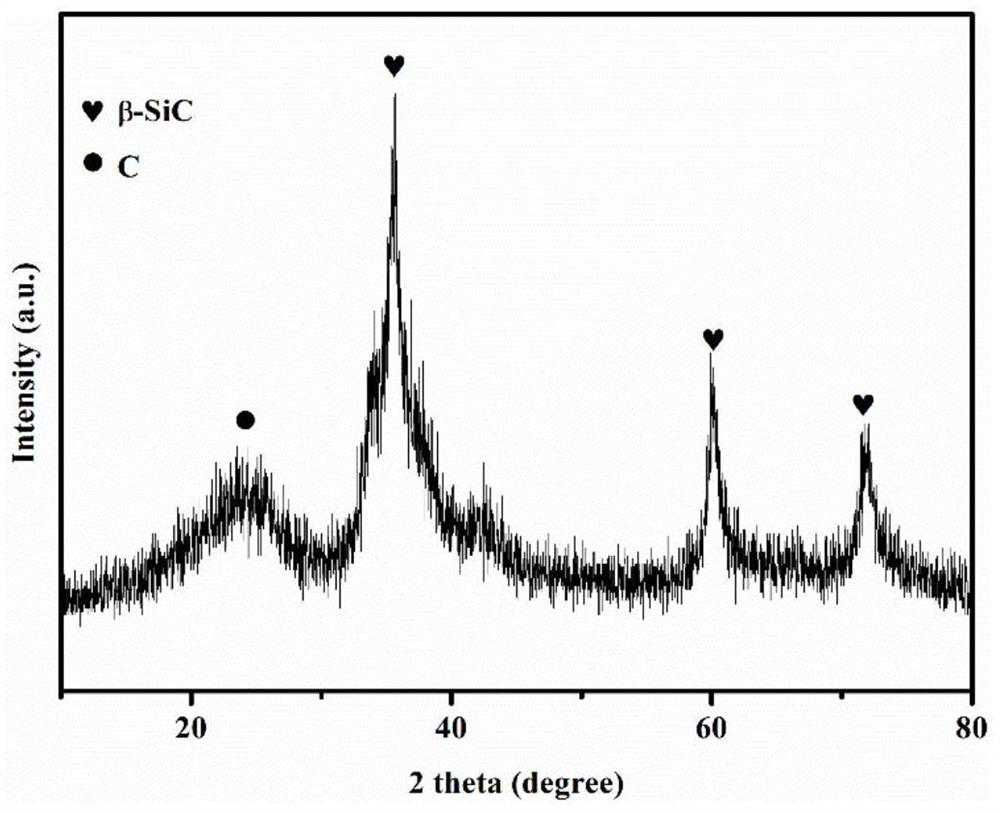
Wave-absorbing SiBCN nanofiber and preparation method thereof
A nanofiber and wave type technology, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of poor electromagnetic wave absorption performance, achieve excellent wave transmission performance, good dielectric performance, and improve the effect of impedance mismatch.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
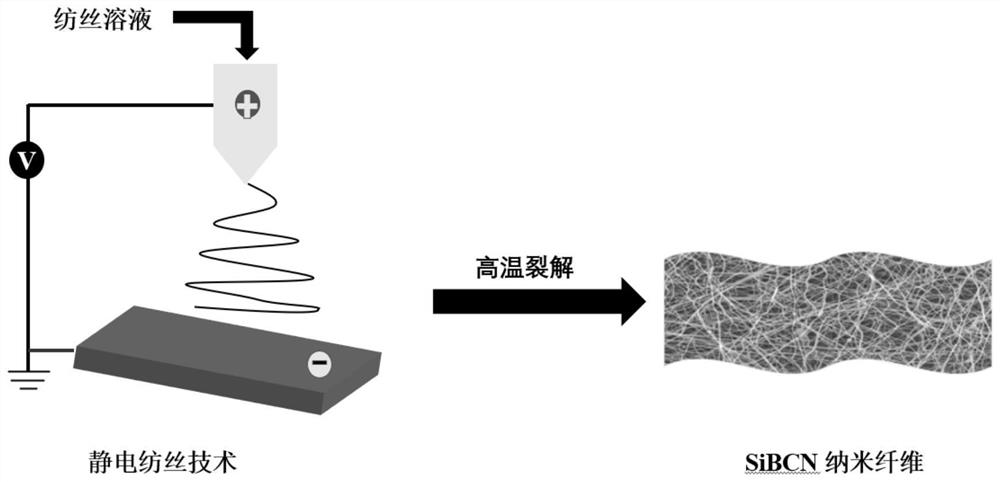
[0042] Another embodiment of the present invention provides the above-mentioned preparation method of absorbing SiBCN nanofibers, combined with figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0043] S1. Preparation of spinning solution: under an inert atmosphere, the colloidal polysilaborazane solid is dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane, and after ultrasonic dispersion, it is left to stand to obtain a spinning solution for electrospinning;
[0044] S2, electrospinning: injecting the spinning solution of step S1 into an electrospinning device for electrospinning to obtain polysilaborazane spinning fibers;
[0045] S3, curing and cross-linking: under an inert atmosphere, the polysilaborazane spinning fiber in step S2 is heated from room temperature to 150-250° C. and kept at a temperature for curing and cross-linking;
[0046] S4, high temperature cracking: in an inert atmosphere, the polysilaborazane spinning fibers after curing and crosslinking in step S3 are heated to 1...
Embodiment 1
[0061] A preparation method of a wave-absorbing SiBCN nanofiber, comprising the following steps:
[0062] S1. Preparation of spinning solution: under an inert atmosphere, dissolve 5 g of polysilaborazane colloidal solid in 5 g of anhydrous dichloromethane, stir magnetically for 2 hours at room temperature, and then use an ultrasonic instrument to fully disperse the solution, and then statically Set for 0.5h to obtain a uniform and transparent spinning solution for electrospinning;
[0063] S2. Electrospinning: inject the spinning solution in step S1 into an electrospinning device for electrospinning to obtain polysilaborazane spinning fibers. The parameters of the electrospinning are: the fiber receiving device is an aluminum plate , plus a needle-tip auxiliary electrode, the receiving distance is 10cm, the solution advancing speed is 25μL / min, the working voltage is 15kV, the ambient humidity is 30%, and the ambient temperature is controlled at 25°C; the polysilaborazane spin...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 is basically the same as Example 1, with the difference that: in step S1, spinning solutions with polysilaborazane colloidal solid mass concentrations of 40%, 45%, 50%, and 55% are prepared respectively for subsequent step S2. -S4, and in step S4, the polysilaborazane spinning fiber after curing and crosslinking in step S3 is heated from 200°C to 1600°C at a rate of 5°C / min under an inert atmosphere and kept for 2 hours.
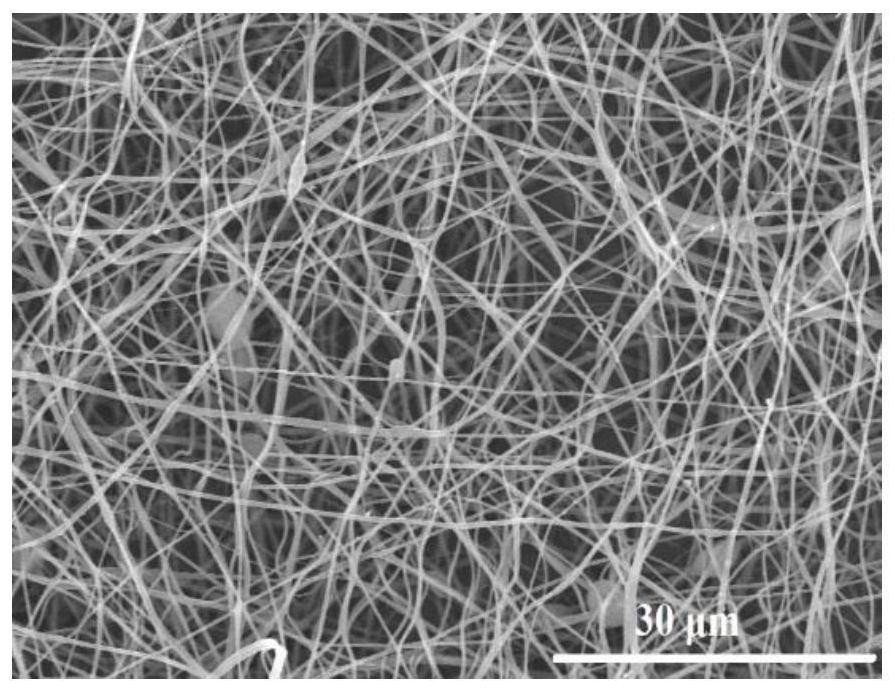
[0071] The morphologies of SiBCN nanofibers obtained by spinning solutions with different concentrations are as follows: Image 6 shown, by Image 6 It can be seen that the fiber prepared by using the spinning solution with a mass concentration of 50% has a smooth surface and a complete morphology, which is the preferred mass concentration.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com