Lactobacillus rhamnosus derived from human milk and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and breast milk, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and can solve problems such as toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: the screening of bacterial strain
[0023] 1. Sample collection and strain isolation
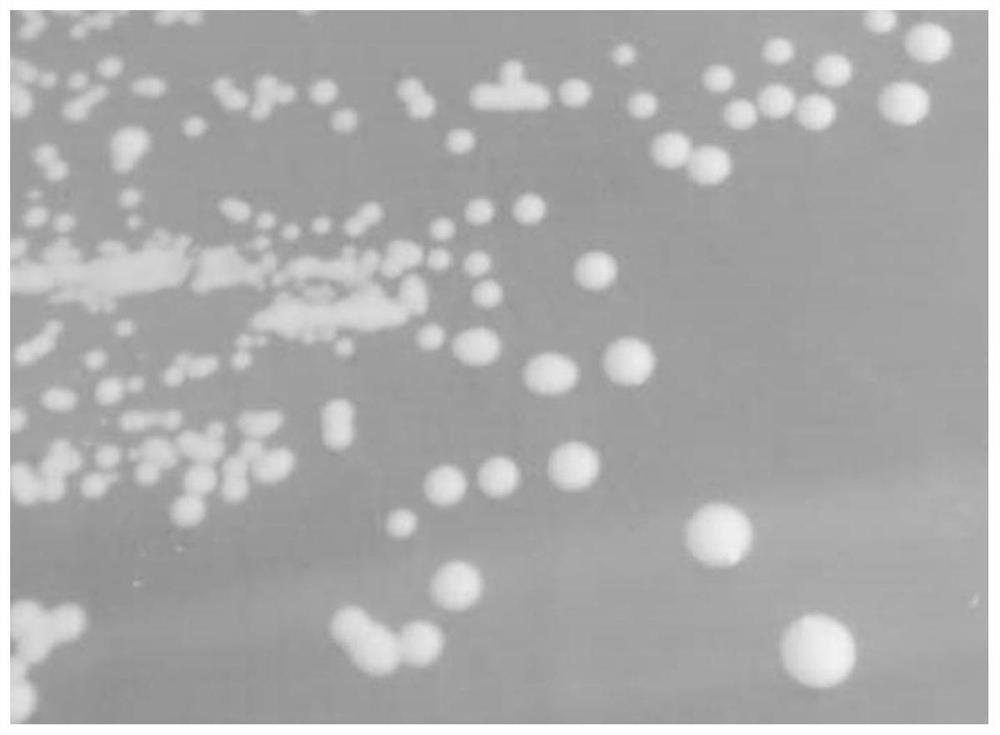
[0024] Before collecting samples, the nipples of healthy volunteers were strictly sanitized, and then about 10 mL of breast milk was collected and placed in sterile centrifuge tubes. Take 2 mL of breast milk sample and pour it on the MRS agar medium prepared in advance, shake it to make it spread on the surface of the medium, seal the culture dish with a sealing film, and cultivate it at 37°C for 24-48 hours until a single colony grows, and select the lactic acid bacteria. Typical morphology is a characteristic single colony of white or milky white.
[0025] 2. Strain screening
[0026] Streak inoculation of the isolated strains on MRS agar medium containing bromocresol purple, and culture at 37°C for 48h. After growing a single colony, select a single colony that turns the medium yellow, observe the shape of the bacteria under a microscope, and carry out subsequent e...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal conditions of Lactobacillus rhamnosus AUH2101
[0040] 1) Test of tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal conditions
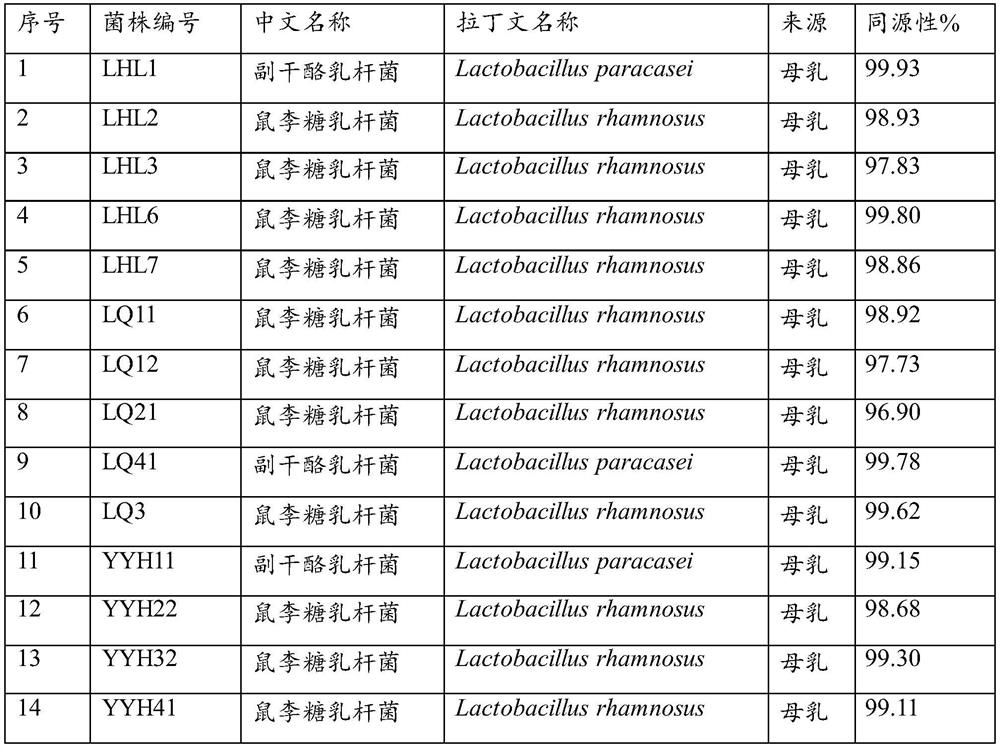
[0041] Preparation of strain fermented yogurt: Brew milk powder at a ratio of 14.7% (wt / v), fully dissolve, sterilize at 110°C for 12 minutes, cool to room temperature (about 20°C), and divide the sterilized milk into 40mL tubes. After the 16 strains obtained from the screening were activated by anaerobic culture, they were inoculated into sterilized milk at an inoculation amount of 3%, fermented at 37°C for about 4 hours, and then overnight at 4°C. The content of lactic acid bacteria was 10 9 cfu / ml.
[0042] Preparation of simulated saliva: 6.2g / L NaCl, 2.2g / L KCl, 0.22g / L CaCl 2 ,1.2g / L NaHCO 3 ;
[0043] Preparation of simulated gastric juice: 0.21g NaCl, 80.2mg pepsin, adjust the pH to 5.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid, adjust the volume to 100ml with double distilled water, the activity ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Testing of bacterial strains for antibiotic resistance
[0051] With reference to the implementation standard of EFSA microbial anti-drug susceptibility test, the six strains screened and CECT5716 (Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 strain) were tested for drug resistance in this embodiment, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0052] table 3
[0053]
[0054] Note: S means sensitive; I means intermediate; R means resistant.
[0055] It can be seen from Table 3 that there are differences in the drug resistance of each strain. Among them, strain LHL1 is sensitive to penicillin G and roxithromycin, strain LHL7 is sensitive to penicillin G and roxithromycin, strains LHL2, LHL3, LHL6 and AUH2101 are sensitive to penicillin G, tetracycline and roxithromycin at the same time, and have good safety sex. In addition, strain AUH2101 was also sensitive to azithromycin. Compared with the approved strain CECT5716 for infants, the Lactobacillus rhamnosus AUH2101 pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com