Polyimide composite fiber membrane, preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery
A technology of polyimide fiber and composite fiber membrane, applied in the direction of fiber type, secondary battery, fiber processing, etc., can solve battery safety problems and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] A preparation method of a polyimide composite fiber membrane is one of the preparation methods of the above-mentioned polyimide composite fiber membrane, and the preparation method of the polyimide composite fiber membrane comprises the following steps:
[0031] Step S100: dissolving the low-melting polymer in an organic solvent to obtain a filling solution of the low-melting polymer.
[0032] Further, the melting point of the low melting point polymer is 100°C to 160°C. Specifically, the low-melting point polymer is selected from low-density polyethylene (LDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyethylene oxide (PEO), polyethylene succinate At least one of alcohol esters (PES).
[0033] Specifically, the organic solvent is selected from one of toluene, xylene, acetone, chloroform, glacial acetic acid, and tetrahydrofuran. The organic solvent is capable of dissolving the low-melting polymer into a homogeneous polymer solution.
[00...
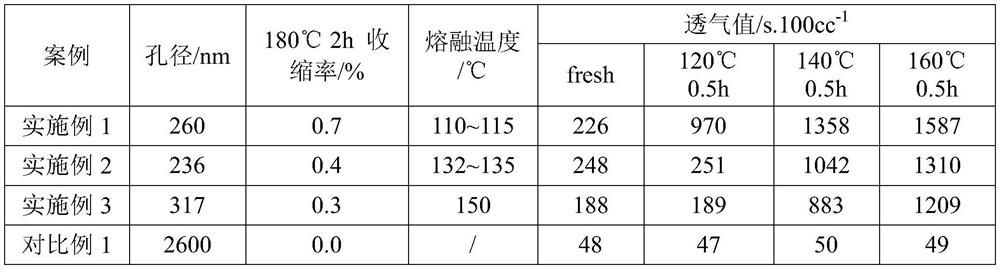
Embodiment 1
[0056] The preparation steps of the polyimide composite fiber membrane of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0057] (1) Preparation of polyimide fiber base film:
[0058] At room temperature, 10 g of polyamic acid, a precursor of polyimide, was weighed, then added to 100 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide, and mechanically stirred for 6 hours to obtain a uniform and viscous polyamic acid spinning solution. The spinning solution was prepared into a polyamic acid fiber membrane by using an electrospinning apparatus, and the spinning conditions were: voltage 20kV, ambient temperature 25°C; ambient humidity 40%; receiving distance 20cm. The polyamic acid fiber membrane is then subjected to thermal imidization treatment, and heat-treated at 100° C., 200° C., and 300° C. for 1 hour respectively, to obtain a layer of polyimide fiber base membrane. Among them, the specifications of the polyimide fiber base membrane are: the thickness is 8±1 μm; the fiber diameter is 0.4±0.1 μm, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The preparation steps of the polyimide composite fiber membrane of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0065] (1) Preparation of polyimide fiber base film:
[0066] At room temperature, 16 g of polyamic acid, a precursor of polyimide, was weighed, and then added to 100 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide, and mechanically stirred for 6 hours to obtain a uniform and viscous polyamic acid spinning solution. The spinning solution was prepared into a polyamic acid fiber membrane by using an electrospinning apparatus, and the spinning conditions were as follows: voltage 25kV, ambient temperature 20°C; ambient humidity 45%; receiving distance 16cm. The polyamic acid fiber membrane is then thermally imidized, and heat-treated at 100°C, 200°C, and 300°C for 1 hour, respectively, to obtain a layer of polyimide fiber base film. Among them, the specifications of the polyimide fiber base membrane are: the thickness is 12±1 μm; the fiber diameter is 0.7±0.1 μm, and the pore diameter i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com