Super-hydrophilic composite membrane suitable for oil-water separation in severe environment and preparation method of super-hydrophilic composite membrane
An oil-water separation and composite membrane technology, which is applied in separation methods, liquid separation, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve the problem that polymer membranes cannot meet the requirements of direct separation of high-temperature oily wastewater, the micro-nano structure is easy to fall off, and the pollution resistance is not strong. problems, to achieve the effect of improving anti-pollution performance, high mechanical strength, and good anti-destructive performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
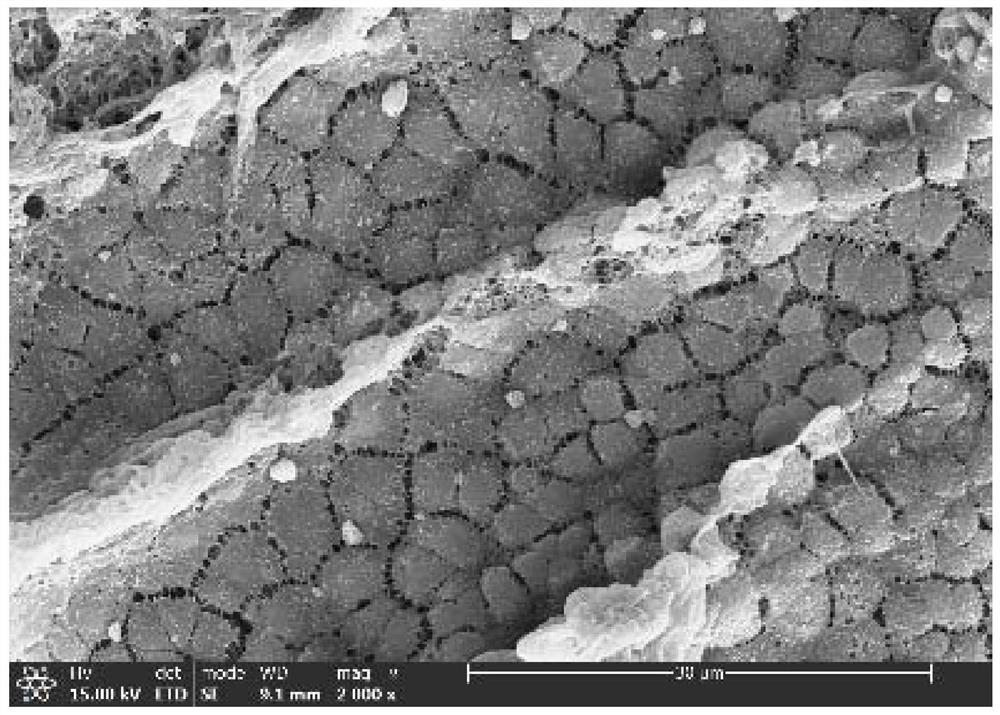
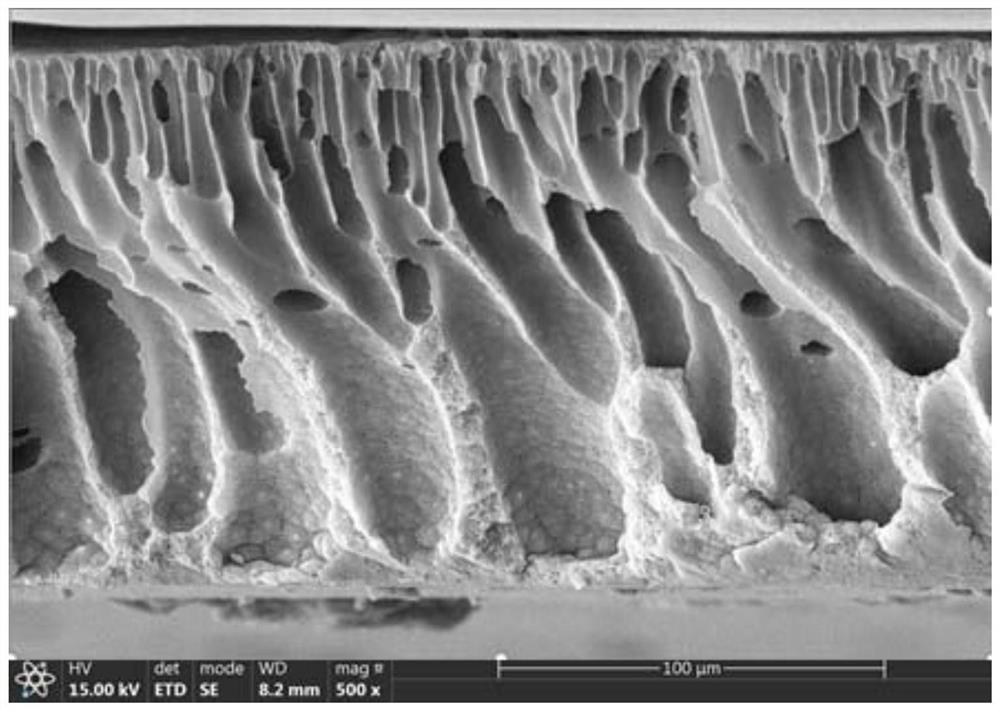
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043]S1: 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile, bisphenol A, phenolphthalein and N-methylpyrrolidone are used as raw materials in a 1:0.5:0.5 molar ratio; toluene is used as a water-carrying agent; N,N-dimethyl formamide as solvent. The system is heated to 145±2°C with stable water, and after about 3 hours of reaction, the system is basically completed with water; then the water and toluene in the system are removed, and the system is maintained at 190±1°C for about 2 hours to achieve the target viscosity, and the material is discharged in the deionized It is solidified in the mixed solution of water and ethanol, and then the remaining solvent, toluene and inorganic salts are removed by crushing and boiling the material for about 5 times, and it is vacuum-dried at 145°C for 5 hours before use.
[0044] S2: According to mass percentage, 15 parts of PEN-COOH, 10 parts of pore-forming agent and 75 parts of organic solvent are prepared into a casting solution. Pour the casting solution on th...
Embodiment 2~4
[0047] The only difference with Example 1 is that in S3, the components of the soaking system are different, as shown in Table 1:
[0048] Table 1 Example 1~4 Soaking System Component Table
[0049] Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 DA (mg) 40 40 60 50 PEI (mg) 60 70 50 60 TiO 2 (mg / mL)
experiment example 1
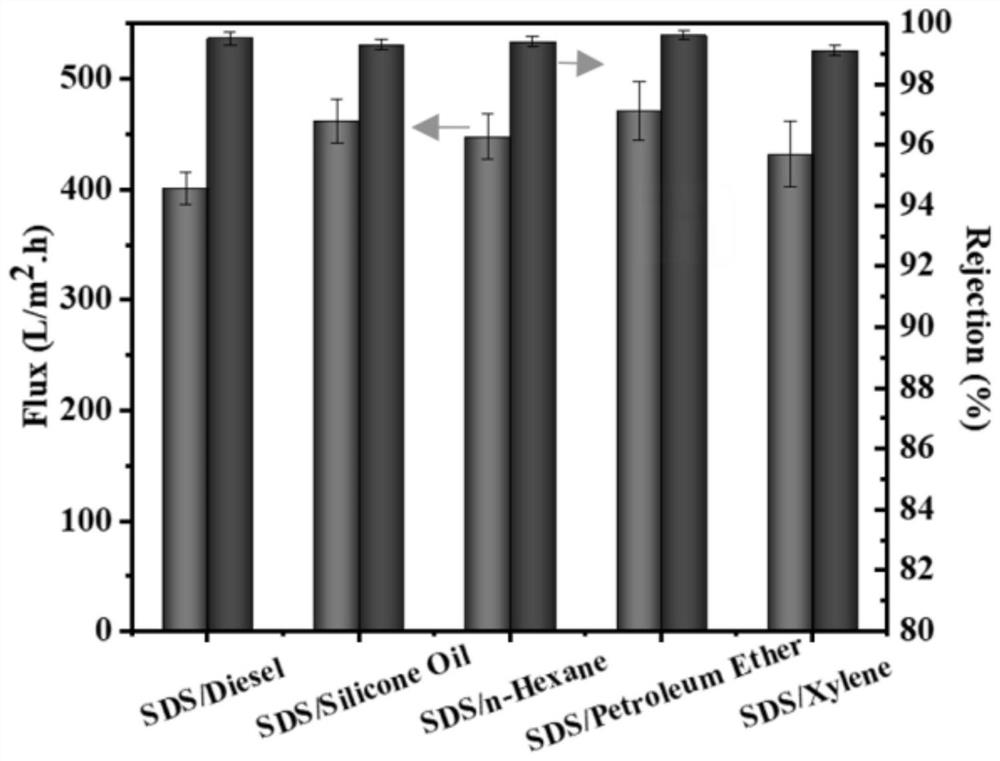
[0059] The constant pressure vacuum filtration system was used to test the water flux and retention rate.
[0060] The water flux test conditions are as follows: test pressure 0.09MP, test temperature 25°C, membrane sample size and diameter 4cm, membrane effective area 12.56cm 2 , all samples should be tested for more than 5 minutes, and the same sample should be tested at least 5 times to ensure the accuracy of the experimental data.
[0061] The water flux calculation formula is as follows:
[0062] Jwo=V / (A·t)
[0063] In the formula: Jwo is the pure water flux of the membrane, L / (m2 h); V is the permeate volume, m3; A is the effective area of the membrane, m2; t is the effective time of the membrane being tested, h.
[0064] The test conditions for emulsion retention rate are as follows: Take 5 mL of alkane reagent and add 100 mL of deionized water containing surfactant to ultrasonic for 20 minutes to form a stable oil-in-water emulsion. The test pressure is 0.09MP, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specification | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com