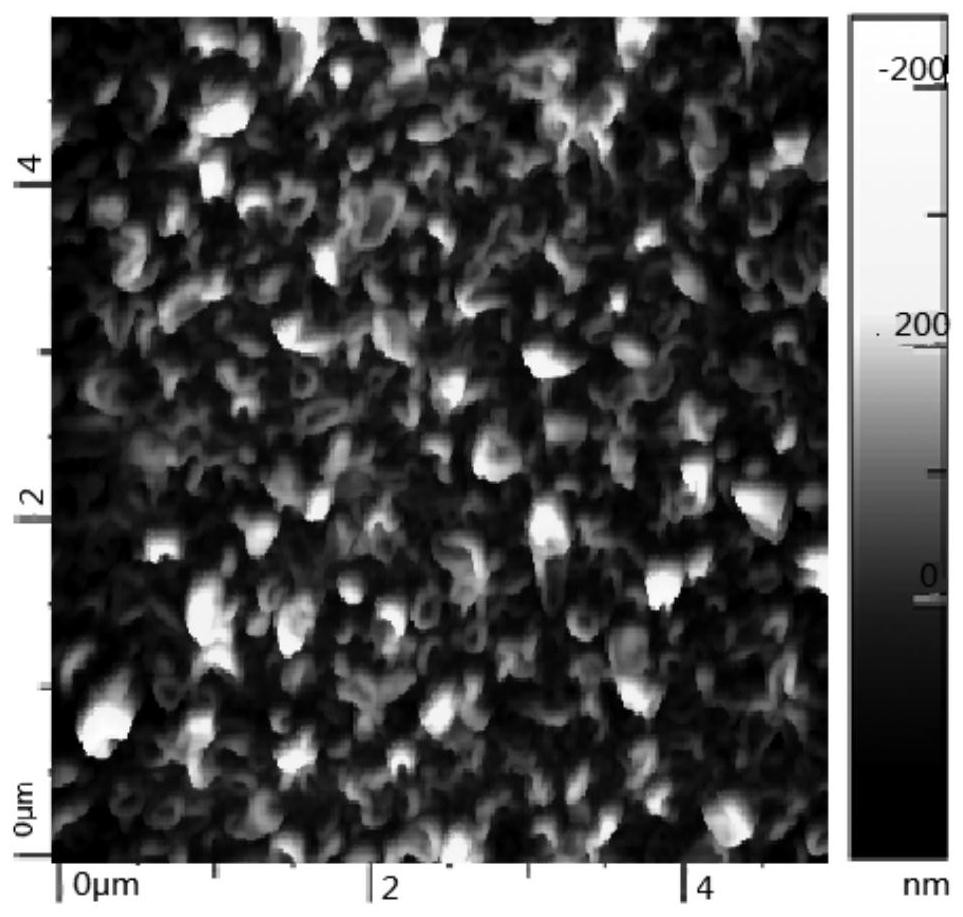
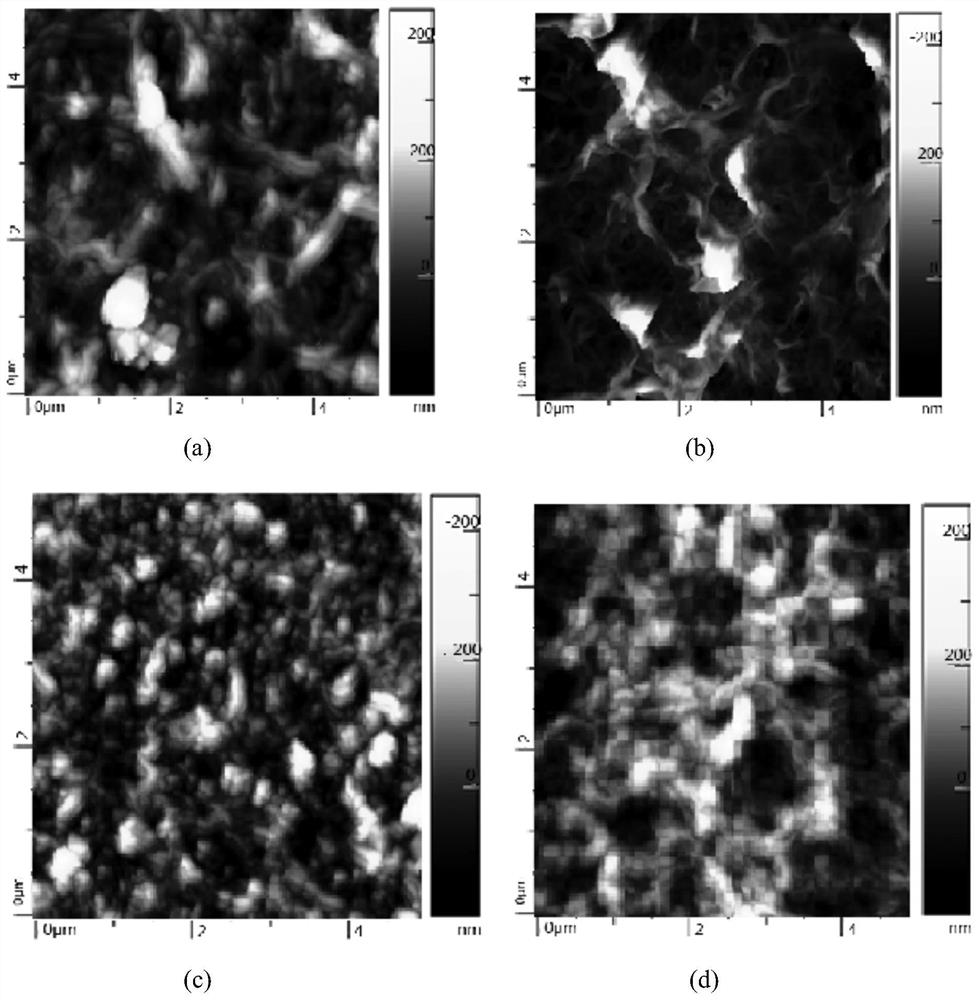
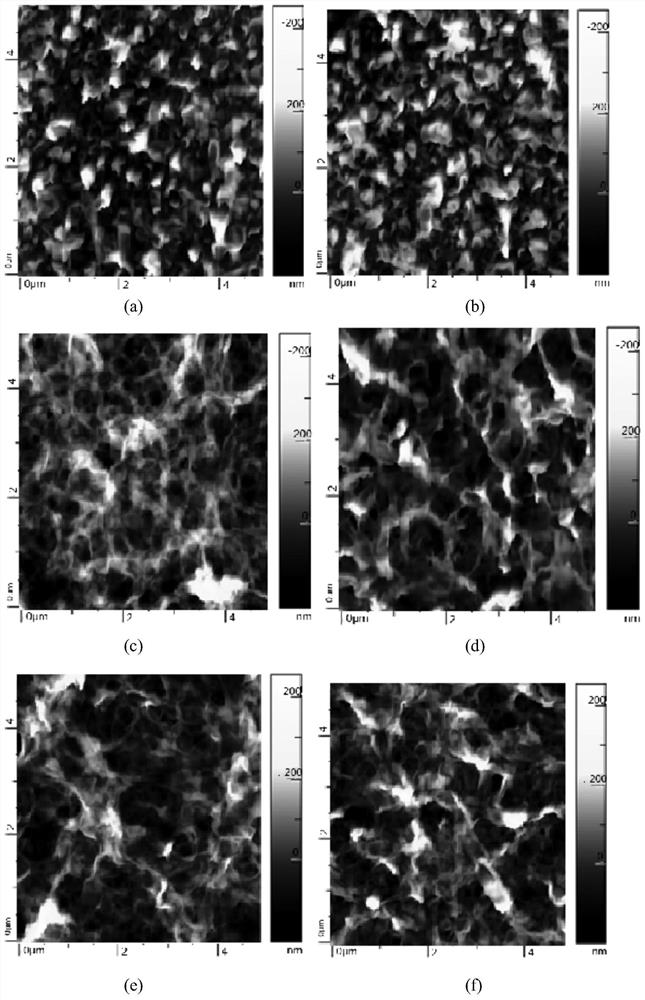
Nanofiltration membrane for treating printing and dyeing wastewater and preparation method thereof
A technology of printing and dyeing wastewater and nanofiltration membrane, which is applied in water/sewage treatment, general water supply saving, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of loss of desalination rate, high filtration pressure, low retention rate, etc., and achieve moderate surface density. , not easy to block and scale, reduce the effect of membrane fouling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] A method for preparing a nanofiltration membrane for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0061] S1. First clamp the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane in the plexiglass frame with the surface facing up, wipe off the water droplets on the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, and then pour the aqueous solution containing m-phenylenediamine, camphorsulfonic acid and triethylamine To the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, stay 10s, then pour off the excess aqueous solution, and use nitrogen to sweep the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane until there is no residual aqueous solution; wherein, the weight percentage of m-phenylenediamine is 0.7wt%, and the content of camphorsulfonic acid The weight percent is 2wt%, and the weight percent of triethylamine is 1wt%;
[0062] S2. The n-hexane solution containing trimesoyl chloride and acetone is poured onto the surface of the film obtained i...
Embodiment 2
[0065] A method for preparing a nanofiltration membrane for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0066] S1. First clamp the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane in the plexiglass frame with the surface facing up, wipe off the water droplets on the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, and then pour the aqueous solution containing m-phenylenediamine, camphorsulfonic acid and triethylamine To the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, stay 20s, then pour off the excess aqueous solution, and use nitrogen to sweep the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane until there is no residual aqueous solution; wherein, the weight percentage of m-phenylenediamine is 1.35wt%, and the content of camphorsulfonic acid The weight percent is 2.25wt%, and the weight percent of triethylamine is 1.25wt%;
[0067] S2. Pour the n-hexane solution containing trimesoyl chloride and acetone onto the surface of the film obtained...
Embodiment 3
[0070] A method for preparing a nanofiltration membrane for treating printing and dyeing wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0071] S1. First clamp the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane in the plexiglass frame with the surface facing up, wipe off the water droplets on the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, and then pour the aqueous solution containing m-phenylenediamine, camphorsulfonic acid and triethylamine To the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane, stay 30s, then pour off the excess aqueous solution, and use nitrogen to sweep the surface of the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane until there is no residual aqueous solution; wherein, the weight percent of m-phenylenediamine is 2wt%, and the weight percent of camphorsulfonic acid The percentage is 2.5wt%, and the weight percent of triethylamine is 1.5wt%;
[0072] S2. Pour the Isopar G solution containing trimesoyl chloride and acetone onto the surface of the film obtained in s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com