Method for treating zinc-containing materials in zinc hydrometallurgy production
A technology of hydrometallurgy and treatment method, which is applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve problems such as inability to efficiently recycle, difficult to recycle, and low iron content, so as to save operating procedures, simplify zinc smelting process, and improve comprehensive The effect of recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
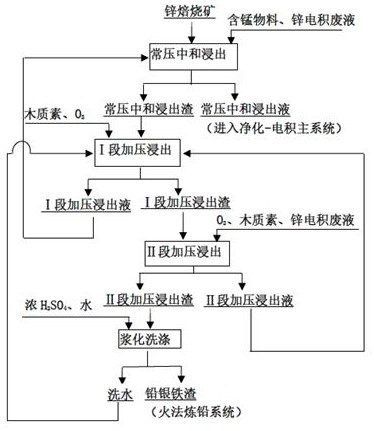
[0050] A method for processing zinc-containing materials in zinc hydrometallurgy production, the specific steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) The zinc roasted ore (mass percentage content of main elements: zinc 56.4%, iron 6.0%, lead 3.0%, silver 0.01%) is mixed with water and then mechanically activated in a wet ball mill to obtain the particle size of the zinc roasted ore 100 mesh finely ground pulp;
[0052] (2) After the finely ground pulp produced in step (1) is mixed with pyrolusite, zinc electrowinning waste liquid, and stage I pressurized leaching liquid through the metering pump in the 1# stirring and leaching tank, the 2#, 3 #, 4#, and 5# agitation and leaching tanks carry out four-stage normal pressure neutralization and leaching, and the reaction slurry overflows from 1# agitation tank to 2# to 5# agitation and leaching tanks through the chute, and controls 1# to 5# agitation The reaction temperature of the leaching tank is 60°C, 65°C, 65°C, 65°C, and 65°C in seque...
Embodiment 2
[0058] A method for processing zinc-containing materials in zinc hydrometallurgy production, the specific steps are as follows:
[0059] (1) The zinc roasted ore (mass percentage content of main elements: zinc 45.0%, iron 9.2%, lead 1.6%, silver 0.005%) is mixed with water and then mechanically activated in a wet ball mill to obtain the particle size of the zinc roasted ore 150 mesh finely ground pulp.
[0060] (2) After the finely ground pulp produced in step (1) is mixed with pyrolusite, anode slime, zinc electrowinning waste liquid, and stage I pressurized leaching liquid through the metering pump in the 1# stirring and leaching tank, the 2 #, 3#, 4#, and 5# agitated leaching tanks carry out four-stage normal pressure neutralization and leaching, and the reaction slurry overflows from 1# agitating tank through the chute to 2# to 5# agitating leaching tanks, and controls the 1# to 5# agitating leaching tanks. The reaction temperature of 5# agitated leaching tank is 85°C, 80...
Embodiment 3
[0066] A method for processing zinc-containing materials in zinc hydrometallurgy production, the specific steps are as follows:
[0067] (1) The zinc roasted ore (mass percentage content of main elements: zinc 60.0%, iron 12.4%, lead 0.5%, silver 0.015%) is mixed with water, and then mechanically activated in a wet ball mill to obtain the particle size of the zinc roasted ore 200 mesh finely ground pulp.
[0068] (2) After the finely ground pulp produced in step (1) is mixed with anode slime, zinc electrowinning waste liquid, and stage I pressurized leaching liquid through the metering pump in the 1# stirring leaching tank, the 2#, 3 #, 4#, and 5# agitation and leaching tanks carry out four-stage normal pressure neutralization and leaching, and the reaction slurry overflows from 1# agitation tank to 2# to 5# agitation and leaching tanks through the chute, and controls 1# to 5# agitation The reaction temperature of the leaching tank is 75°C, 75°C, 75°C, 75°C, and 75°C in seque...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com