Preparation method and product of earthworm breeding companion soil remediation agent
A soil remediation agent and a production method technology are applied in the field of making earthworm reproduction companion soil remediation agents, which can solve problems such as soil deterioration, biomass loss, and poisoning, and achieve the effects of promoting tight junctions, preventing cell necrosis, and promoting secretion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
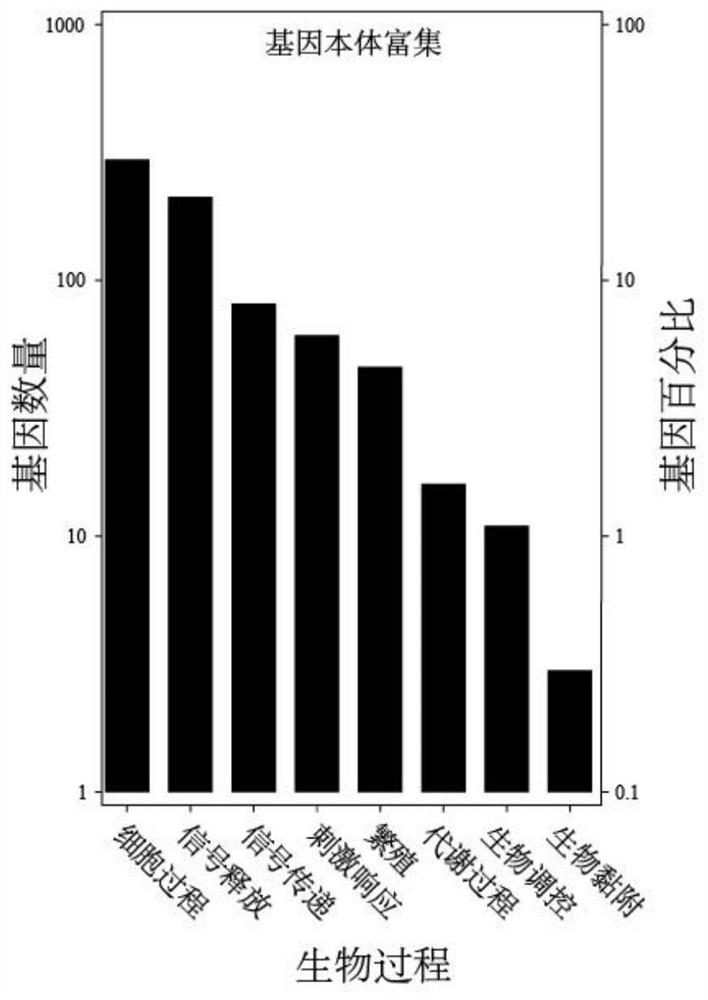
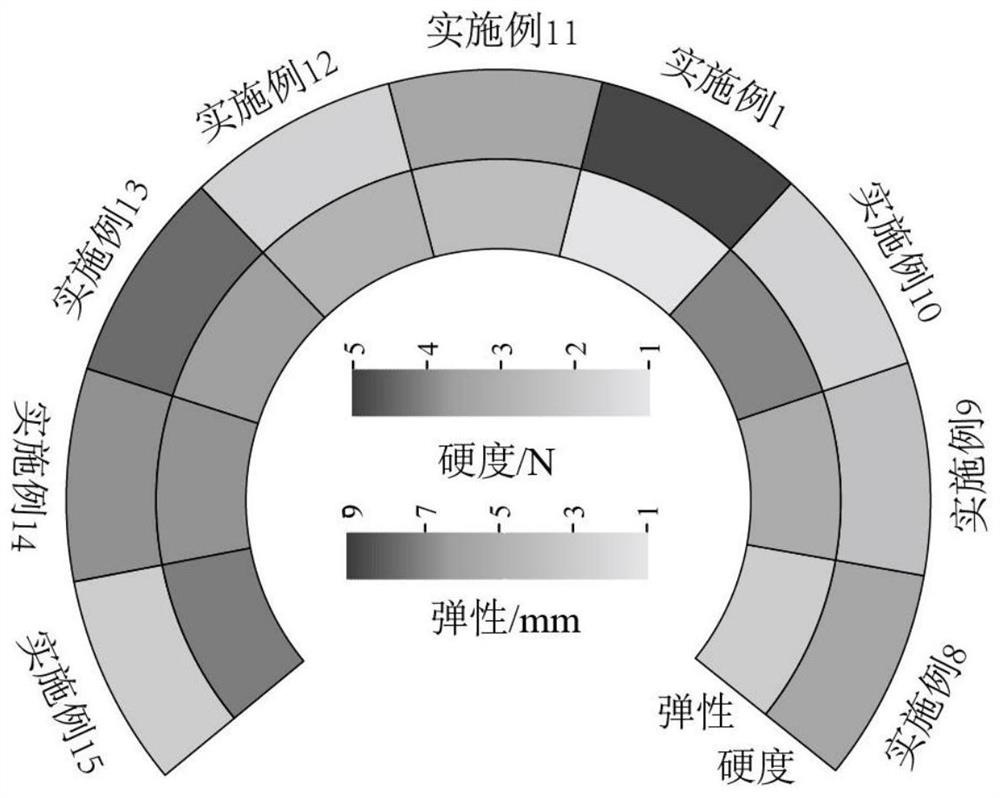
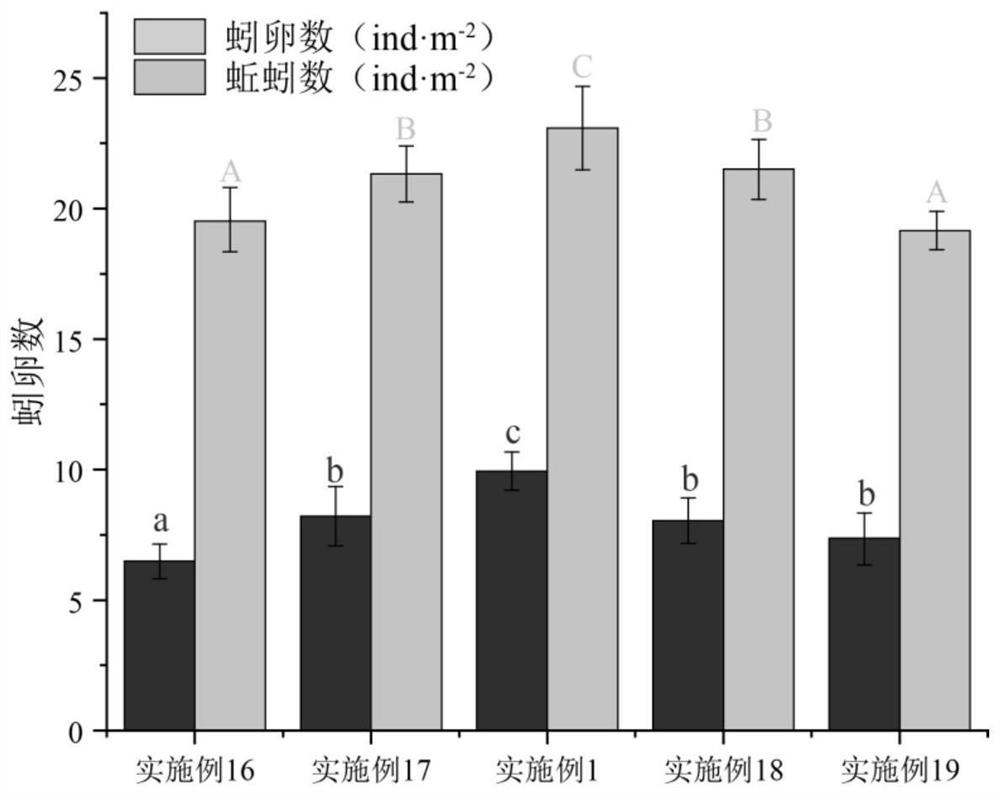
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of earthworm breeding companion soil restoration agent, comprising:
[0052] (1) Preparation of thermogenic ion-enriching bacterial agent: compound the mass ratio of composting Nocardia sp., Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus oryzae to prepare thermoionic ion-enriching bacterial agent;
[0053] (2) Preparation of paragonadal ion stress matrix: mix soybean meal, plant ash, and bone meal to obtain material, add 1 kg of thermogenic ion-enriching bacterial agent for every 10 tons of material, mix well, and pile up the material into a cone shape. The natural fermentation keeps the water content at 50%, and when the fermentation temperature reaches 40°C, it is turned over once a day, and fermented for 15 days to obtain the paragonad ion stress matrix, wherein, in parts by weight, the soybean meal is 3 part, the plant ash is 3 parts, and the bone meal is 1 part;
[0054] (3) Preparation of ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 (do not have warming starter)
[0064] In this example, compared with Example 1, the decomposing fermentation of the paragonad ion-stressed substrate is natural fermentation—no thermogenic ion-enriching bacterial agent is added, and other preparation process conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0065] The end point of decomposing fermentation was judged by the bio-organic fertilizer standard NY 884-2004, and the temperature and time of fermentation were recorded.
[0066] Table 1 Comparison of decomposing and fermentation time under different temperatures
[0067]
[0068] As can be seen from Table 1, due to the low-temperature fermentation activity of the temperature-starting fermentation agent, the temperature-starting agent can rapidly heat up and start the fermentation of the substrate under low temperature conditions (5-15° C.). Compared with natural fermentation, the fermentation period is shortened. About two months; even under normal tempe...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3 (traditional earthworm propagation substrate)
[0070] Compared with Example 1 in this example, the paragonad ion stress substrate is animal manure and silt soil, and other preparation process conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0071] According to the national standard GB / T 21633-2008 and GB / T 19203-2003, the content of total nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and calcium elements in the decomposed substrate was determined.
[0072] Table 2 Comparison of element content in different substrates
[0073]
[0074] Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and calcium are essential nutrients for crops, and they are also stress elements that increase the reproductive rate of earthworms. As shown in Table 2, compared with the traditional feces + silt soil matrix, the concentration of various elements in the ion stress matrix has been significantly increased, and the nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and calcium elements have increased by 2.74, 2.59, 2.67 and 1.92 ti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com